
Pears are fruits produced and consumed around the world, growing on a tree and harvested in late summer into mid-autumn. The pear tree and shrub are a species of genus Pyrus, in the family Rosaceae, bearing the pomaceous fruit of the same name. Several species of pears are valued for their edible fruit and juices, while others are cultivated as trees.
Perry or pear cider is an alcoholic beverage made from fermented pears, traditionally in England, particularly Gloucestershire, Herefordshire, and Worcestershire, parts of South Wales and France, especially Normandy and Anjou, Canada, Australia and New Zealand.
Specific replant disease is a malady that manifests itself when susceptible plants such as apples, pears, plums, cherries and roses are placed into soil previously occupied by a related species. The exact causes are not known, but in the first year the new plants will grow poorly. Root systems are weak and may become blackened, and plants may fail to establish properly.

Fire blight, also written fireblight, is a contagious disease affecting apples, pears, and some other members of the family Rosaceae. It is a serious concern to apple and pear producers. Under optimal conditions, it can destroy an entire orchard in a single growing season.

Russet apples are varieties and cultivars of apples that regularly exhibit russeting, partial or complete coverage with rough patches of greenish-brown to yellowish-brown colour. While russeting is generally an undesirable trait in modern cultivars, russet varieties are often seen as more traditional, and associated with aromatic flavours.

Phyllachora pomigena is a plant pathogen responsible for Sooty blotch and flyspeck disease, a disease affecting apples and pears. It appears as a brown or black blotch on the fruit. Spots may coalesce to cover the entire fruit. During the summer these diseases develop during cool rainy weather, particularly in dense, unpruned trees with poor air circulation. Although unsightly, the fruit is still edible. The sooty blotch will wipe off of the fruit.
Mucor piriformis is a plant pathogen that causes a soft rot of several fruits known as Mucor rot. Infection of its host fruits, such as apples and pears, takes place post-harvest. The fungi can also infect citrus fruits.

Podosphaera leucotricha is a plant pathogen that can cause powdery mildew of apples and pears.

Schizothyrium pomi is a plant pathogen of the sooty blotch and flyspeck complex, infecting apple, pear and citrus trees and carnations.
Valsa ceratosperma is a plant pathogen infecting apples and pears.
Xiphinema americanum, the American dagger nematode, is a species of plant pathogenic nematodes. It is one of many species that belongs to the genus Xiphinema. It was first described by N. A. Cobb in 1913, who found it on both sides of the United States on the roots of grass, corn, and citrus trees. Not only is Xiphinema americanum known to vector plant viruses, but also X. americanum has been referred to as "the most destructive plant parasitic nematode in America", and one of the four major nematode pests in the Southeastern United States.
Xiphinema brevicolle is a plant pathogenic nematode infecting mangoes.
Xiphinema diversicaudatum is an amphimictic ectoparasitic nematode species. This species has a characteristically long stylet capable of penetrating into a host's vascular tissue. They have a wide host range with some of the extensively studied ones being strawberry, hops and raspberry, due to their economic importance. The direct root damage caused through penetration near the root tip and formation of galls is a secondary concern when compared with the damage caused by vectoring the Arabis mosaic virus. The virus attaches to the interior cuticle lining and can be transferred from infected to uninfected root tissue as the nematode feeds and sheds. Management of this particular nematode relies on nematicides such as 1,3-Dichloropropene (Telone) at 40 gpa.or methyl bromide at 1000 lb/ac to control to 28 in deep.
Xiphinema index, the California dagger nematode, is a species of plant-parasitic nematodes.
Xiphinema insigne is a plant pathogenic nematode infecting tea. They are known to infect cacao trees.
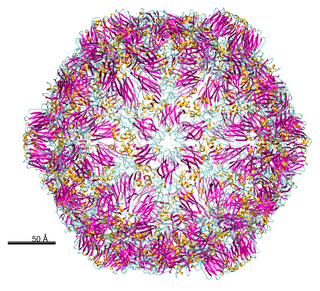
Grapevine fanleaf virus (GFLV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Secoviridae. It infects grapevines, causing chlorosis of the leaves and lowering the fruit quality. Because of its effect on grape yield, GFLV is a pathogen of commercial importance. It is transmitted via a nematode vector, Xiphinema index. This nematode acquires the virus through feeding on roots of an infected plant, and passes it on in the same manner.
Tomato ringspot virus (ToRSV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Secoviridae. It affects species of cucumber, tobacco, tomato, cowpea, among others. It causes ringspots in tobacco plants and raspberries, yellow bud mosaic in peaches, yellow vein in grapes, and stunted growth in gladiolus and Narcissus. Its range is in the temperate regions of North America, especially where its vector, Xiphinema americanum is present. Along with the adult and larval stages of this nematode, the virus is also spread by seed. This type of infection is more common in strawberries and soybeans than any other susceptible plant.

'Delbard Jubilée' or 'Delgollune' is a modern French cultivar of domesticated apple which was developed in 1964 by Delbard nurseries. It is not the same as the Jubilee apple that was developed in Canada.

Ellison's Orange is an English cultivar of domesticated apple, it is a cross between the famous Cox's Orange Pippin and Cellini, which it resembles at most in looks and taste, but can develop a distinct aniseed flavor in storage. The variety is much more disease resistant than Cox's and therefore easier to cultivate.








