
Nematomorpha are a phylum of parasitoid animals superficially similar to nematode worms in morphology, hence the name. Most species range in size from 50 to 100 millimetres, reaching 2 metres (79 in) in extreme cases, and 1 to 3 millimetres in diameter. Horsehair worms can be discovered in damp areas, such as watering troughs, swimming pools, streams, puddles, and cisterns. The adult worms are free-living, but the larvae are parasitic on arthropods, such as beetles, cockroaches, mantises, orthopterans, and crustaceans. About 351 freshwater species are known and a conservative estimate suggests that there may be about 2000 freshwater species worldwide. The name "Gordian" stems from the legendary Gordian knot. This relates to the fact that nematomorphs often coil themselves in tight balls that resemble knots.

Enoplea (enopleans) is a class, which with the classes Secernentea and Chromadorea make up the phylum Nematoda in current taxonomy. The Enoplea are considered to be a more ancestral group than the Chromadorea, and researchers have referred to its members as the "ancestrally diverged nematodes", compared to the "more recently diverged nematodes" of Chromadorea.

Root-knot nematodes are plant-parasitic nematodes from the genus Meloidogyne. They exist in soil in areas with hot climates or short winters. About 2000 plants worldwide are susceptible to infection by root-knot nematodes and they cause approximately 5% of global crop loss. Root-knot nematode larvae infect plant roots, causing the development of root-knot galls that drain the plant's photosynthate and nutrients. Infection of young plants may be lethal, while infection of mature plants causes decreased yield.

Trichinella is the genus of parasitic roundworms of the phylum Nematoda that cause trichinosis. Members of this genus are often called trichinella or trichina worms. A characteristic of Nematoda is the one-way digestive tract, with a pseudocoelom.
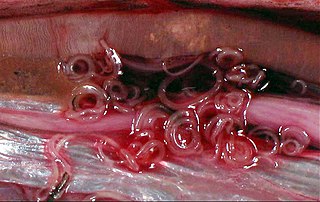
The Chromadorea are a class of the roundworm phylum, Nematoda. They contain a single subclass (Chromadoria) and several orders. With such a redundant arrangement, the Chromadoria are liable to be divided if the orders are found to form several clades, or abandoned if they are found to constitute a single radiation.
Hirschmanniella oryzae, i.e. rice root nematode (RRN), is among the major pests of rice and is the most common plant-parasitic nematode found on irrigated rice. Recent modifications in cultivation practices have led to a substantial increase in rice production, which has been accompanied by heightened levels of RRN. The proportional increases in RRN with rice production can be explained by the nematode's impeccable adaptation towards constantly flooded conditions in which irrigated rice is often being grown.
Heterodera canadensis is a plant pathogenic nematode.

Tobacco rattle virus (TRV) is a pathogenic plant virus. Over 400 species of plants from 50 families are susceptible to infection.

The nematodesroundworms or eelworms, constitute the phylum Nematoda. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but there are many that are parasitic. The parasitic worms (helminths) are the cause of soil-transmitted helminthiases.
Enoplida is an order of nematodes. It is one of two orders in Enoplia, which is one of two subclasses in Class Enoplea.

Huffmanela is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Trichosomoididae.
Dorylaimia is a subclass of nematodes.
The Enoplia are a subclass of nematodes in the class Enoplea.
Longidorus is a genus of needle nematodes. Some of its species are plant pests.
Paratrichodorus is a genus of terrestrial root feeding (stubby-root) nematodes in the Trichodoridae family (trichorids), being one of five genera. They are economically important plant parasites and virus vectors. The females are didelphic, and are distributed worldwide.
Triplonchida is an order of terrestrial nematodes, and is one of two orders making up the subclass Enoplia.
Diphtherophorina is a suborder of terrestrial nematodes, being one of three that constitute suborder Triplonchida.
Trichodoridae is a family of terrestrial root feeding nematodes, being one of two that constitute suborder Triplonchida. They are economically important plant parasites and virus vectors.

Trichodorus is a genus of terrestrial root feeding (stubby-root) nematodes in the Trichodoridae family (trichorids), being one of five genera. They are economically important plant parasites and virus vectors.

František Moravec is a Czech parasitologist who specialises on the Nematodes, especially the nematodes parasites of fishes. His research is mainly in the field of taxonomy of the Nematoda.








