The Porter-Gaud School is an independent coeducational college preparatory day school in Charleston, in the U.S. state of South Carolina. Porter-Gaud has an enrollment of some 1100 students, comprising a lower school, middle school, and high school, and is located on the banks of the Ashley River. The school has historic ties to the Episcopal Church.
Nikolay Petrovich Dubinin was a Soviet and Russian biologist and academician.
Gaud Saraswat Brahmins (GSB), also known as Shenvis are a Hindu community of contested caste status and identity. They primarily speak Konkani and its various dialects as their mother tongue.
Kensington North was a parliamentary constituency centred on the Kensington district of west London. It returned one Member of Parliament (MP) to the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom.
The lappet-eared free-tailed bat is a species of bat in the family Molossidae. It is found in Benin, Burkina Faso, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Liberia, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Sudan, Tanzania, Togo, and Uganda. Its natural habitats are dry savanna and moist savanna.
The Analgoidea are a superfamily of the Acarina (mite) order Sarcoptiformes. They contain many feather mites, being ectoparasites of birds and occasionally mammals.
Volodia Dubinin was a Pioneer Hero of the Soviet Union.

Kudaldeshkar Gaud Brahmin is a Brahmin sub-caste from the western coast of India, residing in the Konkan division of Maharashtra and Goa. They also known as Kudaldeshkar Aadya Gaud Brahmin, Kudaldeshkar and sometimes Kudalkar Brahmins. They speak Marathi, and the Malwani dialect of Konkani.

Amphicyoninae is a subfamily of extinct amphicyonids, large terrestrial carnivores sometimes called "bear-dogs", belonging to the suborder Caniformia, which inhabited North America, Eurasia, and Africa from the middle Eocene to the late Miocene.

Veratalpa lugdunensiana is a fossil mammal from the Miocene of France. Known from a single astragalus, the species was assigned to its own genus, Veratalpa, by Florentino Ameghino in 1905. He placed it in Talpidae, the family of the moles, but in 1974, John Howard Hutchison argued that the astragalus was not talpid and more likely came from a rodent. The astragalus is about 4.5 mm long, broad for a talpid, and has the head oriented farther from the axis of the foot than in talpids.
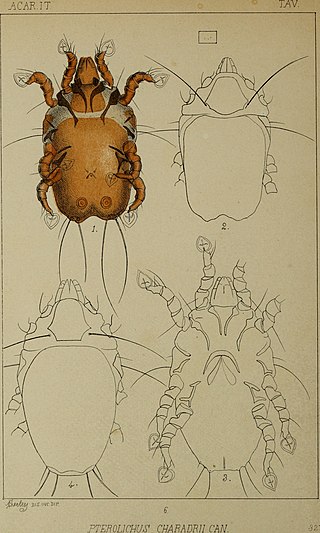
Avenzoariidae is a family of feather mites in the order Astigmata. There are at least 15 genera in Avenzoariidae. They are found on the feathers of aquatic birds, and in the case of one species, birds of prey.
Freyanidae is a family of feather mites in the order Astigmata. There are more than 15 genera in Freyanidae.

Halacaridae is a family of meiobenthic mites found in marine, brackish, and freshwater habitats around the world. It includes more than 1100 described species belonging to 64 genera It is the largest marine radiation of arachnids.
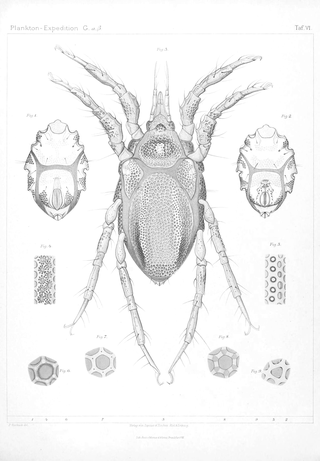
Copidognathus is a genus of mites in the family Halacaridae. Copidognathus is a large genus with over 380 accepted species.
Eustathiidae is a family of mites belonging to the order Sarcoptiformes.
Psoroptoididae is a family of mites belonging to the order Sarcoptiformes.

Syringobiidae is a family of mites belonging to the order Sarcoptiformes.
Trouessartiidae is a family of mites belonging to the order Sarcoptiformes.

Alloptidae is a family of mites belonging to the order Sarcoptiformes.

Proviverrinae is an extinct subfamily of placental mammals within the extinct order Hyaenodonta. Fossil remains of these mammals are known from early to late Eocene deposits in Europe.









