
Anserimimus is a genus of ornithomimid theropod dinosaur, from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now Mongolia. It was a lanky, fast-running animal, possibly an omnivore. From what fossils are known, it probably closely resembled other ornithomimids, except for its more powerful forelimbs.

Archaeornithomimus is a genus of ornithomimosaurian theropod dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period, around 96 million years ago in the Iren Dabasu Formation.

Bagaceratops is a genus of small protoceratopsid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous, around 72 to 71 million years ago. Bagaceratops remains have been reported from the Barun Goyot Formation and Bayan Mandahu Formation. One specimen may argue the possible presence of Bagaceratops in the Djadochta Formation.
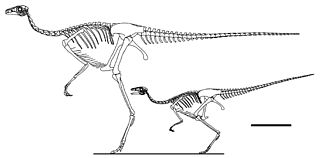
Sinornithomimus is a genus of ornithomimid that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period. The first remains were found in 1997, in the Late Cretaceous strata of the Ulansuhai Formation located at Alshanzuo Banner, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Northern China.

Pukyongosaurus is a genus of titanosauriform dinosaur that lived in South Korea during the Early Cretaceous period. It may have been closely related to Euhelopus, and is known from a series of vertebrae in the neck and back. The characteristics that were originally used to distinguish this genus have been criticized as being either widespread or too poorly preserved to evaluate, rendering the genus an indeterminate nomen dubium among titanosauriforms. The 2022 study noted that Pukyongosaurus is probably a somphospondylan.

Notosuchus is an extinct genus of South American notosuchian crocodylomorph. It was terrestrial, living approximately 85 million years ago in the Santonian stage of the Late Cretaceous.

Yamaceratops is a genus of primitive ceratopsian that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period in what is now the Javkhlant Formation. Initially, the rocks where it was found in were thought to be from the Early Cretaceous, but the age was reevaluated in 2009. It was a relatively small dinosaur, reaching 50 cm (1.6 ft) in length and 2 kg (4.4 lb) in body mass.

Lonchodectidae or Lonchodraconidae is a group of pterosaurs within the clade Pterodactyloidea. It has variously been considered to be within Ctenochasmatoidea, Azhdarchoidea and Pteranodontia. They are notable for their high, conical tooth sockets and raised alveolar margins.

Luanchuanraptor is a genus of dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous of China. The genus is based on a partial skeleton from the Qiupa Formation in Luanchuan, Henan. They were medium-sized dromaeosaurids, the first Asian dromaeosaurid taxa described from outside the Gobi Desert or northeastern China.

Axelrodichthys is an extinct genus of mawsoniid coelacanth from the Cretaceous of Africa, North and South America, and Europe. Several species are known, the remains of which were discovered in the Lower Cretaceous (Aptian-Albian) of Brazil, North Africa, and possibly Mexico, as well as in the Upper Cretaceous of Morocco (Cenomanian), Madagascar and France. The Axelrodichthys of the Lower Cretaceous frequented both brackish and coastal marine waters while the most recent species lived exclusively in fresh waters. The French specimens are the last known fresh water coelacanths. Most of the species of this genus reached 1 metre to 2 metres in length. Axelrodichthys was named in 1986 by John G. Maisey in honor of the American ichthyologist Herbert R. Axelrod.

Gobiconodon is an extinct genus of carnivorous mammals belonging to the family Gobiconodontidae. Undisputed records of Gobiconodon are restricted to the Early Cretaceous of Asia and North America, but isolated teeth attributed to the genus have also been described from formations in England and Morocco dating as far back as the Middle Jurassic. Species of Gobiconodon varied considerably in size, with G. ostromi, one of the larger species, being around the size of a modern Virginia opossum. Like other gobiconodontids, it possessed several speciations towards carnivory, such as shearing molariform teeth, large canine-like incisors and powerful jaw and forelimb musculature, indicating that it probably fed on vertebrate prey. Unusually among predatory mammals and other eutriconodonts, the lower canines were vestigial, with the first lower incisor pair having become massive and canine-like. Like the larger Repenomamus there might be some evidence of scavenging.

Yaguarasaurus is an extinct genus of mosasauroid from the Late Cretaceous (Turonian) period of Colombia, South America. The remains discovered were defined as a new genus and species of mosasaurid, Yaguarasaurus columbianus, by the Colombian paleontologist María Páramo, former director of the Museo de Geología José Royo y Gómez of INGEOMINAS in Bogotá. The first fossils remains of this animal suggested a cranial length of 47 centimetres (19 in) and a total length of 5 metres (16 ft); an additional skull that measures 87 centimetres (34 in) long implies a larger size.

The Santa Marta Formation is a geologic formation in Antarctica. It, along with the Hanson Formation and the Snow Hill Island Formation, are the only formations yet known on the continent where dinosaur fossils have been found. The formation outcrops on James Ross Island off the coast of the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. In its entirety, the Santa Marta Formation is on average one kilometer thick.
Arkharavia is a dubious genus of somphospondylan sauropod, but at least some of the remains probably belong to a hadrosaurid. It lived in what is now Russia, during the Late Cretaceous. It was described in 2010 by Alifanov and Bolotsky. The type species is A. heterocoelica.
Dalingheornis is a genus of enantiornithean birds which lived during the early Cretaceous period, about 122 Ma ago, and are known from a single juvenile fossil found in the upper part of the Yixian Formation at Dawangzhangzi, Liaoning province, People's Republic of China. It is the first known Mesozoic bird with heterodactyl feet specifically adapted for climbing, and was probably among the most arboreal of the enantiornithines. Unlike its relatives, it had an unusually long (17mm) skeletal tail made up of 20 vertebrae, similar to the tails of dromaeosaurids. However, this may have been a juvenile feature. The fossil was named after Yang Liwei, the first Chinese astronaut in space.
Yaminuechelys is an extinct genus of chelid turtle from Argentina and the Dorotea Formation of Chile. The genus first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and became extinct during the Late Paleocene.

Stenorhynchosaurus is an extinct genus of pliosaurid plesiosaurs which lived in the Early Cretaceous of South America. The type species and only known is Stenorhynchosaurus munozi. It was a medium-sized pliosaur, reaching an adult body length of 7 m (23 ft).
Sinankylosaurus is a genus of dinosaur, originally described as an ankylosaur, from the late Cretaceous Period of Shandong, China. The genus contains a single species, Sinankylosaurus zhuchengensis, known from a nearly complete right ilium. The describers claim that the discovery of Sinankylosaurus further demonstrates the similarity between dinosaurs of eastern Asia and western North America.
Khulsanurus is an extinct genus of alvarezsaurid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Barungoyot Formation of the Khulsan Locality in the Gobi Desert region of Mongolia. The type and only species is Khulsanurus magnificus.

Natovenator is a genus of halszkaraptorine dromaeosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Barun Goyot Formation of Mongolia. The genus is known from a single species, N. polydontus. Natovenator is crucial to the understanding of halszkaraptorines due to it providing more support for the semi-aquatic lifestyle that has been proposed for this clade. This discovery is important as the semi-aquatic lifestyles of halszkaraptorines was contested in early 2022.













