
Vetulicolia is a clade of bilaterian animals encompassing several extinct species belonging to the Cambrian period. The phylum was created by Degan Shu and his research team in 2001, and named after Vetulicola cuneata, the first species of the phylum described in 1987.

The Maotianshan Shales (帽天山页岩) are a series of Early Cambrian sedimentary deposits in the Chiungchussu Formation, famous for their Konservat Lagerstätten, deposits known for the exceptional preservation of fossilized organisms or traces. The Maotianshan Shales form one of some forty Cambrian fossil locations worldwide exhibiting exquisite preservation of rarely preserved, non-mineralized soft tissue, comparable to the fossils of the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada. They take their name from Maotianshan Hill in Chengjiang County, Yunnan Province, China.

Vetulicola is an extinct genus of marine animal discovered from the Cambrian of China. It is the eponymous member of the enigmatic phylum Vetulicolia, which is of uncertain affinities but may belong to the deuterostomes. The name was derived from Vetulicola cuneata, the first species described by Hou Xian-guang in 1987 from the Lower Cambrian Chiungchussu Formation in Chengjiang, China.

Didazoon haoae is an extinct species of vetulicolid vetulicolian described by Shu, et al. based on fossils found in the Qiongzhusi (Chiungchussu) Formation, Yu'anshan Member, Lower Cambrian, in the Dabanqiao area (Kunming), about 60 km northwest of Chengjiang, China.

Pomatrum is an extinct vetulicolian, the senior synonym of Xidazoon; the latter taxon was described by Shu, et al. (1999) based on fossils found in the Qiongzhusi (Chiungchussu) Formation, Yu'anshan Member, Lower Cambrian, Haikou, (Kunming), about 50 km west of Chengjiang, China. It has been likened to the chordate Pipiscius.

Banffia is a genus of animals described from Middle Cambrian fossils. The genus commemorates Banff, Alberta, near where the first fossil specimens were discovered. Its placement in higher taxa is controversial. It is considered to be a member of the enigmatic phylum Vetulicolia.

Amplectobelua is an extinct genus of late Early Cambrian amplectobeluid radiodont, a group of stem arthropods that mostly lived as free-swimming predators during the first half of the Paleozoic Era.

Triops longicaudatus is a freshwater crustacean of the order Notostraca, resembling a miniature horseshoe crab. It is characterized by an elongated, segmented body, a flattened shield-like brownish carapace covering two thirds of the thorax, and two long filaments on the abdomen. The genus name Triops comes from Greek ὤψ or ṓps, meaning "eye" prefixed with Latin tri-, "three", in reference to its three eyes. Longicaudatus is a Latin neologism combining longus ("long") and caudatus ("tailed"), referring to its long tail structures. Triops longicaudatus is found in fresh water ponds and pools, often in places where few higher forms of life can exist.

Facivermis is a genus of sessile lobopodian from the Lower Cambrian Maotianshan shales of China

Radiodonta is an extinct order of stem-group arthropods that was successful worldwide during the Cambrian period. Radiodonts are distinguished by their distinctive frontal appendages, which are morphologically diverse and used for a variety of functions. Radiodonts included the earliest large predators known, but they also included sediment sifters and filter feeders. Some of the most famous species of radiodonts are the Cambrian taxa Anomalocaris canadensis, Hurdia victoria, Peytoia nathorsti, Titanokorys gainesi, Cambroraster falcatus and Amplectobelua symbrachiata. The later surviving members include the subfamily Aegirocassisinae from the Early Ordovician of Morocco and the Early Devonian member Schinderhannes bartelsi from Germany.

Vetulicola cuneata is a species of extinct animal from the Early Cambrian Chengjiang biota of China. It was described by Hou Xian-guang in 1987 from the Lower Cambrian Chiungchussu Formation, and became the first animal under an eponymous phylum Vetulicolia.

Eoredlichia is an extinct genus of trilobite of average to large size. It lived during the early Cambrian in the Chengjiang fauna of Yunnan, China, and in Australia and Thailand. Eoredlichia is compounded of the Greek ἠώς and Redlichia, a later but related genus, so it means "early Redlichia". The species epithet intermedia means intermediate, indicating it is morphologically intermediate between other species. Eofallotaspis gives rise to Lemdadella, and thence to Eoredlichia and the other Redlichiidae.

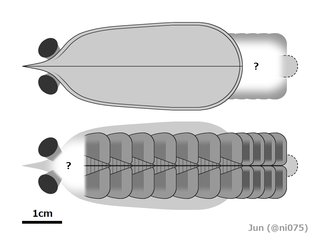
Ooedigera peeli is an extinct vetulicolian from the Early Cambrian of North Greenland. The front body was flattened horizontally, oval-shaped, likely bearing a reticulated or anastomosing pattern, and had 5 evenly-spaced gill pouches along the midline. The tail was also bulbous and flattened horizontally, but was divided into 7 plates connected by flexible membranes, allowing movement. Ooedigera likely swam by moving side-to-side like a fish. It may have lived in an oxygen minimum zone alongside several predators in an ecosystem based on chemosynthetic microbial mats, and was possibly a deposit or filter feeder living near the seafloor.

Skeemella is a genus of elongate animals from what is now the Middle Cambrian Wheeler Shale and Marjum lagerstätte of Utah. It has been classified with the vetulicolians.

Vetulicola rectangulata is a species of extinct animal from the Early Cambrian of the Chengjiang biota of China. Regarded as a deuterostome, it has characteristic rectangular anterior body on which the posterior tail region is attached. It was described by Luo Huilin and Hu Shi-xue in 1999.

Pachyophis is an extinct genus of Simoliophiidae snakes that were extant during the Cenomanian stage of the Late Cretaceous period. More specifically, it was found to be from the Cenomanian Age about 93.9-100.5 million years ago in the suburb area of Bileca, Herzegovina.

Paleomerus is a genus of strabopid, a group of extinct arthropods. It has been found in deposits from the Cambrian period. It is classified in the family Strabopidae of the monotypic order Strabopida. It contains two species, P. hamiltoni from Sweden and P. makowskii from Poland. The generic name is composed by the Ancient Greek words παλαιός (palaiós), meaning "ancient", and μέρος (méros), meaning "part".

Collinsovermis is a genus of extinct panarthropod belonging to the group Lobopodia and known from the middle Cambrian Burgess Shale in British Columbia, Canada. It is monotypic having only one species, Collinsovermis monstruosus. After its initial discovery in 1983, Desmond H. Collins popularised it as a unique animal and was subsequently dubbed "Collins' monster" for its unusual super armoured body. The formal scientific description and name were given in 2020.
Erratus is an extinct genus of marine arthropod from the Cambrian of China. Its type and only species is Erratus sperare. Erratus is likely one of the most basal known arthropods, and its discovery has helped scientists understand the early evolution of arthropod trunk appendages. Some of the stem-arthropods like radiodonts did not have legs, instead they had flap like appendages that helped them swim. Erratus on the other hand had not only flaps but also a set of primitive legs. It also supported the theory that the gills of aquatic arthropods probably evolved into the wings and lungs of terrestrial arthropods later in the Paleozoic.
The Cambrian chordates are an extinct group of animals belonging to the phylum Chordata that lived during the Cambrian, between 538 and 485 million years ago. The first Cambrian chordate known is Pikaia gracilens, a lancelet-like animal from the Burgess Shale in British Columbia, Canada. The discoverer, Charles Doolittle Walcott, described it as a kind of worm (annelid) in 1911, but it was later identified as a chordate. Subsequent discoveries of other Cambrian fossils from the Burgess Shale in 1991, and from the Chengjiang biota of China in 1991, which were later found to be of chordates, several Cambrian chordates are known, with some fossils considered as putative chordates.




















