
In human anatomy, the abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta.

In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric vein (SMV) is a blood vessel that drains blood from the small intestine. Behind the neck of the pancreas, the superior mesenteric vein combines with the splenic vein to form the portal vein that carries blood to the liver. The superior mesenteric vein lies to the right of the similarly named artery, the superior mesenteric artery, which originates from the abdominal aorta.

In human anatomy, the marginal artery of the colon, also known as the marginal artery of Drummond, the artery of Drummond, and simply as the marginal artery, is an artery that connects the inferior mesenteric artery with the superior mesenteric artery. It is sometimes absent, as an anatomical variant.

The right colic artery is an artery of the abdomen, a branch of the superior mesenteric artery supplying the ascending colon. It divides into two terminal branches - an ascending branch and a descending branch - which form anastomoses with the middle colic artery, and ileocolic artery (respectively).

The middle colic artery is an artery of the abdomen; a branch of the superior mesenteric artery distributed to parts of the ascending and transverse colon. It usually divides into two terminal branches - a left one and a right one - which go on to form anastomoses with the left colic artery, and right colic artery (respectively), thus participating in the formation of the marginal artery of the colon.

The left colic artery is a branch of the inferior mesenteric artery distributed to the descending colon, and left part of the transverse colon. It ends by dividing into an ascending branch and a descending branch; the terminal branches of the two branches go on to form anastomoses with the middle colic artery, and a sigmoid artery (respectively).

The ileocolic artery is the lowest branch arising from the concavity of the superior mesenteric artery. It supplies the cecum, ileum, and appendix.
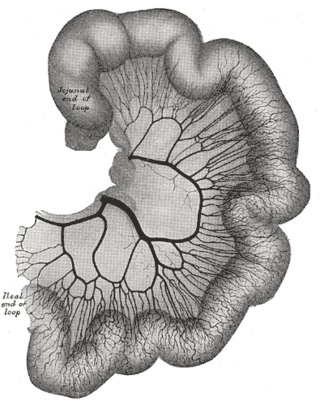
The intestinal arteries arise from the convex side of the superior mesenteric artery. They are usually from twelve to fifteen in number, and are distributed to the jejunum and ileum.

In the anatomy of the human digestive tract, there are two colic flexures, or curvatures in the transverse colon. The right colic flexure is also known as the hepatic flexure, and the left colic flexure is also known as the splenic flexure. Note that "right" refers to the patient's anatomical right, which may be depicted on the left of a diagram.

The superior mesenteric plexus is a continuation of the lower part of the celiac plexus, receiving a branch from the junction of the right vagus nerve with the plexus.

The anterior cecal artery is a branch of the ileocolic artery which supplies the anterior region of the cecum.

The posterior cecal artery is a branch of the ileocolic artery.

The appendicular artery, also known as the appendiceal artery, commonly arises from the terminal branch of the ileocolic artery, or less commonly from the posterior cecal artery or an ileal artery. It descends behind the termination of the ileum and enters the mesoappendix of the vermiform appendix. It runs near the free margin of the mesoappendix and ends in branches which supply the appendix.
In anatomy, arterial tree is used to refer to all arteries and/or the branching pattern of the arteries. This article regards the human arterial tree. Starting from the aorta:

The testicular artery is a branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies blood to the testicle. It is a paired artery, with one for each of the testicles.

The arterial arcades are a series of anastomosing arterial arches between the arterial branches of the jejunum and ileum.
Colic artery may refer to the:

The left colic vein is a vein that drains the left colic flexure and descending colon. It empties into the inferior mesenteric vein. It accompanies the left colic artery.

The ileal branch of ileocolic artery is a branch of the ileocolic artery.

The superior mesenteric lymph nodes may be divided into three principal groups:
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.











