
The thoracoacromial artery is a short trunk that arises from the second part of the axillary artery, its origin being generally overlapped by the upper edge of the pectoralis minor.

The radial recurrent artery arises from the radial artery immediately below the elbow.

The lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm is a sensory nerve representing the continuation of the musculocutaneous nerve beyond the lateral edge of the tendon of the biceps brachii muscle. The lateral cutaneous nerve provides sensory innervation to the skin of the lateral forearm. It pierces the deep fascia of forearm to enter the subcutaneous compartment before splitting into a volar branch and a dorsal branch.

The medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm is a sensory branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus derived from the ventral rami of spinal nerves C8-T1. It provides sensory innervation to the skin of the medial forearm and skin overlying the olecranon. It descends through the (upper) arm within the brachial fascia alongside the basilic vein, then divides into an anterior branch and a posterior branch upon emerging from the brachial fascia; the two terminal branches travel as far distally as the wrist.

The superior pancreaticoduodenal artery is an artery that supplies blood to the duodenum and pancreas.

The descending palatine artery is a branch of the third part of the maxillary artery supplying the hard and soft palate.

The sphenopalatine artery is an artery of the head, commonly known as the artery of epistaxis. It passes through the sphenopalatine foramen to reach the nasal cavity. It is the main artery of the nasal cavity.

The superficial branch of the radial nerve passes along the front of the radial side of the forearm to the commencement of its lower third. It is a sensory nerve.
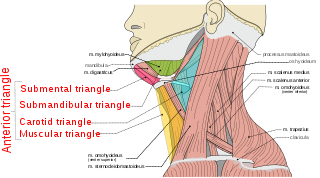
The anterior triangle is a region of the neck.

The superior rectal artery is an artery that descends into the pelvis to supply blood to the rectum.

The marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve arises from the facial nerve in the parotid gland at the parotid plexus. It passes anterior-ward deep to the platysma and depressor anguli oris muscles. It provides motor innervation to muscles of the lower lip and chin: the depressor labii inferioris muscle, depressor anguli oris muscle, and mentalis muscle. It communicates with the mental branch of the inferior alveolar nerve.

The buccal branches of the facial nerve, are of larger size than the rest of the branches, pass horizontally forward to be distributed below the orbit and around the mouth.

The dorsal branch of ulnar nerve arises about 5 cm. proximal to the wrist; it passes backward beneath the Flexor carpi ulnaris, perforates the deep fascia, and, running along the ulnar side of the back of the wrist and hand, divides into two dorsal digital branches; one supplies the ulnar side of the little finger; the other, the adjacent sides of the little and ring fingers.

The carotid triangle is a portion of the anterior triangle of the neck.

The temporal branches of the facial nerve crosses the zygomatic arch to the temporal region, supplying the auriculares anterior and superior, and joining with the zygomaticotemporal branch of the maxillary nerve, and with the auriculotemporal branch of the mandibular nerve.

The cervical branch of the facial nerve is a nerve in the neck. It is a branch of the facial nerve (VII). It supplies the platysma muscle, among other functions.

The digastric branch of facial nerve provides motor innervation to the posterior belly of the digastric muscle. It branches from the facial nerve near to the stylomastoid foramen as the CN VII exits the facial canal. It commonly arises in common with the stylohyoid branch of facial nerve.
The pharyngeal branches of the glossopharyngeal nerve are three or four filaments which unite, opposite the constrictor pharyngis medius, with the pharyngeal branches of the vagus and sympathetic, to form the pharyngeal plexus.

The tympanic plexus is a nerve plexus within the tympanic cavity formed upon the promontory of tympanic cavity by the tympanic nerve, and the superior and inferior caroticotympanic nerves.

The lesser palatine nerves (posterior palatine nerve) are branches of the maxillary nerve (CN V2). They descends through the greater palatine canal alongside the greater palatine nerve, and emerge (separately) through the lesser palatine foramen to pass posteriorward. They supply the soft palate, tonsil, and uvula.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.












