The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following the cephalic phase in which the sight and smell of food and the act of chewing are stimuli. In the stomach a chemical breakdown of food takes place by means of secreted digestive enzymes and gastric acid.

In human anatomy, the abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta.

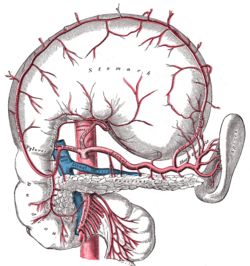
In human anatomy, the splenic artery or lienal artery, an older term, is the blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the spleen. It branches from the celiac artery, and follows a course superior to the pancreas. It is known for its tortuous path to the spleen.

In anatomy, the gastroduodenal artery is a small blood vessel in the abdomen. It supplies blood directly to the pylorus and proximal part of the duodenum. It also indirectly supplies the pancreatic head.

The lesser omentum is the double layer of peritoneum that extends from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach, and to the first part of the duodenum. The lesser omentum is usually divided into these two connecting parts: the hepatogastric ligament, and the hepatoduodenal ligament.

In human anatomy, the left gastric artery arises from the celiac artery and runs along the superior portion of the lesser curvature of the stomach before anastomosing with the right gastric artery. It also issues esophageal branches that supply lower esophagus and ascend through the esophageal hiatus to form anastomoses with the esophageal branches of thoracic part of aorta.

The hepatic artery proper is the artery that supplies the liver and gallbladder. It raises from the common hepatic artery, a branch of the celiac artery.

The short gastric veins, four or five in number, drain the fundus and left part of the greater curvature of the stomach, and pass between the two layers of the gastrolienal ligament to end in the splenic vein or in one of its large tributaries.
The left gastroepiploic vein receives branches from the antero-superior and postero-inferior surfaces of the stomach and from the greater omentum; it runs from right to left along the greater curvature of the stomach and ends in the commencement of the splenic vein.

The inferior phrenic artery is a bilaterally paired artery of the abdominal cavity which represents the main source of arterial supply to the diaphragm. Each artery usually arises either from the coeliac trunk or the abdominal aorta, however, their origin is highly variable and the different sites of origin are different for the left artery and right artery. The superior suprarenal artery is a branch of the inferior phrenic artery.

The right gastroepiploic artery is one of the two terminal branches of the gastroduodenal artery. It runs from right to left along the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, anastomosing with the left gastroepiploic artery, a branch of the splenic artery.

The left gastroepiploic artery, the largest branch of the splenic artery, runs from left to right about a finger's breadth or more from the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, and anastomoses with the right gastroepiploic.

The middle colic artery is an artery of the abdomen; a branch of the superior mesenteric artery distributed to parts of the ascending and transverse colon. It usually divides into two terminal branches - a left one and a right one - which go on to form anastomoses with the left colic artery, and right colic artery (respectively), thus participating in the formation of the marginal artery of the colon.

The right gastric artery usually arises from the proper hepatic artery. It descends to the pyloric end of the stomach before passing from right to left along its lesser curvature, supplying it with branches, and finally anastomosing with the left gastric artery.

The greater omentum is a large apron-like fold of visceral peritoneum that hangs down from the stomach. It extends from the greater curvature of the stomach, passing in front of the small intestines and doubles back to ascend to the transverse colon before reaching to the posterior abdominal wall. The greater omentum is larger than the lesser omentum, which hangs down from the liver to the lesser curvature. The common anatomical term "epiploic" derives from "epiploon", from the Greek epipleein, meaning to float or sail on, since the greater omentum appears to float on the surface of the intestines. It is the first structure observed when the abdominal cavity is opened anteriorly.

The right gastroepiploic vein is a blood vessel that drains blood from the greater curvature and left part of the body of the stomach into the superior mesenteric vein. It runs from left to right along the greater curvature of the stomach between the two layers of the greater omentum, along with the right gastroepiploic artery.

The left gastric vein is a vein that derives from tributaries draining the lesser curvature of the stomach.

The right gastric vein drains blood from the lesser curvature of the stomach into the hepatic portal vein. It is part of the portal circulation.

The curvatures of the stomach are the long, convex, lateral surface, and the shorter, concave, medial surface of the stomach, which are referred to as the greater and lesser curvatures, respectively. The greater curvature, which begins at the cardiac notch, and arches backwards, passing inferiorly to the left, is four or five times longer than the lesser curvature, which attaches to the hepatogastric ligament and is supplied by the left gastric artery and right gastric branch of the hepatic artery.
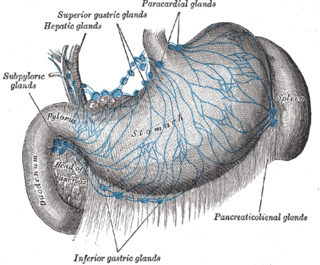
The gastric lymph nodes are lymph nodes which drain the stomach and consist of two sets, superior and inferior: