The Central Provinces and Berar was a province of British India and later the Dominion of India which existed from 1903 to 1950. It was formed by the merger of the Central Provinces with the province of Berar, which was territory leased by the British from the Hyderabad State. Through an agreement signed on 5 November 1902, 6th Nizam Mahbub Ali Khan, Asaf Jah VI leased Berar permanently to the British for an annual payment of 25 lakhs rupees. Lord Curzon decided to merge Berar with the Central Provinces, and this was proclaimed on 17 September 1903.

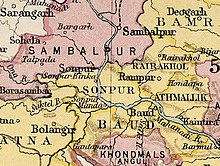
Sambalpur District is a district in the western part of state of Odisha, India. The historic city of Sambalpur is the district headquarters.

Subarnapur District, also called Sonepur District or Sonapur District, is an administrative district in Odisha state in eastern India. The town of Sonpur is the district headquarters. Sonepur is known as the Mandiramalini town of Odisha with more than hundred temples. The people of the Sonepur region are referred to as Sonepuria. From ancient times, Sonepur is considered as a holy city.

Bamra State or Bamanda State, covering an area of 5,149 km2, was one of the princely states of India during the British Raj. Its capital was in Debagarh (Deogarh). Bamra State acceded to India in 1948.

The Eastern States Agency was an agency or grouping of princely states in eastern India, during the latter years of the British Raj. It was created in 1933, by the unification of the former Chhattisgarh States Agency and the Orissa States Agency; the agencies remained intact within the grouping. In 1936, the Bengal States Agency was added.

Boudh District is an administrative and a municipal district, one of the thirty in the Odisha, India. The district headquarters of the Boudh District is the city of Boudh.
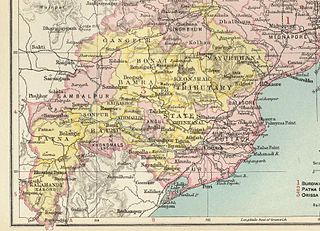
The Orissa Tributary States, also known as the Gadajats (ଗଡ଼ଜାତ) and as the Orissa Feudatory States, were a group of princely states of British India now part of the present-day Indian state of Odisha.

Chhattisgarh Division was an administrative division of the Central Provinces of British India. It was located in the east of the Central Provinces and encompassed the upper Mahanadi River basin, in the central part of present-day Chhattisgarh state of India.
Sonepur or Sonapur may refer to:
Western Odisha is the western part of the state of Odisha in India, extending from the Kalahandi district in the south to the Sundargarh district in the north.

Patna State was a princely state in the Eastern States Agency of India during the British Raj. It had its capital at Balangir. Its area was 6,503 km2 (2,511 sq mi).

Subarnameru Temple is situated in Sonepur town in Subarnapur district of Odisha, India. It is a shrine for the worshipping of Shiva and commonly known as Second Varanasi of India.

Gangpur State, also known as Gangpore State, was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. Until 1905 it was one of the Chhota Nagpur States under the Eastern States Agency.

Sambalpur is a district of Odisha. Sambalpur city is the headquarter of Sambalpur district. It is named after the presiding goddess Samaleshwari. Although it has prehistoric links and mythological mentions, the current settlement was established in the 14th century. Sambalpur is the cultural capital of Western Odisha.
Sonepur, is the district headquarters of Subarnapur district of Odisha, has a special place on the political and cultural map of India since the pre-historic period. It is bounded on the north by Sambalpur district, on the south and the South-East by Boudh district, on the east by Rairakhol sub-division of Sambalpur district and on the west by the ex-state Patna.

Kalahandi State, also known as Karond State, was one of the princely states of India during the British Raj. It was recognized as a state in 1874 and had its capital in Bhawanipatna. Its last ruler signed the accession to the Indian Union on 1 January 1948. The present titular head of the former state is Anant Pratap Deo who resides in the Kalahandi Palace in Bhawanipatna

Sarangarh was a princely state in India during the British Raj ruled by a Raj Gond dynasty. The emblem of the state was a turtle.

Sambalpur State, also known as Hirakhand Kingdom, was a kingdom founded in 1570. It ruled over Western Odisha and Eastern Chhattisgarh in central-eastern India prior to the Maratha occupation in 1800 AD. From 1849 AD, it was integrated with British Raj as a British District. Its capital was present-day Sambalpur city in Western Odisha.

Mayurbhanj State was one of the princely states of India during the British Raj. It was one of the largest states of the Eastern States Agency and one of the four salute states of the Orissa States Agency. The emblem of the state was two peacocks, for according to legend the ancestors of the rulers had originated from a peafowl's eyes.

Rairakhol State was a minor princely state during the British Raj in India. It was one of the Chota Nagpur States and had its capital at Rairakhol (Redhakhol), located in the present-day Sambalpur district of Odisha. It had an area of 2,157 square kilometres (833 sq mi) and a population of 26,888 in 1901. The average revenue was Rs. 55,000 in 1904.