Related Research Articles

Richmond is the capital city of the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. Incorporated in 1742, Richmond has been an independent city since 1871. The city's population in the 2020 census was 226,610, up from 204,214 in 2010, making it Virginia's fourth-most populous city. The Richmond metropolitan area, with over 1.3 million residents, is the Commonwealth's third-most populous.

Hanover County is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 109,979. Its county seat is Hanover.

Goochland County is a county located in the Piedmont of the Commonwealth of Virginia. Its southern border is formed by the James River. As of the 2020 census, the population was 24,727. Its county seat is Goochland.

Caroline County is a United States county located in the eastern part of the Commonwealth of Virginia. The northern boundary of the county borders on the Rappahannock River, notably at the historic town of Port Royal. The Caroline county seat is Bowling Green.

Amelia County is a county located just southwest of Richmond in the Commonwealth of Virginia, United States. The county is located in Central Virginia and is included in the Greater Richmond Region. Its county seat is Amelia Court House.

Highland Springs is a census-designated place (CDP) located in Henrico County, Virginia, United States, 4.3 miles (7 km) east of Richmond. The population was 16,604 at the 2020 census.
The Greater Richmond, Virginia area has many neighborhoods and districts.

Oliver White Hill Sr. was an American civil rights attorney from Richmond, Virginia. His work against racial discrimination helped end the doctrine of "separate but equal." He also helped win landmark legal decisions involving equality in pay for black teachers, access to school buses, voting rights, jury selection, and employment protection. He retired in 1998 after practicing law for almost 60 years. Among his numerous awards was the Presidential Medal of Freedom, which U.S. President Bill Clinton awarded him in 1999.

Shockoe Hill is one of several hills on which much of the oldest portion of the City of Richmond, Virginia, U.S., was built. It extends from the downtown area, including where the Virginia State Capitol complex sits, north almost a mile to a point where the hill falls off sharply to the winding path of Shockoe Creek. Interstate 95 now bisects the hill, separating the highly urbanized downtown portion from the more residential northern portion.

Jackson Ward, previously known as Central Wards, is a historically African-American district in Richmond, Virginia, with a long tradition of African-American businesses. It is located less than a mile from the Virginia State Capitol, sitting to the west of Court End and north of Broad Street. It was listed as a National Historic Landmark District in 1978. "Jackson Ward" was originally the name of the area's political district within the city, or ward, from 1871 to 1905, yet has remained in use long after losing its original meaning.

Fulton Hill is a neighborhood located in the East End of Richmond, Virginia. The name is used for the area stretching from Gillies Creek to the Richmond city limits. The Greater Fulton Hill Civic Association includes Fulton Bottom, part of Montrose Heights and part of Rocketts. Fulton Hill is south of Church Hill and Shockoe Bottom, north of Varina, east of the James River, and west of Sandston. The zip code is 23231.

Oakwood Cemetery is a large, city-owned burial ground in the East End of Richmond, Virginia. It holds over 48,000 graves, including many soldiers from the Civil War.
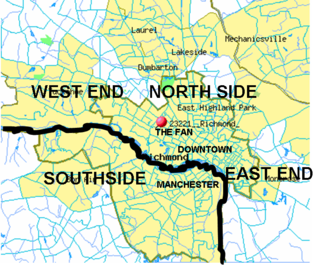
The East End of Richmond, Virginia is the quadrant of the City of Richmond, Virginia, and more loosely the Richmond metropolitan area, east of the downtown.
White House is an unincorporated community in New Kent County, Virginia, United States, on the south shore of the Pamunkey River. White House Plantation, for which it is named, was the home in the 18th century of Martha Dandridge Custis, who as a widow, there courted her future husband, Colonel George Washington. They were married in 1759.
Union Hill is an unincorporated community in Buckingham County, Virginia, that was founded by freed slaves after the American Civil War.
Creighton Court is a neighborhood in Richmond, Virginia's East End region. Creighton Court sits on the border between the City of Richmond and eastern Henrico County. The neighborhood is situated directly north of the Oakwood Cemetery and alongside the interchange of Virginia Route 33 and Interstate 64. North 29th Street and Creighton Road serve as the main arteries of the community. Richmond Redevelopment and Housing Authority redeveloped the housing into mixed-income units in 2022.
Gilpin is a small neighborhood located in Richmond, Virginia and within the boundaries of the North Side of the city limits. Originally part and parcel of the historically Black neighborhood of Jackson Ward, the northern section of that neighborhood was heavily redeveloped with the provision of public housing from the mid-20th century onwards, with the major development taking the name "Gilpin Court". During the same period, a massive expansion of highway building around and through central Richmond saw the Gilpin Court and the rest of the neighborhood essentially cut off from the rest of Jackson Ward.
Randolph is a historically black middle class neighborhood located within the West End of Richmond, Virginia. The neighborhood is named in honor of Virginia E. Randolph, a former African-American educator in Henrico County, Virginia during the 19th century. The neighborhood is bounded by the Downtown Expressway to the north, Harrison Street to the east, Colorado Avenue to the south, and South Meadow street to the west. Some famous landmarks and places of interest in the neighborhood include Petronius Park, the Randolph Community Center, and just adjacent to the neighborhood, the Hollywood Cemetery.

Sherwood Park is one of several historical neighborhoods that comprise the area known as Northside in the city of Richmond, Virginia.
The Shockoe Bottom African Burial Ground, or known historically as the "Burial Ground for Negroes" and the "old Powder Magazine ground", is the older of two municipal burial grounds established for the interment of free people of color and the enslaved in the city of Richmond, Virginia. It is located at 1554 E Broad St., across from the site of Lumpkin's Jail, in Shockoe Bottom. The area now known as Shockoe Bottom, was historically known as Shockoe Valley. Richmond's second African Burial Ground, called the Shockoe Hill African Burying Ground is the larger of the two burial grounds, and is located a mile and a half away at 1305 N 5th St, on Shockoe Hill.