Related Research Articles

Western New Guinea, also known as Papua or Indonesian New Guinea, is the western portion of New Guinea administered by Indonesia. Since the island is alternatively named as Papua, the region is also called West Papua. It is considered part of the Australian continent. The territory is mostly in the Southern Hemisphere and includes the Schouten and Raja Ampat archipelagoes. The region is predominantly covered with ancient rainforest where numerous traditional tribes live such as the Dani of the Baliem Valley although a large proportion of the population live in or near coastal areas with the largest city being Jayapura.

The East Geelvink Bay or East Cenderawasih languages are a language family of a dozen Papuan languages along the eastern coast of Geelvink Bay in Indonesian Papua, which is also known as Sarera Bay or Cenderawasih.
The Lakes Plain languages are a family of Papuan languages, spoken in the Lakes Plain of Indonesian New Guinea. They are notable for being heavily tonal and for their lack of nasal consonants.
Isirawa is a Papuan language spoken by about two thousand people on the north coast of Papua province, Indonesia. It's a local trade language, and use is vigorous. Stephen Wurm (1975) linked it to the Kwerba languages within the Trans–New Guinea family, and it does share about 20% of its vocabulary with neighboring Kwerba languages. However, based on its pronouns, Malcolm Ross (2005) felt he could not substantiate such a link, and left it as a language isolate. The pronouns are not, however, dissimilar from those of Orya–Tor, which Ross links to Kwerba, and Donahue (2002) accept it as a Greater Kwerba language.
The Awyu languages are a cluster of Papuan languages in Indonesian New Guinea. They number between five and eleven, depending on one's criteria for a 'language':
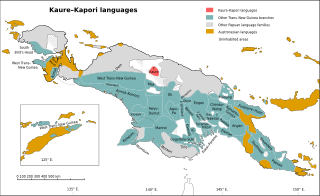
The Kaure–Kosare or Nawa River languages are a small family spoken along the Nawa River in West Papua, near the northern border with Papua New Guinea. The languages are Kaure and Kosare.

The Mek languages are a well established family of Papuan languages spoken by the Mek peoples. They form a branch of the Trans–New Guinea languages (TNG) in the classifications of Stephen Wurm (1975) and of Malcolm Ross (2005).

Koor or Kwoor is a village in West Papua, Indonesia. The village is located in Tambrauw (Regency) on the northern coast of the Bird's Head Peninsula. As of 1994 it was reported to have a population of 589 people.

Abun, also known as Yimbun, Anden, Manif, or Karon, is a Papuan language spoken along the northern coast of the Bird's Head Peninsula in Abun District, Tambrauw Regency. It is not closely related to any other language, and though Ross (2005) assigned it to the West Papuan family, based on similarities in pronouns, Palmer (2018), Ethnologue, and Glottolog list it as a language isolate.
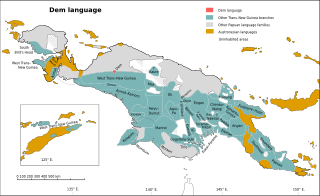
Dem is a divergent Papuan language of West New Guinea. Although Palmer (2018) leaves it unclassified, it was tentatively included in the Trans–New Guinea family in the classification of Malcolm Ross (2005), and Timothy Usher ties it most closely to Amung.
Samarokena is a poorly documented Papuan language spoken in Indonesian Papua.
Yoke is a poorly documented language spoken by about 200 people in the north of Papua, Indonesia. The name is also spelled Yoki, Yauke, and it is also known as Bitovondo. It was spoken in a single village in the interior until the government relocated a third of the population to a new village, Mantarbori, on the coast. In the late 19th century, a word list of "Pauwi" was collected by Robidé van der Aa at Lake Rombebai, where the Yoke say they migrated from; this is transparently Yoke, apart from some words which do not appear in the modern language but are found in related Warembori.
Berik is a Papuan language spoken in eastern Papua. Speakers are located in four village groups on the Tor River towards the northern coast of Indonesian-controlled Irian Jaya.
The Abawiri language, Foau, also known as Doa, is a Lakes Plain language of Papua, Indonesia. Clouse tentatively included Abawiri and neighboring Taburta in an East Lakes Plain subgroup of the Lakes Plain family; due to the minimal data that was available on the languages at that time. With more data, the connection looks more secure.
Semimi, or Etna Bay, is a Papuan language spoken in Kaimana Regency, West Papua, Indonesia.

Wolani (Wodani) is a Papuan language spoken by about 5,000 people in the Paniai lakes region of the Indonesian province of Papua. It is related to the Moni, Ekari, Auye, and Dao languages and may be related to the Dani languages. Documentation is quite limited.
Waritai is a Lakes Plain language of Irian Jaya, Indonesia. It is spoken in Taiyeve.

Duriankari, or Duriankere, is a possibly extinct Papuan language of Indonesian Papua. It is associated with the village of Duriankari at the southern tip of the island of Salawati, which is part of the Raja Ampat Archipelago and is adjacent to the Bird's Head Peninsula of the West Papuan mainland.
The East Pauwasi languages are a family of Papuan languages spoken in north-central New Guinea, on both sides of the Indonesia-Papua New Guinea border. They may either form part of a larger Pauwasi language family along with the Western Pauwasi languages, or they could form an independent language family.
References
- ↑ Airoran at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- Clouse, Duane, Mark Donohue and Felix Ma. 2002. "Survey report of the north coast of Irian Jaya."
- OLAC resources in and about the Airoran language