Related Research Articles

The Aru Islands Regency are a group of about ninety-five low-lying islands in the Maluku province of eastern Indonesia. They also form a regency of Maluku, with a land area of 6,426.77 square kilometres. At the 2011 Census the Regency had a population of 84,138; the 2020 Census produced a total of 102,237.
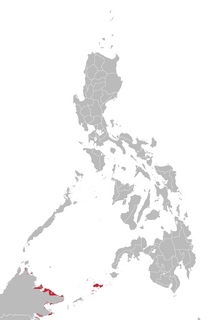
Tausug is an Austronesian language spoken in the province of Sulu in the Philippines and in the eastern area of the state of Sabah, Malaysia, by the Tausūg people. It is widely spoken in the Sulu Archipelago, the Zamboanga Peninsula, southern Palawan, and Malaysia.
Tukang Besi is an Austronesian language spoken in the Tukangbesi Islands in southeast Sulawesi in Indonesia by a quarter million speakers. A Tukang Besi pidgin is used in the area.
The phonology of Bengali, like that of its neighbouring Eastern Indo-Aryan languages, is characterised by a wide variety of diphthongs and inherent back vowels.
Bilua is the most populous Papuan language spoken in the Solomon Islands. It is a Central Solomon language spoken by about 9,000 people on the island of Vella Lavella. It is one of the four non-Austronesian languages spoken in the Solomon Islands.
The Kaingang language is a Southern Jê language spoken by the Kaingang people of southern Brazil. The Kaingang nation has about 30,000 people, and about from 60% to 65% speak the language. Most also speak Portuguese.
The Kwara'ae language is spoken in the north of Malaita Island in the Solomon Islands. In 1999, there were 32,400 people known to speak the language. It is the largest indigenous vernacular of the Solomon Islands.
Bena is a Bantu language spoken by the Bena people of the Iringa region of Tanzania.

The Enggano language, or Engganese, is an Austronesian language spoken on Enggano Island off the southwestern coast of Sumatra, Indonesia.
Western Dani, or Laani, is the most populous Papuan language in Indonesian New Guinea. It is spoken by the Lani people in the province of Papua. The Swart Valley tribes are called Oeringoep and Timorini in literature from the 1920s, but those names are no longer used.
The Bima language, or Bimanese is an Austronesian language spoken on the eastern half of Sumbawa Island, Indonesia, which it shares with speakers of the Sumbawa language. Bima territory includes the Sanggar Peninsula, where the extinct Papuan language Tambora was once spoken. "Bima" is an exonym; the autochthonous name for the territory is "Mbojo" and the language is referred to as "Nggahi Mbojo." There are over half a million Bima speakers. Neither the Bima nor the Sumbawa people have alphabets of their own for they use the alphabets of the Bugis and the Malay language indifferently.
Iranian Persian, Western Persian or Western Farsi, natively simply known as Persian, refers to the varieties of the modern Persian language spoken in Iran and by minorities in neighboring countries, as well as by Iranian communities throughout the world. These are mutually intelligible with other varieties of Persian, including Afghanistan's Dari and Tajikistan's Tajik.
Afenmai (Afemai), or Yekhee, is an Edoid language spoken in Edo State, Nigeria by Afenmai people. Not all speakers recognize the name "Yekhee"; some use the district name Etsako.
Muna is an Austronesian language spoken principally on the island of Muna as well as North-west Buton Island, off the southeast coast of Sulawesi in Indonesia. the island of Tobea Besar. The language is well-documented, especially by linguist René van den Berg. In 2007, the language had around 300,000 speakers.

Mambai language is spoken by the second largest ethnic group in East Timor, the Mambai people. The language is also called Mambae or Manbae.
Pakpak, or Batak Dairi, is an Austronesian language of Sumatra. It is spoken in Dairi Regency, Pakpak Bharat Regency, Parlilitan district of Humbang Hasundutan Regency, Manduamas district of Central Tapanuli Regency, and Subulussalam and Aceh Singkil Regency.
Tarangan is one of the Aru languages, spoken by inhabitants of the Aru Islands in eastern Indonesia. There are two "Tarangan" varieties: East and West Tarangan. These varieties are divergent, perhaps no closer than they are to Manombai, also spoken in the Arus. West Tarangan is a trade language of the southern islands.
Mariri (Mairiri) is an Austronesian language spoken on the Aru Islands of eastern Indonesia. It is close to Batuley.

The Sama language, Sinama, is the language of Sama-Bajau people of the Sulu Archipelago, Philippines; Sabah, Malaysia and parts of Indonesia. The Sama are one of the most widely dispersed peoples in Southeast Asia.

Bantoanon or Asi is a regional Bisayan language spoken, along with Romblomanon and Onhan, in the province of Romblon, Philippines. Asi originated in the island of Banton, Romblon and spread to the neighboring islands of Sibale, Simara, and the towns of Odiongan and Calatrava on Tablas Island. The Asi spoken in Odiongan is called Odionganon, Calatravanhon in Calatrava, Sibalenhon in Concepcion, Simaranhon in Corcuera, and Bantoanon in Banton.
References
- ↑ Batuley at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)