Related Research Articles
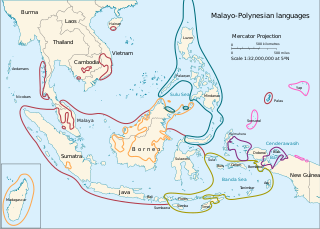
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula, with Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken in the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier.
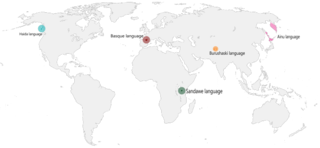
A language isolate is a language that has no demonstrable genetic relationship with another language. Basque in Europe, Ainu in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, Haida and Zuni in North America, Kanoê in South America, and Tiwi in Australia are all examples of language isolates. The exact number of language isolates is yet unknown due to insufficient data on several languages.

Uto-Aztecan, Uto-Aztekan or Uto-Nahuatl is a family of indigenous languages of the Americas, consisting of over thirty languages. Uto-Aztecan languages are found almost entirely in the Western United States and Mexico. The name of the language family was created to show that it includes both the Ute language of Utah and the Nahuan languages of Mexico.
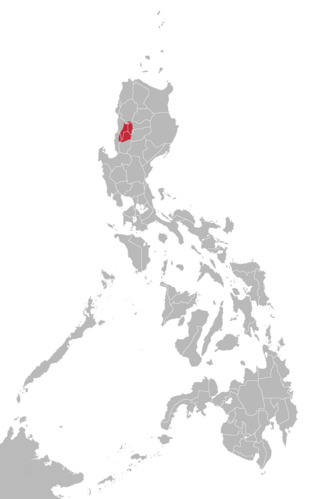
Kankanaey is a South-Central Cordilleran language under the Austronesian family spoken on the island of Luzon in the Philippines primarily by the Kankanaey people. Alternate names for the language include Central Kankanaey, Kankanai, and Kankanay. It is widely used by Cordillerans, alongside Ilocano, specifically people from Mountain Province and people from the northern part of the Benguet Province. Kankanaey has a slight mutual intelligibility with the Ilocano language.
Tukang Besi is an Austronesian language spoken in the Tukangbesi Islands in southeast Sulawesi in Indonesia by a quarter million speakers. A Tukang Besi pidgin is used in the area.
Mongondow, or Bolaang Mongondow, is one of the Philippine languages spoken in Bolaang Mongondow Regency and neighbouring regencies of North Sulawesi (Celebes) and Gorontalo Provinces, Indonesia. With more than 200,000 speakers, it is the major language of the regency. Historically, it served as the official language of the Bolaang Mongondow Kingdom.
The Senagi languages are a small family of Papuan languages in the classification of Malcolm Ross, that had been part of Stephen Wurm's Trans–New Guinea proposal. They consist of the two languages Angor and Dera.
The Yuat languages are an independent family of five Papuan languages spoken along the Yuat River in East Sepik Province, Papua New Guinea. They are an independent family in the classification of Malcolm Ross, but are included in Stephen Wurm's Sepik–Ramu proposal. However, Foley and Ross could find no lexical or morphological evidence that they are related to the Sepik or Ramu languages.
The Yalë language, also known as Yadë, Nagatman, or Nagatiman, is spoken in northwestern Papua New Guinea. It may be related to the Kwomtari languages, but Palmer (2018) classifies it as a language isolate.
Tause, also known as Doa or Darha, is a poorly-known Papuan language of Indonesia spoken by approximately 500 people, mainly in Derapos village.
Wetarese is an Austronesian language of Wetar, an island in the south Maluku, Indonesia, and of the nearby islands Liran and Atauro, the latter island separate from the mainland of East Timor, north of Dili.
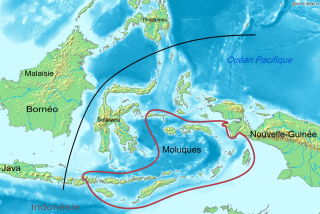
The Central Malayo-Polynesian languages (CMP) are a proposed branch in the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian language family. The languages are spoken in the Lesser Sunda and Maluku Islands of the Banda Sea, in an area corresponding closely to the Indonesian provinces of East Nusa Tenggara and Maluku and the nation of East Timor, but with the Bima language extending to the eastern half of Sumbawa Island in the province of West Nusa Tenggara and the Sula languages of the Sula archipelago in the southwest corner of the province of North Maluku. The principal islands in this region are Sumbawa, Sumba, Flores, Timor, Buru, and Seram. The numerically most important languages are Bima, Manggarai of western Flores, Uab Meto of West Timor, and Tetum, the national language of East Timor.

The Sama–Bajaw languages are a well-established group of languages spoken by the Sama-Bajau peoples of the Philippines, Indonesia and Malaysia.
West Makian is a divergent North Halmahera language of Indonesia. It is spoken on the coast near Makian Island, and on the western half of that island.
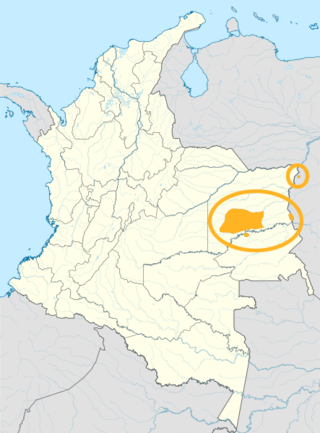
Piapoco is an Arawakan language of Colombia and Venezuela.

Dupaningan Agta, or Eastern Cagayan Agta, is a language spoken by a semi-nomadic hunter-gatherer Negrito people of Cagayan and Isabela provinces in northern Luzon, Philippines. Its Yaga dialect is only partially intelligible.
Fordata is an Austronesian language spoken in the Tanimbar Islands of the Moluccas. It is closely related to Kei, and more distantly to Yamdena, both also spoken in the Tanimbar Islands.
Tondano is an Austronesian language spoken in the Tondano area of northeast Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is most similar to Tombulu and to Tonsea.
Luang, also known as Literi Lagona, is an Austronesian language spoken in the Leti Islands and the Babar Islands in Maluku, Indonesia. It is closely related to the neighboring Leti language, with 89% shared basic vocabulary.
Lenakel, or West Tanna, is a dialect chain spoken on the western coast of Tanna Island in Vanuatu.
References
- ↑ Selaru at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ Coward, David F. (2005). An Introduction to the Grammar of Selaru (PDF). SIL International.