Related Research Articles

Zambales is a province in the Philippines located in the Central Luzon region. Its capital is Iba, which is located in the middle of the province. Zambales borders Pangasinan to the north and northeast, Tarlac to the east, Pampanga to the southeast, Bataan to the south and the South China Sea to the west. With a total land area of 3,830.83 square kilometres (1,479.09 sq mi), Zambales is the second largest among the seven provinces of Central Luzon after Nueva Ecija. The province is noted for its mangoes, which are abundant from January to April.

Kalinga is a dialect continuum of Kalinga Province in the Philippines, spoken by the Kalinga people, alongside Ilocano. The Banao Itneg variety is not one of the neighboring Itneg languages.
The Iraya language is a language spoken by Mangyans on the island of Mindoro in the Philippines. Zorc (1974) places the Iraya language within the North Mangyan group of Malayo-Polynesian languages, though Lobel (2013) notes that it shows "considerable differences" to Tadyawan and Alangan, the other languages in this group. There are 6,000 to 8,000 Iraya speakers, and that number is growing. The language status of Iraya is developing, meaning that this language is being put to use in a strong and healthy manner by its speakers, and it also has its own writing system.
The legislative districts of Zambales are the representations of the province of Zambales and the highly urbanized city of Olongapo in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The province and the city are currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through their first and second congressional districts.
The Sambalic languages are a part of the Central Luzon language family spoken by the Sambals, an ethnolinguistic group on the western coastal areas of Central Luzon and the Zambales mountain ranges.
The Indi language or Mag-indi is a Sambalic language with around 5,000 speakers. It is spoken within Philippine Aeta communities in San Marcelino, Zambales, and in the Pampango municipalities of Floridablanca and Porac. There are also speakers in Lumibao and Maague-ague.
Mariveleño is a Sambalic language. It has around 500 speakers and is spoken within an Aeta community in Mariveles in the Philippines.
The Northern Mindoro languages are one of two small clusters of languages spoken by the Mangyan people of Mindoro Island in the Philippines.
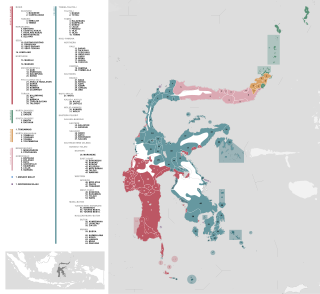
On the Indonesian island of Sulawesi, 114 native languages are spoken, all of which belong to the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian language family. With a total number of 17,200,000 inhabitants, Sulawesi displays a high linguistic diversity when compared with the most densely populated Indonesian island Java, which hosts 4–8 languages spoken by 145,100,000 inhabitants.
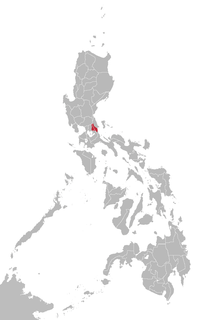
Remontado, also known as Sinauna, Kabalat, Remontado Dumagat, and Hatang-Kayi, is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken in Tanay, Rizal, General Nakar, Quezon, Rodriguez, Rizal and Antipolo, in the Philippines. It is one of the Philippine Negrito languages.
The Greater Central Philippine languages are a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian language family. They are spoken in the central and southern parts of the Philippines, and in northern Sulawesi. This subgroup was first proposed by Robert Blust (1991) based on lexical and phonological evidence, and is accepted by most specialists in the field.
Arta is a highly endangered Negrito language of the northern Philippines.
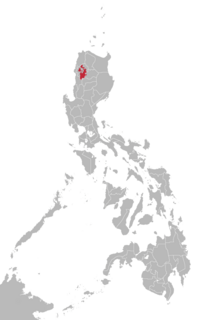
Itneg is a South-Central Cordilleran dialect continuum found in the island of Luzon, Philippines. This language and Ilocano are spoken by the Itneg people in Abra.
The Negrito peoples of the Philippines speak various Philippine languages. They have more in common with neighboring languages than with each other, and are listed here merely as an aid to identification.
Atta is an Austronesian dialect cluster spoken by the Aeta (Agta) Negritos of the northern Philippines.
Inagta Rinconada is a Bikol language spoken by a semi-nomadic hunter-gatherer Agta (Negrito) people of the Philippines. It is spoken to the east of Iriga City up to the shores of Lake Buhi. The language is largely intelligible with Mount Iraya Agta on the other side of the lake.
Central Cagayan Agta, also known as Labin Agta, is an Aeta language of northern Cagayan Province, Philippines. It is spoken by the Aeta Negritos in inland areas located to the east and northeast of Baggao (Ethnologue).
Umiray Dumaget Agta is an Aeta language spoken in southern Luzon Island.
The Southern Cordilleran languages are a group of closely related languages within the Northern Luzon subgroup of the Austronesian language family. They are spoken in an area stretching from the southern shore of the Lingayen Gulf to the highlands of Quirino province. The most widely spoken Southern Cordilleran language is Pangasinan, one of the eight major languages of the Philippines.
The Central Cordilleran languages are a group of closely related languages within the Northern Luzon subgroup of the Austronesian language family. They are spoken in the interior highlands of Northern Luzon in the Cordillera Central mountain range.
References
- ↑ Ambala at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
- ↑ Ramos 2004
- ↑ "Ayta, Ambala". Ethnologue. Retrieved 2021-10-25.
- ↑ Reid, Lawrence A. (1994). "Possible Non-Austronesian Lexical Elements in Philippine Negrito Languages". Oceanic Linguistics. 33 (1): 37–72. doi:10.2307/3623000. JSTOR 3623000.
- ↑ Himes, Ronald S. (2012). "The Central Luzon Group of Languages". Oceanic Linguistics. 51 (2): 490–537. doi:10.1353/ol.2012.0013. JSTOR 23321866.