
Flores island is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands, a group of islands in the eastern half of Indonesia. The population was 2,039,373 in the 2020 Census and the largest town is Maumere. The name Flores is the Portuguese word for "Flowers".

The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula. Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan serve as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken in the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier. The languages spoken south-westward from central Micronesia until Easter Island are sometimes referred to as the Polynesian languages.

East Nusa Tenggara is the southernmost province of Indonesia. It comprises the eastern portion of the Lesser Sunda Islands, facing the Indian Ocean in the south and the Flores Sea in the north. It consists of more than 500 islands, with the largest ones being Sumba, Flores, and the western part of Timor; the latter shares a land border with the separate nation of East Timor. The province is subdivided into twenty-one regencies and the regency-level city of Kupang, which is the capital and largest city.
The Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian (CEMP) languages form a proposed branch of the Malayo-Polynesian languages consisting of over 700 languages.
Ngadha is an Austronesian language, one of six languages spoken in the central stretch of the Indonesian island of Flores. From west to east these languages are: Ngadha, Nage, Keo, Ende, Lio, and Palu'e. These languages form the proposed Central Flores group of the Sumba–Flores languages, according to Blust (2009).

Ende is the seat capital of the Ende Regency, East Nusa Tenggara province of Indonesia. Ende is located on the southern coast of Flores Island. The town has a population of 93,894 residents in 2018 which makes it the largest town on the island.

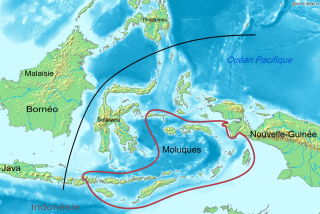
The Central Malayo-Polynesian languages (CMP) are a proposed branch in the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian language family. The languages are spoken in the Lesser Sunda and Maluku Islands of the Banda Sea, in an area corresponding closely to the Indonesian provinces of East Nusa Tenggara and Maluku and the nation of East Timor, but with the Bima language extending to the eastern half of Sumbawa Island in the province of West Nusa Tenggara and the Sula languages of the Sula archipelago in the southwest corner of the province of North Maluku. The principal islands in this region are Sumbawa, Sumba, Flores, Timor, Buru, and Seram. The numerically most important languages are Bima, Manggarai of western Flores, Uab Meto of West Timor, and Tetum, the national language of East Timor.

H. Hasan Aroeboesman Airport, also known as Ende Airport or Isi Airport, is an airport in Ende, Flores island, East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. The airport serves as the point of entry to the Kelimutu National Park, which is located 60 km from the airport.

The Manggarai are an ethnic group found in western Flores in the East Nusa Tenggara province, Indonesia. Manggarai people are spread across three districts in the province, namely the West Manggarai Regency, Manggarai Regency and East Manggarai Regency.
The Sumba–Hawu languages are a group of closely related Austronesian languages, spoken in East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia.
The Sumba–Flores languages, which correspond to the traditional "Bima–Sumba" subgroup minus Bima, are a proposed group of Austronesian languages spoken on and around the islands of Sumba and western–central Flores in the Lesser Sundas. The main languages are Manggarai, which has half a million speakers on the western third of Flores, and Kambera, with a quarter million speakers on the eastern half of Sumba Island.

Mandailing or Batak Mandailing is an Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, the northern island of Sumatra. It is spoken mainly in Mandailing Natal Regency, North Padang Lawas Regency, Padang Lawas Regency, and eastern parts of Labuhan Batu Regency, North Labuhan Batu Regency, South Labuhan Batu Regency and northwestern parts of Riau Province. It is written using the Latin script but historically used Batak script.

The Manggarai language is the language of the Manggarai people from the western parts of the island of Flores, in East Nusa Tenggara Province, Indonesia.
Lamaholot, also known as Solor or Solorese, is a Central Malayo-Polynesian dialect cluster of Flores, Indonesia. The varieties may not be all mutually intelligible; Keraf (1978) reports that there are 18 languages under the name.
Lio is an Austronesian language spoken in the central part of Flores, one of the Lesser Sunda Islands in the eastern half of Indonesia. It belongs to the Central Flores subgroup.
Ende may refer to the following languages:
Lio is a Belgian singer and actress.
The Flores–Lembata languages are a group of related Austronesian languages spoken in the Lesser Sundas, on eastern Flores and small islands immediately east of Flores. They are suspected of having a non-Austronesian substratum, for example in Sika, but not to any greater extent than the Central Malayo-Polynesian languages in general.
The Central Flores languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian language family. They are spoken in the central part of Flores, one of the Lesser Sunda Islands in the eastern half of Indonesia. The speech area of the Central Flores languages is bordered to the west by the Manggarai language, and to the east by the Sikka language.









