Related Research Articles
Tukang Besi is an Austronesian language spoken in the Tukangbesi Islands in southeast Sulawesi in Indonesia by a quarter million speakers. A Tukang Besi pidgin is used in the area.
Chuukese, also rendered Trukese, is a Chuukic language of the Austronesian language family spoken primarily on the islands of Chuuk in the Caroline Islands in Micronesia. There are communities of speakers on Pohnpei, and Guam. Estimates show that there are about 45,900 speakers in Micronesia.
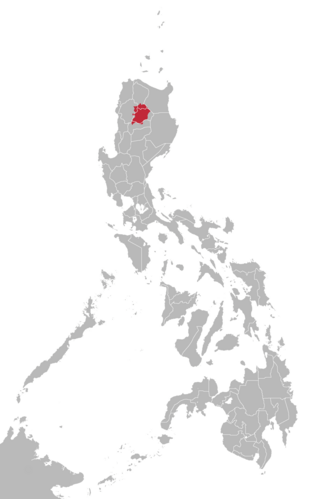
Kalinga is a dialect continuum of Kalinga Province in the Philippines, spoken by the Kalinga people, alongside Ilocano. The Banao Itneg variety is not one of the neighboring Itneg languages.
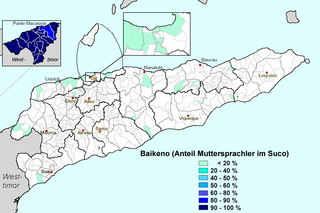
Uab Meto or Dawan is an Austronesian language spoken by Atoni people of West Timor. The language has a variant spoken in the East Timorese exclave of Oecussi-Ambeno, called Baikenu. Baikenu uses words derived from Portuguese, for example, obrigadu for 'thank you', instead of the Indonesian terima kasih.
Wetarese is an Austronesian language of Wetar, an island in the south Maluku, Indonesia, and of the nearby islands Liran and Atauro, the latter island separate from the mainland of East Timor, north of Dili.
Buyang is a Kra language spoken in Guangnan and Funing counties, Yunnan Province, China by the Buyang people. It is important to the reconstruction of the hypothetical macrofamily Austro-Tai as it retains the disyllabic roots characteristic of Austronesian languages. Examples are "to die", "eye", "head", and "eight".

The Santa Cruz language is the main language spoken on the island of Nendö or 'Santa Cruz', in the Solomon Islands.
The Saluan–Banggai languages are a group of closely related languages spoken in eastern Central Sulawesi province, Indonesia. They belong to the Celebic subgroup of the Austronesian family.
The Central Maluku languages are a proposed subgroup of the Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian branch of the Austronesian language family which comprises around fifty languages spoken principally on the Seram, Buru, Ambon, Kei, and the Sula Islands. None of the languages have as many as fifty thousand speakers, and several are extinct.
The Buru–Sula languages are a group of Austronesian languages spoken on the Buru and Sula Islands in the eastern Moluccas. Buru itself has almost forty thousand speakers, and Sula about twenty thousand.
Ma'ya is an Austronesian language of the Raja Ampat islands in Southwest Papua, Indonesia. It is spoken by about 6,000 people in coastal villages on the islands Misool, Salawati, and Waigeo. It is spoken on the boundary between Austronesian and Papuan languages.
The Bima language, or Bimanese, is an Austronesian language spoken on the eastern half of Sumbawa Island, Indonesia, which it shares with speakers of the Sumbawa language. Bima territory includes the Sanggar Peninsula, where the extinct Papuan language Tambora was once spoken. Bima is an exonym; the autochthonous name for the territory is Mbojo and the language is referred to as Nggahi Mbojo. There are over half a million Bima speakers. Neither the Bima nor the Sumbawa people have alphabets of their own for they use the alphabets of the Bugis and the Malay language indifferently.
Muyuw language is one of the Kilivila–Louisiades languages, spoken on the Woodlark Islands, in the Solomon Sea within Papua New Guinea.
Kayan is a dialect cluster spoken by the Kayan people of Borneo. It is a cluster of closely related dialects with limited mutual intelligibility, and is itself part of the Kayan-Murik group of Austronesian languages.
Kalagan is an Austronesian dialect cluster of the Davao Region of Mindanao in the Philippines. It is also spoken in a few parts of Caraga, still in Mindanao.
Kulisusu is an Austronesian language of Southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is part of a dialect chain with two minor languages, Koroni and Taloki.
Lamaholot, also known as Solor or Solorese, is a Central Malayo-Polynesian dialect cluster of Flores, Indonesia. The varieties may not be all mutually intelligible; Keraf (1978) reports that there are 18 languages under the name.
Calamian Tagbanwa is spoken in the Calamian Islands just north of Palawan Island, Philippines. It is not mutually intelligible with the other languages of the Tagbanwa people. Ethnologue reports that it is spoken in Busuanga, Coron, Culion, and Linapacan municipalities.
Mengen and Poeng are rather divergent dialects of an Austronesian language of New Britain in Papua New Guinea.
Rejang is an Austronesian language predominantly spoken by the Rejang people in southwestern parts of Sumatra (Bengkulu), Indonesia. There are five dialects, spread from mountainous region to the coastal region of Bengkulu, including the Musi (Musai) dialect, the Lebong dialect, the Kebanagung dialect, the Rawas (Awes) dialect, and the Pesisir dialect.
References
- ↑ Taliabo at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
Kadai at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required) - ↑ Charles Grimes & Owen Edwards (in process) Wallacean subgroups: unravelling the prehistory and classification of the Austronesian languages of eastern Indonesia and Timor-Leste. Summary presentation at the 15th International Conference on Austronesian Linguistics.
- ↑ Ridwan, Farida M.; Mulae, Sunaidin O.; Asriyani, Sherly (2020). Phonological Variation of Taliabu Language Dialects. Retorika Jurnal Bahasa Sastra dan Pengajarannya.
- ↑ Blust, Robert (1981). The Soboyo Reflexes of Proto-Austronesian *S. Historical Linguistics in Indonesia, Part 1. pp. 21–30.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)