Related Research Articles

Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guinea. Indonesia is the world's largest archipelagic state and the 14th-largest country by area, at 1,904,569 square kilometres. With over 275 million people, Indonesia is the world's fourth-most populous country and the most populous Muslim-majority country. Java, the world's most populous island, is home to more than half of the country's population.

Papua, is a province of Indonesia, comprising the northern coast of Western New Guinea together with island groups in Cenderawasih Bay to the west. It roughly follows the borders of Papuan customary region of Tabi Saireri. It is bordered by the sovereign state of Papua New Guinea to the east, the Pacific Ocean to the north, Cenderawasih Bay to the west, and the provinces of Central Papua and Highland Papua to the south. The province also shares maritime boundaries with Palau in the Pacific. Following the splitting off of twenty regencies to create the three new provinces of Central Papua, Highland Papua, and South Papua on 30 June 2022, the residual province is divided into eight regencies (kabupaten) and one city (kota), the latter being the provincial capital of Jayapura. The province has a large potential in natural resources, such as gold, nickel, petroleum, etc. Papua, along with four other Papuan provinces, has a higher degree of autonomy level compared to other Indonesian provinces.
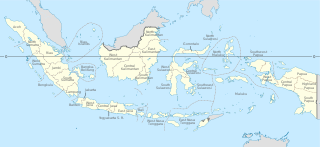
Provinces of Indonesia are the 37 administrative division of Indonesia and the highest tier of the local government. Provinces are further divided into regencies and cities, which are in turn subdivided into districts (kecamatan).

Jayapura is the capital and largest city of the Indonesian province of Papua. It is situated on the northern coast of New Guinea island and covers an area of 940.0 km2 (362.9 sq mi). The city borders the Pacific Ocean and Yos Sudarso Bay to the north, the sovereign state of Papua New Guinea to the east, Keerom Regency to the south, and Jayapura Regency to the west.

"Free Papua Movement" is an umbrella term for the independence movement established during 1965 in the West Papuan or West New Guinea territory which is currently being administrated by Indonesia as the provinces of Papua and West Papua, also formerly known as Papua, Irian Jaya and West Irian.

West Papua, formerly Irian Jaya Barat, is a province of Indonesia. It covers the two western peninsulas of the island of New Guinea, the Bird's Head Peninsula and the Bomberai Peninsula, along with nearby islands. The province is bordered to the north by the Pacific Ocean, to the west by the Halmahera Sea and the Ceram Sea, to the south by the Banda Sea, and to the east by the province of Central Papua and the Cenderawasih Bay. Manokwari is the province's capital, while Sorong is its largest city. West Papua is the fourth-least populous province in Indonesia, with a population of 1,134,068 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate for mid 2021 was 1,156,840.

The indigenous peoples of New Guinea in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, commonly called Papuans, are Melanesians. There is genetic evidence for two major historical lineages in New Guinea and neighboring islands. A first wave from the Malay Archipelago perhaps 50,000 years ago when New Guinea and Australia were a single landmass called Sahul and, much later, a wave of Austronesian people from the north who introduced Austronesian languages and pigs about 3,500 years ago. They also left a small but significant genetic trace in many coastal Papuan peoples.

Western New Guinea, also known as Papua, Indonesian New Guinea, or Indonesian Papua, is the western portion of the Melanesian island of New Guinea which is administered by Indonesia. Since the island is alternatively named as Papua, the region is also called West Papua. Lying to the west of Papua New Guinea and considered a part of the Australian continent, the territory is mostly in the Southern Hemisphere and includes the Schouten and Raja Ampat archipelagoes. The region is predominantly covered with ancient rainforest where numerous traditional tribes live such as the Dani of the Baliem Valley although a large proportion of the population live in or near coastal areas with the largest city being Jayapura.

Indonesia is divided into provinces. Provinces are made up of regencies (kabupaten) and cities (kota). Provinces, regencies and cities have their own local governments and parliamentary bodies.

More than 700 living languages are spoken in Indonesia. These figures indicate that Indonesia has about 10% of the world's languages, establishing its reputation as the second most linguistically diverse nation in the world after Papua New Guinea. Most languages belong to the Austronesian language family, while there are over 270 Papuan languages spoken in eastern Indonesia.
This is a list of some of the regions of Indonesia. Many regions are defined in law or regulations by the central government. At different times of Indonesia's history, the nation has been designated as having regions that do not necessarily correlate to the current administrative or physical geography of the territory of the nation.

Papua New Guinea, a sovereign state in Oceania, is the most linguistically diverse country in the world. According to Ethnologue, there are 839 living languages spoken in the country. In 2006, Papua New Guinea Prime Minister Sir Michael Somare stated that "Papua New Guinea has 832 living languages ." Languages with statutory recognition are Tok Pisin, English, Hiri Motu, and Papua New Guinean Sign Language. Tok Pisin, an English-based creole, is the most widely spoken, serving as the country's lingua franca. Papua New Guinean Sign Language became the fourth officially recognised language in May 2015, and is used by the deaf population throughout the country.

New Guinea is the world's second-largest island with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi). Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the 150-kilometre wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the independent state of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Papua, Central Papua, Highland Papua, South Papua, and West Papua. The largest cities on the island are Jayapura and Port Moresby.

The Papua conflict is an ongoing conflict in Western New Guinea between Indonesia and the Free Papua Movement. Subsequent to the withdrawal of the Dutch administration from the Netherlands New Guinea in 1962 and implementation of Indonesian administration in 1963, the Free Papua Movement has conducted a low-intensity guerrilla war against Indonesia through the targeting of its military, police, and civilian populations.

Indonesia – Papua New Guinea relations are foreign relations between Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, two bordering countries north of Australia.
The term district, in the context of Indonesia, refers to the third-level administrative subdivision, below regency or city. The local term kecamatan is used in majority of Indonesian areas, except in Papua, West Papua, and the Special Region of Yogyakarta. The term distrik is used in Papua and West Papua. In the Special Region of Yogyakarta, the term kapanewon is used for districts within the regencies, while the term kemantren is used for districts within Yogyakarta, the province's only city. According to Statistics Indonesia, there are a total of 7,252 districts in Indonesia as at 2019, subdivided into 83,820 administrative villages.
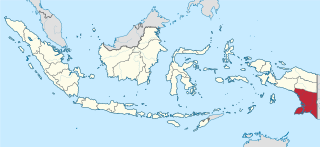
South Papua, officially the South Papua Province, is an Indonesian province located in the southern portion of Papua, following the borders of Papuan customary region of Anim Ha. Formally established on 25 July 2022 and including the four most southern regencies that were previously part of the province of Papua and before 2002 were part of Merauke Regency, it covers an area of 127,280.69 km2 and had a population of 517,623 according to the official estimates for mid 2021.

Central Papua, officially the Central Papua Province is an Indonesian province located in the central region of Western New Guinea. It was formally established on 25 July 2022 from the former eight western regencies of the province of Papua. It covers an area of 66,130.49 km2 and had an estimated population of about 1,409,000 in mid 2021. It is bordered by the Indonesian provinces of West Papua to the west, the residual Papua to the north, and by Highland Papua and South Papua to the east. The designated administrative capital, Nabire, is the second largest town in Central Papua, the economic centre of the province, and the seat of the Central Papua provincial government.

Highland Papua is a province of Indonesia, which roughly follows the borders of Papuan customary region of Lano-Pago shortened to La Pago. It covers an area of 69,685.31 km2 and had a population of 1,408,641 according to the official estimates as at mid 2021.
References
- ↑ Manem at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)