Related Research Articles

Afroasiatic (Afro-Asiatic), also known as Afrasian or Hamito-Semitic, Semito-Hamitic, or Erythraean, is a large language family of about 300 languages that are spoken predominantly in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa and parts of the Sahel. With the exception of Semitic, all branches of the Afroаsiatic family are spoken exclusively on the African continent.

The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are Indo-European languages spoken primarily by the Slavic peoples or their descendants. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic, spoken during the Early Middle Ages, which in turn is thought to have descended from the earlier Proto-Balto-Slavic language, linking the Slavic languages to the Baltic languages in a Balto-Slavic group within the Indo-European family.

Turkish, also referred to as Istanbul Turkish or Turkey Turkish, is the most widely spoken of the Turkic languages, with around 70 to 80 million speakers. It is the national language of Turkey. Significant smaller groups of Turkish speakers exist in Iraq, Syria, Germany, Austria, Bulgaria, North Macedonia, Northern Cyprus, Greece, the Caucasus, and other parts of Europe and Central Asia. Cyprus has requested that the European Union add Turkish as an official language, even though Turkey is not a member state.
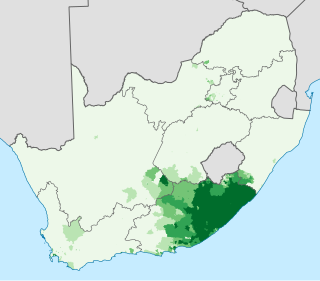
Xhosa also isiXhosa as an endonym, is a Nguni language and one of the official languages of South Africa and Zimbabwe. Xhosa is spoken as a first language by approximately 8.2 million people and by another 11 million as a second language in South Africa, mostly in Eastern Cape, Western Cape, Gauteng and Northern Cape. It has perhaps the heaviest functional load of click consonants in a Bantu language, with one count finding that 10% of basic vocabulary items contained a click.
Meitei, or Meetei is a Tibeto-Burman language and the predominant language and lingua franca of the state of Manipur in northeastern India. It is one of the official languages of the Government of India.

The Persian alphabet is a writing system used for the Persian language spoken in Iran and Afghanistan since the 7th century after Muslim conquest of Persia.
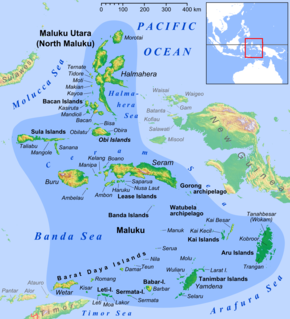
The Babar Islands(Indonesian: Kepulauan Babar) are located in Maluku Province, Indonesia between latitudes 7 degrees 31 minutes South to 8 degrees 13 minutes South and from longitudes 129 degrees 30 minutes East to 130 degrees 05 minutes East. The group now constitutes five districts (kecamatan) within the Maluku Barat Daya Regency of Maluku province.

Gaagudju is an extinct Australian Aboriginal language formerly spoken in the environs of Kakadu National Park, in Arnhem Land, Northern Territory, Australia.
Warluwarra is an extinct Australian Aboriginal language of Queensland. Waluwarra has a traditional language region in the local government area of Shire of Boulia, including Walgra Station and Wolga, from Roxborough Downs north to Carandotta Station and Urandangi on the Georgina River, on Moonah Creek to Rochedale, south-east of Pituri Creek.

The Malayic languages are a branch of the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian language family. The most prominent member is Standard Malay, which is the national language of Brunei, Singapore and Malaysia; it further serves as basis for Indonesian, the national language of Indonesia. The Malayic branch also includes the local languages spoken by ethnic Malays, further several languages spoken by various other ethnic groups of Sumatra and Borneo. The most probable candidate for the urheimat of the Malayic languages is western Borneo.
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, originally spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after Anglia, a peninsula on the Baltic Sea, and the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the area of Great Britain that later took their name: England. Living languages most closely related to English include the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, while English's vocabulary has been significantly influenced by Old Norman French and Latin, as well as by other Germanic languages, particularly Old Norse.
Yeyi is a Bantu language spoken by many of the approximately 50,000 Yeyi people along the Okavango River in Namibia and Botswana. Yeyi, influenced by Juu languages, is one of several Bantu languages along the Okavango with clicks. Indeed, it has the largest known inventory of clicks of any Bantu language, with dental, alveolar, palatal, and lateral articulations. Though most of its older speakers prefer Yeyi in normal conversation, it is being gradually phased out in Botswana by a popular move towards Tswana, with Yeyi only being learned by children in a few villages. Yeyi speakers in the Caprivi Strip of north-eastern Namibia, however, retain Yeyi in villages, but may also speak the regional lingua franca, Lozi.
Laghuu is a Loloish language spoken in northwestern Vietnam. In Nậm Sài, Sa Pa Town, the speakers' autonym is, while in Sơn La Province it is. The people are also called the Phù Lá Lão by the Vietnamese.

Dutch is a West Germanic language spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million people as a second language, constituting most of the population of the Netherlands and about 60% of the population of Belgium. It is the third most widely spoken Germanic language, after its close relatives English and German.
Leti is an Austronesian language spoken on the island of Leti in Maluku. Although it shares much vocabulary with the neighboring Luang language, it is marginally mutually intelligible.
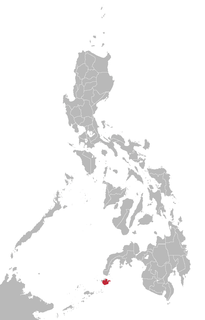
Yakan is an Austronesian language primarily spoken on Basilan Island in the Philippines. It is the native language of the Yakan people, the indigenous as well as the largest ethnic group on the island. It has a total of 110,000 native speakers. Despite being located in the Philippines, it is not closely related to other languages of the country. It is a member of the Sama-Bajaw languages, which in turn are related to the Barito languages spoken in southern Borneo, Madagascar and Mayotte.
Manusela is an Austronesian language spoken in Seram, Indonesia. It is classified by Collins (1983) as a member of the Central Maluku subgroup.
Irmen culture is an indigenous Late Bronze Age culture of animal breeders in the steppe and forest steppe area of the Ob river middle course, north of Altai in western Siberia, dated to around the 9th to 8th centuries BCE. Monuments of this advanced bronze-producing culture include numerous settlements and kurgan cemeteries, the culture was named after Irmen kurgan cemetery now flooded by Novosibirsk reservoir. Irmen culture was discovered and described by N.L.Chlenova in 1970.
Serua is an extinct Austronesian language originally spoken on Serua Island in Maluku, Indonesia. Speakers were relocated to Seram due to volcanic activity on Serua.

Bantoanon or Asi is a regional Bisayan language spoken, along with Romblomanon and Onhan, in the province of Romblon, Philippines. Asi originated in the island of Banton, Romblon and spread to the neighboring islands of Sibale, Simara, and the towns of Odiongan and Calatrava on Tablas Island. The Asi spoken in Odiongan is called Odionganon, Calatravanhon in Calatrava, Sibalenhon in Concepcion, Simaranhon in Corcuera, and Bantoanon in Banton.
References
- Svetlana Chlenova. 2002. "Daweloor, A Southwest Moluccan Language," Malaisko-indoneziiskie Issledovanlija 15:145-175.