Related Research Articles

Chinese is a group of languages spoken natively by the ethnic Han Chinese majority and many minority ethnic groups in Greater China. About 1.3 billion people speak a variety of Chinese as their first language.
C is a general-purpose computer programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie, and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems, device drivers, protocol stacks, though decreasingly for application software. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems.

French is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the (Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French.
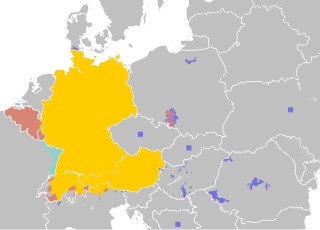
German is a West Germanic language mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also a co-official language of Luxembourg and Belgium, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. Outside Germany, it is also spoken by German communities in France (Bas-Rhin), Czech Republic, Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary (Sopron).

Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy, southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems.

Hindi, or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi, is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been described as a standardised and Sanskritised register of the Hindustani language, which itself is based primarily on the Khariboli dialect of Delhi and neighbouring areas of North India. Hindi, written in the Devanagari script, is one of the two official languages of the Government of India, along with English. It is an official language in nine states and three union territories and an additional official language in three other states. Hindi is also one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Republic of India.

Japanese is spoken as a native language by about 128 million people, primarily Japanese people and primarily in Japan, the only country where it is the national language. Japanese belongs to the Japonic or Japanese-Ryukyuan language family. There have been many attempts to group the Japonic languages with other families such as the Ainu, Austroasiatic, Koreanic, and the now-discredited Altaic, but none of these proposals has gained widespread acceptance.

Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and written forms, and may also be conveyed through sign languages. The vast majority of human languages have developed writing systems that allow for the recording and preservation of the sounds or signs of language. Human language is characterized by its cultural and historical diversity, with significant variations observed between cultures and across time. Human languages possess the properties of productivity and displacement, which enable the creation of an infinite number of sentences, and the ability to refer to objects, events, and ideas that are not immediately present in the discourse. The use of human language relies on social convention and is acquired through learning.

Latin is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition.

A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs. Most programming languages are text-based formal languages, but they may also be graphical. They are a kind of computer language.

Russian is an East Slavic language mainly spoken in Russia. It is the native language of the Russians and belongs to the Indo-European language family. It is one of four living East Slavic languages, and is also a part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages. Besides Russia itself, Russian is an official language in Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan, and is used widely as a lingua franca throughout Ukraine, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to some extent in the Baltic states. It was the de facto language of the former Soviet Union, and continues to be used in public life with varying proficiency in all of the post-Soviet states.

Spanish is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from colloquial Latin spoken on the Iberian Peninsula. Today, it is a global language with more than 487 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain. Spanish is the official language of 20 countries. It is the world's second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's fourth-most spoken language overall after English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance language. The largest population of native speakers is in Mexico.

Tamil is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. Tamil is an official language of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, the sovereign nations of Sri Lanka and Singapore, and the Indian Union territory of Puducherry. Tamil is also spoken by significant minorities in the four other South Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is also spoken by the Tamil diaspora found in many countries, including Malaysia, Myanmar, South Africa, United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Australia and Mauritius. Tamil is also natively spoken by Sri Lankan Moors. One of 22 scheduled languages in the Constitution of India, Tamil was the first to be classified as a classical language of India.

Urdu is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan, where it is also an official language alongside English. In India, Urdu is an Eighth Schedule language whose status and cultural heritage is recognized by the Constitution of India; it also has an official status in several Indian states. In Nepal, Urdu is a registered regional dialect.

Languages spoken in the Republic of India belong to several language families, the major ones being the Indo-Aryan languages spoken by 78.05% of Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 19.64% of Indians, both families together are sometimes known as Indic languages. Languages spoken by the remaining 2.31% of the population belong to the Austroasiatic, Sino–Tibetan, Tai–Kadai, and a few other minor language families and isolates. As per the People's Linguistic Survey of India, India has the second highest number of languages (780), after Papua New Guinea (840). Ethnologue lists a lower number of 456.

The Papuan Tip languages are a branch of the Western Oceanic languages consisting of 60 languages.

Google Translate is a multilingual neural machine translation service developed by Google to translate text, documents and websites from one language into another. It offers a website interface, a mobile app for Android and iOS, and an API that helps developers build browser extensions and software applications. As of February 2023, Google Translate supports 133 languages at various levels, and as of April 2016, claimed over 500 million total users, with more than 100 billion words translated daily, after the company stated in May 2013 that it served over 200 million people daily.
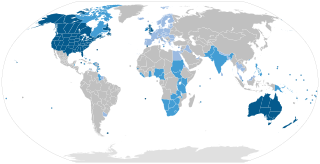
English is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots and then most closely related to the Low German and Frisian languages, English is genealogically Germanic. However, its vocabulary also shows major influences from French and Latin, plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse. Speakers of English are called Anglophones.
BXH or bxh may refer to:
The Katagans are a medieval Mongol tribe related to Genghis Khan. In the period of Mongol conquest and assimilation with enslaved by Turkic tribes played its role in the ethnogenesis of modern Kazakhs, Kyrgyz, Karakalpaks, Uzbeks, Buryats, Uyghurs and others.
References
- ↑ Buhutu at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)