
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover (MER) mission was a robotic space mission involving two Mars rovers, Spirit and Opportunity, exploring the planet Mars. It began in 2003 with the launch of the two rovers to explore the Martian surface and geology; both landed on Mars at separate locations in January 2004. Both rovers far outlived their planned missions of 90 Martian solar days: MER-A Spirit was active until March 22, 2010, while MER-B Opportunity was active until June 10, 2018.

Gusev is a crater on the planet Mars and is located at 14.5°S 175.4°E and is in the Aeolis quadrangle. The crater is about 166 kilometers in diameter and formed approximately three to four billion years ago. It was named after Russian astronomer Matvey Gusev (1826–1866) in 1976.

Meridiani Planum (alternatively Terra Meridiani) is a large plain straddling the equator of Mars. The plain sits on top of an enormous body of sediments that contains a lot of bound water. The iron oxide in the spherules is crystalline (grey) hematite (Fe2O3).

Spirit, also known as MER-A or MER-2, is a Mars robotic rover, active from 2004 to 2010. Spirit was operational on Mars for 2208 sols or 3.3 Martian years. It was one of two rovers of NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Mission managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). Spirit landed successfully within the impact crater Gusev on Mars at 04:35 Ground UTC on January 4, 2004, three weeks before its twin, Opportunity (MER-B), which landed on the other side of the planet. Its name was chosen through a NASA-sponsored student essay competition. The rover got stuck in a "sand trap" in late 2009 at an angle that hampered recharging of its batteries; its last communication with Earth was on March 22, 2010.

Sinus Meridiani is an albedo feature on Mars stretching east-west just south of the planet's equator. It was named by the French astronomer Camille Flammarion in the late 1870s.

Bonneville is an impact crater on Mars. It is located within the much larger crater Gusev. Bonneville was visited by the Mars Exploration Rover Spirit in 2004, during its exploration of the floor of Gusev. Bonneville is also the final resting place of Spirit's heat shield, jettisoned during the landing procedure; the heat-shield could be seen glinting on the opposite wall when Spirit photographed the crater. The crater is 210 metres in diameter, 14 meters deep and its rim rises 6.4 metres above the surrounding terrain.
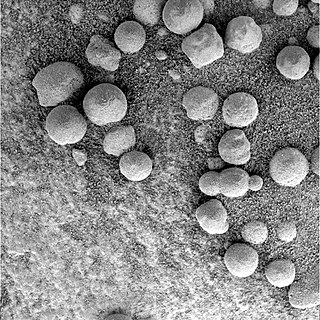
Martian spherules (also known as hematite spherules, blueberries, & Martian blueberries) are small spherules (roughly spherical pebbles) that are rich in an iron oxide (grey hematite, α-Fe2O3) and are found at Meridiani Planum (a large plain on Mars) in exceedingly large numbers.

The Columbia Hills are a range of low hills inside Gusev crater on Mars. They were observed by the Mars Exploration Rover Spirit when it landed within the crater in 2004. They were promptly given an unofficial name by NASA since they were the most striking nearby feature on the surface. The hills lie approximately 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) away from the rover's original landing position. The range is named to memorialize the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster. On February 2, 2004, the individual peaks of the Columbia Hills were named after the seven astronauts who died in the disaster. Spirit spent a few years exploring the Columbia Hills until it ceased to function in 2010. It was also considered a potential landing site for the Mars 2020 Perseverance rover, before the selection of Jezero crater in November 2018.

Adirondack is the nickname for Mars Exploration Rover Spirit's first target rock. Scientists chose Adirondack to be Spirit's first target rock after considering another, called Sashimi, that would have been a shorter, straight-ahead drive. Spirit traversed the sandy martian terrain at Gusev Crater to arrive in front of this football-sized rock on January 18, 2004, just three days after it successfully rolled off the lander.

NASA's 2003 Mars Exploration Rover Mission has amassed an enormous amount of scientific information related to the Martian geology and atmosphere, as well as providing some astronomical observations from Mars. This article covers information gathered by the Opportunity rover during the initial phase of its mission. Information on science gathered by Spirit can be found mostly in the Spirit rover article.

The Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) was a visible-infrared spectrometer aboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter searching for mineralogic indications of past and present water on Mars. The CRISM instrument team comprised scientists from over ten universities and was led by principal investigator Scott Murchie. CRISM was designed, built, and tested by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory.

The formation of carbonates on Mars have been suggested based on evidence of the presence of liquid water and atmospheric carbon dioxide in the planet's early stages. Moreover, due to their utility in registering changes in environmental conditions such as pH, temperature, fluid composition, carbonates have been considered as a primary target for planetary scientists' research. However, since their first detection in 2008, the large deposits of carbonates that were one expected on Mars have not been found, leading to multiple potential explanations that can explain why carbonates did not form massively on the planet.

Martian soil is the fine regolith found on the surface of Mars. Its properties can differ significantly from those of terrestrial soil, including its toxicity due to the presence of perchlorates. The term Martian soil typically refers to the finer fraction of regolith. So far, no samples have been returned to Earth, the goal of a Mars sample-return mission, but the soil has been studied remotely with the use of Mars rovers and Mars orbiters.
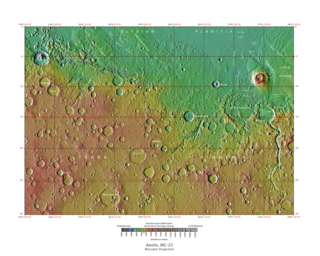
The Aeolis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Aeolis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-23 . The Aeolis quadrangle covers 180° to 225° W and 0° to 30° south on Mars, and contains parts of the regions Elysium Planitia and Terra Cimmeria. A small part of the Medusae Fossae Formation lies in this quadrangle.

Almost all water on Mars today exists as ice, though it also exists in small quantities as vapor in the atmosphere. What was thought to be low-volume liquid brines in shallow Martian soil, also called recurrent slope lineae, may be grains of flowing sand and dust slipping downhill to make dark streaks. While most water ice is buried, it is exposed at the surface across several locations on Mars. In the mid-latitudes, it is exposed by impact craters, steep scarps and gullies. Additionally, water ice is also visible at the surface at the north polar ice cap. Abundant water ice is also present beneath the permanent carbon dioxide ice cap at the Martian south pole. More than 5 million km3 of ice have been detected at or near the surface of Mars, enough to cover the whole planet to a depth of 35 meters (115 ft). Even more ice might be locked away in the deep subsurface. Some liquid water may occur transiently on the Martian surface today, but limited to traces of dissolved moisture from the atmosphere and thin films, which are challenging environments for known life. No evidence of present-day liquid water has been discovered on the planet's surface because under typical Martian conditions, warming water ice on the Martian surface would sublime at rates of up to 4 meters per year. Before about 3.8 billion years ago, Mars may have had a denser atmosphere and higher surface temperatures, potentially allowing greater amounts of liquid water on the surface, possibly including a large ocean that may have covered one-third of the planet. Water has also apparently flowed across the surface for short periods at various intervals more recently in Mars' history. Aeolis Palus in Gale Crater, explored by the Curiosity rover, is the geological remains of an ancient freshwater lake that could have been a hospitable environment for microbial life. The present-day inventory of water on Mars can be estimated from spacecraft images, remote sensing techniques, and surface investigations from landers and rovers. Geologic evidence of past water includes enormous outflow channels carved by floods, ancient river valley networks, deltas, and lakebeds; and the detection of rocks and minerals on the surface that could only have formed in liquid water. Numerous geomorphic features suggest the presence of ground ice (permafrost) and the movement of ice in glaciers, both in the recent past and present. Gullies and slope lineae along cliffs and crater walls suggest that flowing water continues to shape the surface of Mars, although to a far lesser degree than in the ancient past.

Henry is a large crater in the Arabia quadrangle of Mars. It is 171 kilometres (106 mi) in diameter and was named after the brothers Paul Henry and Prosper Henry, both of whom were French telescope makers and astronomers.
Mars may contain ores that would be very useful to potential colonists. The abundance of volcanic features together with widespread cratering are strong evidence for a variety of ores. While nothing may be found on Mars that would justify the high cost of transport to Earth, the more ores that future colonists can obtain from Mars, the easier it would be to build colonies there.
To date, interplanetary spacecraft have provided abundant evidence of water on Mars, dating back to the Mariner 9 mission, which arrived at Mars in 1971. This article provides a mission by mission breakdown of the discoveries they have made. For a more comprehensive description of evidence for water on Mars today, and the history of water on that planet, see Water on Mars.

Rain and snow was a regular occurrence on Mars in the past; especially in the Noachian and early Hesperian epochs. Water was theorized to seep into the ground until it reached a formation that would not allow it to penetrate further. Water then accumulated forming a saturated layer. Deep aquifers may still exist.

The composition of Mars covers the branch of the geology of Mars that describes the make-up of the planet Mars.













































