IA-32 is the 32-bit version of the x86 instruction set architecture, designed by Intel and first implemented in the 80386 microprocessor in 1985. IA-32 is the first incarnation of x86 that supports 32-bit computing; as a result, the "IA-32" term may be used as a metonym to refer to all x86 versions that support 32-bit computing.

The Intel 386, originally released as 80386 and later renamed i386, is a 32-bit microprocessor introduced in 1985. The first versions had 275,000 transistors and were the CPU of many workstations and high-end personal computers of the time. As the original implementation of the 32-bit extension of the 80286 architecture, the i386 instruction set, programming model, and binary encodings are still the common denominator for all 32-bit x86 processors, which is termed the i386-architecture, x86, or IA-32, depending on context.

The Intel 486, officially named i486 and also known as 80486, is a microprocessor. It is a higher-performance follow-up to the Intel 386. The i486 was introduced in 1989. It represents the fourth generation of binary compatible CPUs following the 8086 of 1978, the Intel 80286 of 1982, and 1985's i386.

A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit. The integrated circuit is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, clock-driven, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and provides results as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system.

x86 is a family of complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set architectures initially developed by Intel based on the Intel 8086 microprocessor and its 8088 variant. The 8086 was introduced in 1978 as a fully 16-bit extension of Intel's 8-bit 8080 microprocessor, with memory segmentation as a solution for addressing more memory than can be covered by a plain 16-bit address. The term "x86" came into being because the names of several successors to Intel's 8086 processor end in "86", including the 80186, 80286, 80386 and 80486 processors.

GLONASS is a Russian satellite navigation system operating as part of a radionavigation-satellite service. It provides an alternative to Global Positioning System (GPS) and is the second navigational system in operation with global coverage and of comparable precision.
Iridium Communications Inc. is a publicly traded American company headquartered in McLean, Virginia. Iridium operates the Iridium satellite constellation, a system of 66 active satellites used for worldwide voice and data communication from hand-held satellite phones and other transceiver units. The nearly polar orbit and communication between satellites via inter-satellite links provide global service availability.
Globalstar, Inc. is an American satellite communications company that operates a low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellation for satellite phone and low-speed data communications. The Globalstar second-generation constellation consists of 24 low Earth orbiting (LEO) satellites.

The Am386 CPU is a 100%-compatible clone of the Intel 80386 design released by AMD in March 1991. It sold millions of units, positioning AMD as a legitimate competitor to Intel, rather than being merely a second source for x86 CPUs.

Intel's i960 was a RISC-based microprocessor design that became popular during the early 1990s as an embedded microcontroller. It became a best-selling CPU in that segment, along with the competing AMD 29000. In spite of its success, Intel stopped marketing the i960 in the late 1990s, as a result of a settlement with DEC whereby Intel received the rights to produce the StrongARM CPU. The processor continues to be used for a few military applications.

Weitek Corporation was an American chip-design company that originally focused on floating-point units for a number of commercial CPU designs. During the early to mid-1980s, Weitek designs could be found powering a number of high-end designs and parallel-processing supercomputers.

A satellite telephone, satellite phone or satphone is a type of mobile phone that connects to other phones or the telephone network by radio through orbiting satellites instead of terrestrial cell sites, as cellphones do. The advantage of a satphone is that its use is not limited to areas covered by cell towers; it can be used in most or all geographic locations on the Earth's surface.
In x86 computing, unreal mode, also big real mode, huge real mode, flat real mode, or voodoo mode is a variant of real mode, in which one or more segment descriptors has been loaded with non-standard values, like 32-bit limits allowing access to the entire memory. Contrary to its name, it is not a separate addressing mode that the x86 processors can operate in. It is used in the 80286 and later x86 processors.

The Nokia 9000 Communicator was the first product in Nokia's Communicator series, announced at CeBIT 1996 and introduced into the market on 15 August 1996. The phone was large and heavy at 397 grams (14.0 oz) but powerful at the time. It is powered by an Intel 24 MHz i386 CPU and has 8 MB of memory, which is divided between applications, program memory and user data. The operating system is PEN/GEOS 3.0. The Communicator is one of the earliest smartphones on the market, after the IBM Simon in 1994 and the HP OmniGo 700LX, a DOS-based palmtop PC with integrated cradle for the Nokia 2110 cellular mobile phone, announced in late 1995 and shipped in March 1996.

The Intel 80376, introduced January 16, 1989, was a variant of the Intel 80386SX intended for embedded systems. It differed from the 80386 in not supporting real mode and having no support for paging in the MMU. The 376 was available at 16 or 20 MHz clock rates.

The Intel 80387SX is the math coprocessor, also called an FPU, for the Intel 80386SX microprocessor. Introduced in 1987, it was used to perform floating-point arithmetic operations directly in hardware. The coprocessor was designed only to work with the 386SX, rather than the standard 386DX. This was because the original 80387 could not communicate with the altered 16 bit data bus of the 386SX, which was modified from the original 386DX's 32 bit data bus. The 387SX uses a 68-pin PLCC socket, just like some variants of the 80286 and the less common 80186 CPU, and was made in speeds ranging from 16 MHz to 33 MHz, matching the clock speed range of the Intel manufactured 386SX. Some chips like the IIT 3C87SX could get up to 40 MHz, matching the clock speeds of the fastest 386SX CPUs.
Tolapai is the code name of Intel's embedded system on a chip (SoC) which combines a Pentium M (Dothan) processor core, DDR2 memory controllers and input/output (I/O) controllers, and a QuickAssist integrated accelerator unit for security functions.

A Personal Navigation Assistant (PNA) also known as Personal Navigation Device or Portable Navigation Device (PND) is a portable electronic product which combines a positioning capability and navigation functions.
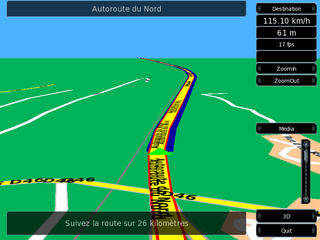
Turn-by-turn Navigation is a feature of some satellite navigation devices where directions for a selected route are continually presented to the user in the form of spoken or visual instructions. The system keeps the user up-to-date about the best route to the destination, and is often updated according to changing factors such as traffic and road conditions. Turn-by-turn systems typically use an electronic voice to inform the user whether to turn left or right, the street name, and the distance to the next turn.














