
The Memnonia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Memnonia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-16.
Arabia Terra is a large upland region in the north of Mars that lies mostly in the Arabia quadrangle, but a small part is in the Mare Acidalium quadrangle. It is densely cratered and heavily eroded. This battered topography indicates great age, and Arabia Terra is presumed to be one of the oldest terrains on the planet. It covers as much as 4,500 km (2,800 mi) at its longest extent, centered roughly at 21°N6°E with its eastern and southern regions rising 4 km (13,000 ft) above the north-west. Alongside its many craters, canyons wind through the Arabia Terra, many emptying into the large northern lowlands of the planet, which borders Arabia Terra to the north.

Margaritifer Terra is an ancient, heavily cratered region of Mars. It is centered just south of the Martian equator at 4.9°S 25°W and covers 2600 km at its widest extent. The area reveals "chaos terrain", outflow channels, and alluvial plains that are indicative of massive flooding. Wind erosion patterns are also in evidence. A region within the terra shows some of the highest valley network densities on the planet. Ares Vallis is another notable feature, where the flood and flow patterns are in evidence; it was the landing site of the Soviet Mars 6 lander and NASA's Mars Pathfinder. It is also one of several proposed landing sites for the Mars 2020 Rover.

The Medusae Fossae Formation is a large geological formation of probable volcanic origin on the planet Mars. It is named for the Medusa of Greek mythology. "Fossae" is Latin for "trenches". The formation is a collection of soft, easily eroded deposits that extends discontinuously for more than 5,000 km along the equator of Mars. Its roughly-shaped regions extend from just south of Olympus Mons to Apollinaris Patera, with a smaller additional region closer to Gale Crater.

The Noachis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Noachis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-27.

The Casius quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the north-central portion of Mars' eastern hemisphere and covers 60° to 120° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Casius quadrangle is also referred to as MC-6. Casius quadrangle contains part of Utopia Planitia and a small part of Terra Sabaea. The southern and northern borders of the Casius quadrangle are approximately 3,065 km and 1,500 km wide, respectively. The north to south distance is about 2,050 km. The quadrangle covers an approximate area of 4.9 million square km, or a little over 3% of Mars' surface area.

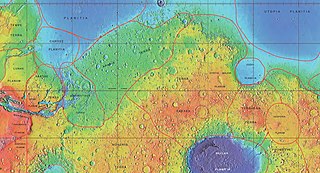
The Arabia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Arabia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-12.

The Lunae Palus quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is also referred to as MC-10. Lunae Planum and parts of Xanthe Terra and Chryse Planitia are found in the Lunae Palus quadrangle. The Lunae Palus quadrangle contains many ancient river valleys.
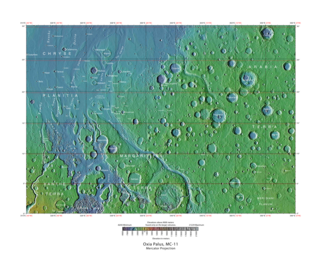
The Oxia Palus quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Oxia Palus quadrangle is also referred to as MC-11.
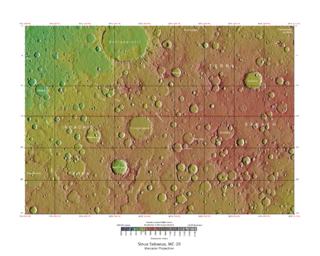
The Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. It is also referred to as MC-20 . The Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle covers the area from 315° to 360° west longitude and 0° to 30° degrees south latitude on Mars. It contains Schiaparelli, a large, easily visible crater that sits close to the equator. The Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle contains parts of Noachis Terra and Terra Sabaea.

The Phoenicis Lacus quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Phoenicis Lacus quadrangle is also referred to as MC-17. Parts of Daedalia Planum, Sinai Planum, and Solis Planum are found in this quadrangle. Phoenicis Lacus is named after the phoenix which according to myth burns itself up every 500 years and then is reborn.

The Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle is also referred to as MC-19. The Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle covers the area from 0° to 45° west longitude and 0° to 30° south latitude on Mars. Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle contains Margaritifer Terra and parts of Xanthe Terra, Noachis Terra, Arabia Terra, and Meridiani Planum.

The Thaumasia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Thaumasia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-25 . The name comes from Thaumas, the god of the clouds and celestial apparitions.

Bernard is a large crater in the Memnonia quadrangle of Mars, located at 23.4° south latitude and 154.2° west longitude. It is 128 km in diameter and was named after P. Bernard, a French atmospheric scientist. The floor of the crater contains large cracks, which may be due to erosion.
Fretted terrain is a type of surface feature common to certain areas of Mars and was discovered in Mariner 9 images. It lies between two different types of terrain. The surface of Mars can be divided into two parts: low, young, uncratered plains that cover most of the northern hemisphere, and high-standing, old, heavily cratered areas that cover the southern and a small part of the northern hemisphere. Between these two zones is a region called the Martian dichotomy and parts of it contain fretted terrain. This terrain contains a complicated mix of cliffs, mesas, buttes, and straight-walled and sinuous canyons. It contains smooth, flat lowlands along with steep cliffs. The scarps or cliffs are usually 1 to 2 km high. Channels in the area have wide, flat floors and steep walls. Fretted terrain shows up in northern Arabia, between latitudes 30°N and 50°N and longitudes 270°W and 360°W, and in Aeolis Mensae, between 10 N and 10 S latitude and 240 W and 210 W longitude. Two good examples of fretted terrain are Deuteronilus Mensae and Protonilus Mensae.
The common surface features of Mars include dark slope streaks, dust devil tracks, sand dunes, Medusae Fossae Formation, fretted terrain, layers, gullies, glaciers, scalloped topography, chaos terrain, possible ancient rivers, pedestal craters, brain terrain, and ring mold craters.

Icaria Planum is a region on Mars in the Thaumasia quadrangle. It is located roughly south-southwest of the Tharsis Rise. Icaria Planum is named after the island of Ikaria, where, according to Greek mythology, Icarus fell and died in the sea.

Hipparchus is an impact crater in the Phaethontis quadrangle of Mars, located at 44.8° S latitude and 151.4° W longitude. It is 93 kilometers in diameter. It was named after the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus in 1973.

Firsoff is an impact crater in the region called Meridiani Planum in the Oxia Palus quadrangle of Mars, located at 2.66°N latitude and 9.42°W longitude. It is 90 km in diameter. It was named after British astronomer Axel Firsoff, and the name was approved in 2010.

Yardangs are common in some regions on Mars, especially in the Medusae Fossae Formation. This formation is found in the Amazonis quadrangle and near the equator. They are formed by the action of wind on sand sized particles; hence they often point in the prevailing direction that the winds were blowing when they were formed. Yardangs exhibit very few impact craters, indicating that the surface exposed is relatively young and the process of erosion may be active. The easily eroded nature of the Medusae Fossae Formation suggests that it is composed of weakly cemented particles, and was most likely formed by the deposition of wind-blown dust or volcanic ash. Yardangs are parts of rock that have been sand blasted into long, skinny ridges by bouncing sand particles blowing in the wind. Layers are seen in parts of the formation. A resistant caprock on the top of yardangs has been observed in Viking, Mars Global Surveyor, and HiRISE photos. Images from spacecraft show that they have different degrees of hardness probably because of significant variations in the physical properties, composition, particle size, and/or cementation.






















