
Interferons are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten their anti-viral defenses.

Ribavirin, also known as tribavirin, is an antiviral medication used to treat RSV infection, hepatitis C and some viral hemorrhagic fevers. For hepatitis C, it is used in combination with other medications such as simeprevir, sofosbuvir, peginterferon alfa-2b or peginterferon alfa-2a. Among the viral hemorrhagic fevers it is sometimes used for Lassa fever, Crimean–Congo hemorrhagic fever, and Hantavirus infection but should not be used for Ebola or Marburg infections. Ribavirin is taken orally or inhaled. Despite widespread usage, since the 2010s it has faced scrutiny for a lack of efficacy in treating viral infections it has historically been prescribed for.

The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small, enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family Flaviviridae. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer and lymphomas in humans.
Pegylated interferon alfa-2b is a drug used to treat melanoma, as an adjuvant therapy to surgery. Also used to treat hepatitis C, it is no longer recommended due to poor efficacy and adverse side-effects. Subcutaneous injection is the preferred delivery method.
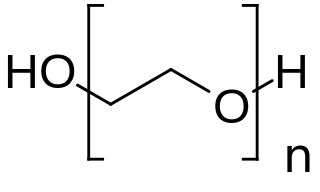
PEGylation is the process of both covalent and non-covalent attachment or amalgamation of polyethylene glycol polymer chains to molecules and macrostructures, such as a drug, therapeutic protein or vesicle, which is then described as PEGylated. PEGylation affects the resulting derivatives or aggregates interactions, which typically slows down their coalescence and degradation as well as elimination in vivo.

Boceprevir is a protease inhibitor used to treat hepatitis caused by hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1. It binds to the HCV nonstructural protein 3 active site.

Telaprevir (VX-950), marketed under the brand names Incivek and Incivo, is a pharmaceutical drug for the treatment of hepatitis C co-developed by Vertex Pharmaceuticals and Johnson & Johnson. It is a member of a class of antiviral drugs known as protease inhibitors. Specifically, telaprevir inhibits the hepatitis C viral enzyme NS3/4A serine protease. Telaprevir is only indicated for use against hepatitis C genotype 1 viral infections and has not been proven to be safe or effective when used for other genotypes of the virus. The standard therapy of pegylated interferon and ribavirin is less effective than telaprevir in those with genotype 1.

Alisporivir (INN), or Debio 025, DEB025, is a cyclophilin inhibitor. Its structure is reminiscent of, and synthesized from ciclosporin.
WGAViewer is a bioinformatics software tool which is designed to visualize, annotate, and help interpret the results generated from a genome wide association study (GWAS). Alongside the P values of association, WGAViewer allows a researcher to visualize and consider other supporting evidence, such as the genomic context of the SNP, linkage disequilibrium (LD) with ungenotyped SNPs, gene expression database, and the evidence from other GWAS projects, when determining the potential importance of an individual SNP.

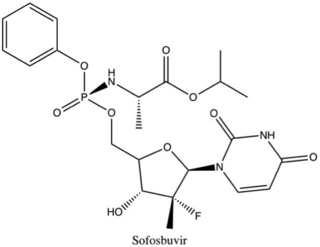
Sofosbuvir, sold under the brand name Sovaldi among others, is a medication used to treat hepatitis C. It is taken by mouth.

Interferon lambda 3 encodes the IFNL3 protein. IFNL3 was formerly named IL28B, but the Human Genome Organization Gene Nomenclature Committee renamed this gene in 2013 while assigning a name to the then newly discovered IFNL4 gene. Together with IFNL1 and IFNL2, these genes lie in a cluster on chromosomal region 19q13. IFNL3 shares ~96% amino-acid identity with IFNL2, ~80% identity with IFNL1 and ~30% identity with IFNL4.

Simeprevir, sold under the brand name Olysio among others, is a medication used in combination with other medications for the treatment of hepatitis C. It is specifically used for hepatitis C genotype 1 and 4. Medications it is used with include sofosbuvir or ribavirin and peginterferon-alfa. Cure rates are in 80s to 90s percent. It may be used in those who also have HIV/AIDS. It is taken by mouth once daily for typically 12 weeks.

Faldaprevir was an experimental drug for the treatment of hepatitis C (HCV). It was being developed by Boehringer-Ingelheim and reached Phase III clinical trials in 2011. Boehringer announced in 2014 that it would not pursue approval of the drug any more because of better HCV treatments having become available.

Deleobuvir was an experimental drug for the treatment of hepatitis C. It was being developed by Boehringer Ingelheim. It is a non-nucleoside hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase inhibitor. Deleobuvir was tested in combination regimens with pegylated interferon and ribavirin, and in interferon-free regimens with other direct-acting antiviral agents including faldaprevir.

Dasabuvir, sold under the brand name Exviera, is an antiviral medication for the treatment of hepatitis C. It is often used together with the combination medication ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir specifically for hepatitis C virus (HCV) type 1. Ribavirin may also additionally be used. These combinations result in a cure in more than 90% of people. It is taken by mouth.
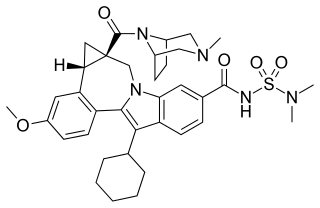
Beclabuvir is an antiviral drug for the treatment of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection that has been studied in clinical trials. In February 2017, Bristol-Myers Squibb began sponsoring a post-marketing trial of beclabuvir, in combination with asunaprevir and daclatasvir, to study the combination's safety profile with regard to liver function. From February 2014 to November 2016, a phase II clinical trial was conducted on the combination of asunaprevir/daclatasvir/beclabuvir on patients infected with both HIV and HCV. Furthermore, a recent meta-analysis of six published six clinical trials showed high response rates in HCV genotype 1-infected patients treated with daclatasvir, asunaprevir, and beclabuvir irrespective of ribavirin use, prior interferon-based therapy, or restriction on noncirrhotic patients, IL28B genotype, or baseline resistance-associated variants
Elbasvir/grazoprevir, sold under the brand name Zepatier, is a fixed-dose combination for the treatment of hepatitis C, containing elbasvir and grazoprevir. It is used to treat chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotypes 1 or 4 infection in both treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced patients.
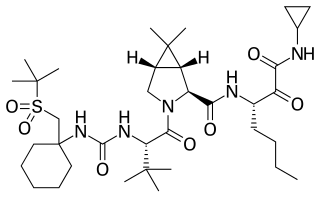
Narlaprevir, is an inhibitor of NS3/4A serine protease, intended for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C caused by genotype 1 virus in combination with other antiviral drugs.
Non-structural protein 5B (NS5B) inhibitors are a class of direct-acting antivirals widely used in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Depending on site of action and chemical composition, NS5B inhibitors may be categorized into three classes—nucleoside active site inhibitors (NIs), non-nucleoside allosteric inhibitors, and pyrophosphate analogues. Subsequently, all three classes are then subclassified. All inhibit RNA synthesis by NS5B but at different stages/sites resulting in inability of viral RNA replication. Expression of direct-acting NS5B inhibitors does not take place in cells that are not infected by hepatitis C virus, which seems to be beneficial for this class of drugs.

Interferon lambda 4 is one of the most recently discovered human genes and the newest addition to the interferon lambda protein family. This gene encodes the IFNL4 protein, which is involved in immune response to viral infection.















