| Vesicovaginal fistula | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty | Urology |
Vesicovaginal fistula (VVF) is a subtype of female urogenital fistula (UGF).
| Vesicovaginal fistula | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty | Urology |
Vesicovaginal fistula (VVF) is a subtype of female urogenital fistula (UGF).
Vesicovaginal fistula, or VVF, is an abnormal fistulous tract extending between the bladder ( vesica ) and the vagina that allows the continuous involuntary discharge of urine into the vaginal vault.[ citation needed ]
In addition to the medical sequela from these fistulas, they often have a profound effect on the patient's emotional well-being.[ citation needed ]
It may be the result of a congenital birth condition such as VACTERL association. It is often caused by childbirth (in which case it is known as an obstetric fistula), when a prolonged labor presses the unborn child tightly against the pelvis, cutting off blood flow to the vesicovaginal wall. The affected tissue may necrotize (die), leaving a hole.[ citation needed ]
Vaginal fistulas can also result from particularly violent cases of rape, especially those involving multiple rapists and/or foreign objects. Some health centers in countries such as the Democratic Republic of Congo have begun to specialize in the surgical repair of vaginal fistulas. [1] [2] It can also be associated with hysterectomy, [3] cancer operations, radiation therapy and cone biopsy.
Vesicovaginal fistulae are typically repaired either transvaginally or laparoscopically, although patients who have had multiple transvaginal procedures sometimes attempt a final repair through a large abdominal incision, or laparotomy.[ citation needed ]
The laparoscopic (minimally invasive) approach to VVF repair has become more prevalent due to its greater visualization, higher success rate, and lower rate of complications. [4]
Before the 19th century, women who suffered from VVF were judged harshly and rejected by society. Throughout the 19th century, treatment for VVF was limited because the practice of gynecology was perceived as taboo. Doctors were almost entirely male at this time and looking at a nude female, even for medical purposes, was seen as divergent from 19th-century values. [6]
One of the most famous gynecological surgeons of this time was Dr. J. Marion Sims, who developed a successful technique for treating VVF in the mid-1800s, for which he is hailed as a pioneer of gynecology. [7]
Black enslaved women in the American South were particularly prone to VVF because they were denied proper nutrients and medical care. Sims performed on these women without anesthesia, which had not been introduced until after he started his experiments, and which in its infancy Sims hesitated to use. [7] (Ether anesthesia was publicly demonstrated in Boston in 1846, a year after Sims began his experimentation.) Sims did not have a white female patient until he made ether available to them, although he publicly noted that he never resorted to using anesthetics because he believed that the pain did not justify the risks. [7] A detailed case study of Sims even discusses the case of a white woman who underwent three operations, all without anesthesia. [7] It was considered acceptable to operate on them without anesthetic because, Sims claimed, African-American women have a naturally higher pain tolerance. [8]
The healing process of the VVF procedure is still arduous. To have a successful recovery from the surgery, it must be successful on the first attempt. [9] Sims's operations on African-American enslaved women showcase the dangerous nature of the procedure. [7] There still have not been clear instructions on how to properly recover from the procedure other than taking prescribed antibiotics. [9]
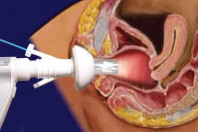
Gynaecology or gynecology is the area of medicine that involves the treatment of women's diseases, especially those of the reproductive organs. It is often paired with the field of obstetrics, forming the combined area of obstetrics and gynaecology (OB-GYN).
In anatomy, a fistula is an abnormal connection joining two hollow spaces, such as blood vessels, intestines, or other hollow organs to each other, often resulting in an abnormal flow of fluid from one space to the other. An anal fistula connects the anal canal to the perianal skin. An anovaginal or rectovaginal fistula is a hole joining the anus or rectum to the vagina. A colovaginal fistula joins the space in the colon to that in the vagina. A urinary tract fistula is an abnormal opening in the urinary tract or an abnormal connection between the urinary tract and another organ. An abnormal communication between the bladder and the uterus is called a vesicouterine fistula, while if it is between the bladder and the vagina it is known as a vesicovaginal fistula, and if between the urethra and the vagina: a urethrovaginal fistula. When occurring between two parts of the intestine, it is known as an enteroenteral fistula, between the small intestine and the skin as an enterocutaneous fistula, and between the colon and the skin as a colocutaneous fistula.
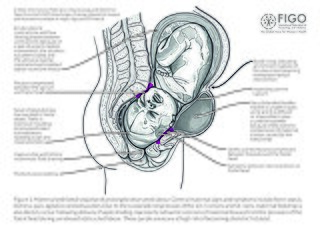
Obstetric fistula is a medical condition in which a hole develops in the birth canal as a result of childbirth. This can be between the vagina and rectum, ureter, or bladder. It can result in incontinence of urine or feces. Complications may include depression, infertility, and social isolation.

A speculum is a medical tool for investigating body orifices, with a form dependent on the orifice for which it is designed. In old texts, the speculum may also be referred to as a diopter or dioptra. Like an endoscope, a speculum allows a view inside the body; endoscopes, however, tend to have optics while a speculum is intended for direct vision.

Hysterectomy is the partial or total surgical removal of the uterus. It may also involve removal of the cervix, ovaries (oophorectomy), fallopian tubes (salpingectomy), and other surrounding structures. Partial hysterectomies allow for hormone regulation while total hysterectomies do not.

Vaginoplasty is any surgical procedure that results in the construction or reconstruction of the vagina. It is a type of genitoplasty. Pelvic organ prolapse is often treated with one or more surgeries to repair the vagina. Sometimes a vaginoplasty is needed following the treatment or removal of malignant growths or abscesses to restore a normal vaginal structure and function. Surgery to the vagina is done to correct congenital defects to the vagina, urethra and rectum. It will correct protrusion of the urinary bladder into the vagina (cystocele) and protrusion of the rectum (rectocele) into the vagina. Often, a vaginoplasty is performed to repair the vagina and its attached structures due to trauma or injury. Labiaplasty, which alters the appearance of the vulva, can be performed as a discrete surgery, or as a subordinate procedure within a vaginoplasty.

A rectovaginal fistula is a medical condition where there is a fistula or abnormal connection between the rectum and the vagina.

James Marion Sims was an American physician in the field of surgery. His most famous work was the development of a surgical technique for the repair of vesicovaginal fistula, a severe complication of obstructed childbirth. He is also remembered for inventing Sims speculum, Sims sigmoid catheter, and the Sims position. Against significant opposition, he established, in New York, the first hospital specifically for women. He was forced out of the hospital he founded because he insisted on treating cancer patients; he played a small role in the creation of the nation's first cancer hospital, which opened after his death.

Myomectomy, sometimes also called fibroidectomy, refers to the surgical removal of uterine leiomyomas, also known as fibroids. In contrast to a hysterectomy, the uterus remains preserved and the woman retains her reproductive potential. It still may impact hormonal regulation and the menstrual cycle.

The cystocele, also known as a prolapsed bladder, is a medical condition in which a woman's bladder bulges into her vagina. Some may have no symptoms. Others may have trouble starting urination, urinary incontinence, or frequent urination. Complications may include recurrent urinary tract infections and urinary retention. Cystocele and a prolapsed urethra often occur together and is called a cystourethrocele. Cystocele can negatively affect quality of life.

Vaginectomy is a surgery to remove all or part of the vagina. It is one form of treatment for individuals with vaginal cancer or rectal cancer that is used to remove tissue with cancerous cells. It can also be used in gender-affirming surgery. Some people born with a vagina who identify as trans men or as nonbinary may choose vaginectomy in conjunction with other surgeries to make the clitoris more penis-like (metoidioplasty), construct of a full-size penis (phalloplasty), or create a relatively smooth, featureless genital area.

Uterine prolapse is a form of pelvic organ prolapse in which the uterus and a portion of the upper vagina protrude into the vaginal canal and, in severe cases, through the opening of the vagina. It is most often caused by injury or damage to structures that hold the uterus in place within the pelvic cavity. Symptoms may include vaginal fullness, pain with sexual intercourse, difficulty urinating, and urinary incontinence. Risk factors include older age, pregnancy, vaginal childbirth, obesity, chronic constipation, and chronic cough. Prevalence, based on physical exam alone, is estimated to be approximately 14%.
The health of slaves on American plantations was a matter of concern to both slaves and their owners. Slavery had associated with it the health problems commonly associated with poverty. It was to the economic advantage of owners to keep their working slaves healthy, and those of reproductive age reproducing. Those who could not work or reproduce because of illness or age were sometimes abandoned by their owners, expelled from plantations, and left to fend for themselves.
Transvaginal oocyte retrieval (TVOR), also referred to as oocyte retrieval (OCR), is a technique used in in vitro fertilization (IVF) in order to remove oocytes from the ovary of a woman, enabling fertilization outside the body. Transvaginal oocyte retrieval is more properly referred to as transvaginal ovum retrieval when the oocytes have matured into ova, as is normally the case in IVF. It can be also performed for egg donation, oocyte cryopreservation and other assisted reproduction technology such as ICSI.

Medical Apartheid: The Dark History of Medical Experimentation on Black Americans from Colonial Times to the Present is a 2007 book by Harriet A. Washington. It is a history of medical experimentation on African Americans. From the era of slavery to the present day, this book presents the first detailed account of black Americans' abuse as unwitting subjects of medical experimentation.
Urogynecology or urogynaecology is a surgical sub-specialty of urology and gynecology.
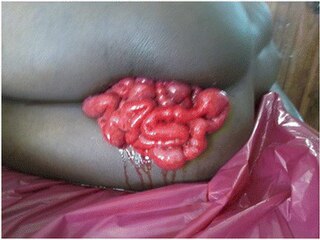
Vaginal evisceration is an evisceration of the small intestine that occurs through the vagina, typically subsequent to vaginal hysterectomy, and following sexual intercourse after the surgery. It is a surgical emergency.
A urogenital fistula is an abnormal tract that exists between the urinary tract and bladder, ureters, or urethra. A urogenital fistula can occur between any of the organs and structures of the pelvic region. A fistula allows urine to continually exit through and out the urogenital tract. This can result in significant disability, interference with sexual activity, and other physical health issues, the effects of which may in turn have a negative impact on mental or emotional state, including an increase in social isolation. Urogenital fistulas vary in etiology. Fistulas are usually caused by injury or surgery, but they can also result from malignancy, infection, prolonged and obstructed labor and deliver in childbirth, hysterectomy, radiation therapy or inflammation. Of the fistulas that develop from difficult childbirth, 97 percent occur in developing countries. Congenital urogenital fistulas are rare; only ten cases have been documented. Abnormal passageways can also exist between the vagina and the organs of the gastrointestinal system, and these may also be termed fistulas.
Anarcha Westcott was an enslaved woman who underwent a series of painful experimental surgical procedures conducted by physician J. Marion Sims, without the use of anesthesia, to treat a combination of vesicovaginal fistula and rectovaginal fistula. Sims's medical experimentation with Anarcha and other enslaved women, and its role in the development of modern gynaecology, has generated controversy among medical historians.
Transvaginal mesh, also known as vaginal mesh implant, is a net-like surgical tool that is used to treat pelvic organ prolapse (POP) and stress urinary incontinence (SUI) among female patients. The surgical mesh is placed transvaginally to reconstruct weakened pelvic muscle walls and to support the urethra or bladder.