Related Research Articles
(89959) 2002 NT7 (provisional designation 2002 NT7) is a near-Earth object with a diameter of 1.4 kilometers and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group. It has a well determined orbit with an observation arc of 64 years including precovery images by Palomar Observatory dating back to 1954.
(417634) 2006 XG1 provisional designation 2006 XG1, is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, that had a low but non-zero probability of impacting Earth on 31 October 2041. The asteroid was discovered on 20 September 2006, by astronomers of the Catalina Sky Survey, using a dedicated 0.68-meter telescope at Mount Lemmon Observatory in Arizona, United States.
(481482) 2007 CA19 is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group. It led the impact hazard list, with a Torino Scale impact risk value of 1, for one week, ending on February 19, 2007. Before and after 2007 CA19, 99942 Apophis was the object with the highest Palermo Scale rating. With an observation arc of 4.8 days, it had a Palermo Scale of −0.88.

2007 VK184 is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object of the Apollo group, and estimated to be approximately 130 meters (430 ft) in diameter. It was listed on the Sentry Risk Table with a Torino Scale rating of 1 for a potential impactor in June 2048. It was removed from the Sentry Risk Table on 28 March 2014.
1994 WR12 is an asteroid and near-Earth object approximately 130 meters (430 feet) in diameter. As a member of the Aten group almost all of its orbit is closer to the Sun than Earth is. On 24 November 1994 it passed about 374100 km from the Moon. First imaged at Kitami Observatory on 26 November 1994, it was discovered two nights later by American astronomer Carolyn S. Shoemaker at Palomar Observatory on 28 November 1994. The asteroid then went unobserved from 1994 until it was recovered by Mauna Kea in March 2016. It was removed from the Sentry Risk Table on 2 April 2016.
(614433) 2009 KK is an Apollo near-Earth asteroid which was listed for several weeks in May and June 2009 on the Sentry Risk Table with a Torino Scale rating of 1. There was a 1 in 10000 chance of an impact on 29 May 2022. On 22 May 2009, it was listed as one of two near-earth objects assessed above Level 0 for potential impacts within 100 years, the other being 2007 VK184. As of 10 June 2009 it was downgraded to Level 0 as the cumulative Earth-impact probability was assessed as 7.9e-06 or 1 in 127,000. On 17 June 2009, JPL removed 2009 KK from the list of potential Earth impactors. It is now known that on 4 May 2022 the asteroid will be 0.475 AU from Earth.
(529366) 2009 WM1, provisional designation 2009 WM1, is a sub-kilometer asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 280 meters (920 feet) in diameter. After its discovery by the Catalina Sky Survey at the Catalina Station in Arizona, United States, this potentially hazardous asteroid was briefly listed at a Torino Scale of 1 and a cumulative Palermo Scale of −0.87. It was removed from the Sentry Risk Table on 26 June 2013.
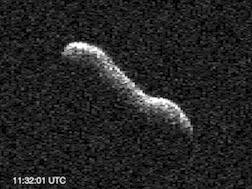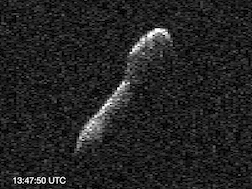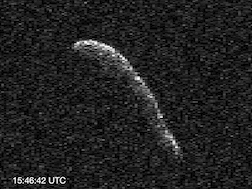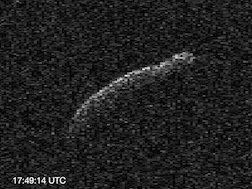
(367789) 2011 AG5, provisional designation 2011 AG5, is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group. It has a diameter of about 140 meters (460 ft). It was removed from the Sentry Risk Table on 21 December 2012 and as such it now has a rating of 0 on the Torino Scale. It was recovered in December 2022 extending the observation arc from 4.8 years to 14 years. As of 2023, the distance between the orbits of Earth and 2011 AG5 is 0.0004 AU (60,000 km; 0.16 LD)

2012 EG5 is an Apollo near-Earth asteroid with an estimated diameter of 47 meters (154 ft). The asteroid was discovered on March 13, 2012. The asteroid came within 0.001539 AU of Earth during its closest approach on April 1, 2012, just over half the distance between Earth and the Moon's orbit. It was briefly listed on the Sentry Risk Table with a 1 in 2,778,000 chance of an impact in 2107. It was removed from the Sentry Risk Table on 1 April 2012.
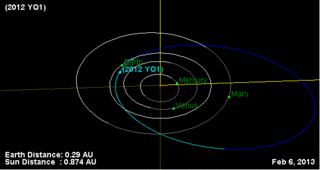
(669555) 2012 YQ1 is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object and a potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 200 meters in diameter. It was first observed on 19 December 2012, by astronomers Andrey Oreshko and Timur Kryachko at the Elena Remote Observatory (G32) located in the Chilean Atacama desert.
(523662) 2012 MU2, provisional designation 2012 MU2, is a sub-kilometer asteroid on an eccentric orbit, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group. It was discovered on 18 June 2012 by astronomers of the Catalina Sky Survey at an apparent magnitude of 19.9 using a 0.68-meter (27 in) Schmidt–Cassegrain telescope. It has an estimated diameter of 240 meters (790 ft). The asteroid was listed on Sentry Risk Table with a Torino Scale rating of 1 on 23 June 2012.
(163132) 2002 CU11, provisional designation 2002 CU11, is a bright, sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group. Based on absolute magnitude, it is the second largest asteroid known to have passed closer than the Moon.
2013 TV135 is an Apollo near-Earth asteroid estimated to have a diameter of 450 meters (1,480 ft). On 16 September 2013, it passed about 0.0448 AU (6,700,000 km; 4,160,000 mi) from Earth. On 20 September 2013, it came to perihelion (closest approach to the Sun). The asteroid was discovered on 12 October 2013 by Ukrainian amateur astronomer Gennadiy Borisov with a custom 0.2-meter (7.9 in) telescope using images dating back to 8 October 2013. It was rated level 1 on the Torino Scale from 16 October 2013 until JPL solution 26 on 3 November 2013. It reached a Palermo Technical Impact Hazard Scale rating of -0.73. It was removed from the JPL Sentry Risk Table on 8 November 2013 using JPL solution 32 with an observation arc of 27 days.
(177049) 2003 EE16, provisionally known as 2003 EE16, is an Apollo near-Earth asteroid and potentially hazardous object. It was discovered on 8 March 2003 by LPL/Spacewatch II at an apparent magnitude of 20 using a 1.8-meter (71 in) reflecting telescope. It has an estimated diameter of 320 meters (1,050 ft). The asteroid was listed on Sentry Risk Table with a Torino Scale rating of 1 on 2 April 2003.

(415029) 2011 UL21, provisional designation 2011 UL21, is an Apollo class potentially hazardous asteroid discovered on October 17, 2011, by the Catalina Sky Survey project. The asteroid is estimated to have a diameter of 2.5 kilometres (1.6 mi). It was rated at Torino Scale 1 on October 27, 2011, with an observation arc of 9.6 days.
(585310) 2017 YZ1, provisional designation: 2017 YZ1, is a sub-kilometer asteroid on an eccentric orbit, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 250 meters (800 feet) in diameter. It was first observed on 20 December 2017, by astronomers with the Mount Lemmon Survey at Mount Lemmon Observatory near Tucson, Arizona, in the United States. On 29 January 2018, it passed Earth at 125 lunar distances.
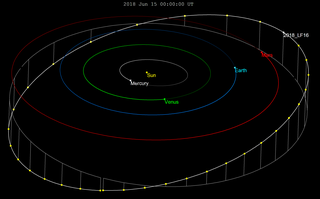
2018 LF16 is a small Mars crossing asteroid roughly 213 m (699 ft) in diameter. It was first observed by astronomers with the Pan-STARRS survey at Haleakala Observatory on 14 June 2018. It was removed from the Sentry Risk Table on 29 July 2021. With an observation arc of 15 years the orbit is very well known and it does not make any notable approaches to Earth.
2022 QX4 is a Tunguska event-sized asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object of the Aten group, approximately 40 meters (130 feet) in diameter. It was discovered by ATLAS on 24 August 2022, when it was 0.03 AU (4.5 million km) from Earth. On 4 September 2022 with an observation arc of 8 days, it was listed with a 1-in-109 chance of impacting Earth with a Torino scale of 1 for a virtual impactor on 4 September 2068 00:52 UTC. Five precovery images from August 2013 were published on 11 September 2022 extending the observation arc to 9 years and 2022 QX4 was removed from the Sentry Risk Table. The nominal approach is expected to occur 26 August 2068.
2023 DW is a near-Earth asteroid of the Aten group. It is approximately 50 meters in diameter, roughly the size of the asteroid that caused the Tunguska event, and was discovered by Georges Attard and Alain Maury, from the MAP (Maury/Attard/Parrott) asteroid search program in San Pedro de Atacama on 26 February 2023, when it was 0.07 AU (10 million km) from Earth. On 28 February 2023, with an observation arc of 1.2 days, it was rated 1 on the Torino scale for a virtual impactor on 14 February 2046 at 21:36 UTC. The nominal approach is expected to occur about eight hours before the impact scenario at 14 February 2046 13:15 ± 72 minutes. Between 5–8 March, the asteroid was not observed as it was within 40 degrees of the waxing gibbous moon. On 14 March 2023 the European Space Agency was the first to drop to a Torino scale rating of 0. Sentry dropped to a Torino scale rating of 0 on 16 March 2023. It was completely removed from both risk tables on 20 March 2023.
2023 GQ2 is an asteroid roughly 400 meters in diameter, classified as a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous object of the Apollo group. It was first discovered on 12 April 2023, when it was 1.3 AU (190 million km) from Earth, with the Bok Telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory. On 19 April 2023, with an observation arc of 6.7 days, it was rated 1 on the Torino scale for a virtual impactor on 16 November 2028 at 00:58 UTC. When it had a Palermo scale rating of –0.70, the odds of impact were about 5 times less than the background hazard level and this gave the asteroid one of the highest Palermo scale ratings ever issued. On 20 April 2023 precovery images from May 2019 were announced extending the observation arc to 3.9 years, and the 2028 virtual impactor was removed from the Sentry Risk Table. It is now known the nominal approach will safely occur about 13 hours after the impact scenario on 16 November 2028 13:36 ± 40 minutes.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 292220 (2006 SU49)" (2016-10-02 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 20 January 2018.
- 1 2 "292220 (2006 SU49)". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 20 January 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 "2006 SU49 Impact Risk". Near Earth Object Program. NASA. Archived from the original on 28 September 2006.
- ↑ "Sentry: Earth Impact Monitoring – Removed Objects". NASA/JPL CNEOS – Center for Near-Earth Object Studies. Retrieved 20 January 2018.