1566 Icarus is a large near-Earth object of the Apollo group and the lowest numbered potentially hazardous asteroid. It has an extremely eccentric orbit (0.83) and measures approximately 1.4 km (0.87 mi) in diameter. In 1968, it became the first asteroid ever observed by radar. Its orbit brings it closer to the Sun than Mercury and further out than the orbit of Mars, which also makes it a Mercury-, Venus-, and Mars-crossing asteroid. This stony asteroid and relatively fast rotator with a period of 2.27 hours was discovered on 27 June 1949, by German astronomer Walter Baade at the Palomar Observatory in California. It was named after the mythological Icarus.
4197 Morpheus, provisional designation 1982 TA, is a highly eccentric asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 3 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 11 October 1982, by American astronomers Eleanor Helin and Eugene Shoemaker at Palomar Observatory in California, United States. The asteroid was later named for Morpheus from Greek mythology.
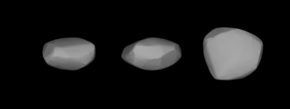
63 Ausonia is a stony Vestian asteroid from the inner region of the asteroid belt, approximately 100 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered by Italian astronomer Annibale de Gasparis on 10 February 1861, from the Astronomical Observatory of Capodimonte, in Naples, Italy. The initial choice of name for the asteroid was "Italia", after Italy, but this was modified to Ausonia, an ancient classical name for the Italian region.

96 Aegle is a carbonaceous asteroid and the namesake of the Aegle family located in the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 170 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 17 February 1868, by French astronomer Jérôme Coggia at the Marseille Observatory in southeastern France. The rare T-type asteroid has a rotation period of 13.8 hours and has been observed several times during occultation events. It was named after Aegle ("brightness"), one of the Hesperides from Greek mythology.
123 Brunhild is a stony S-type main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by German-American astronomer C. H. F. Peters on July 31, 1872, and named after Brünnehilde, a Valkyrie in Norse mythology. Brunhild has been mistaken for the non-existent variable star KN Gem.

137 Meliboea is a large, dark main-belt asteroid that was discovered by Austrian astronomer J. Palisa at the Austrian Naval Observatory on 21 April 1874, the second of his many asteroid discoveries. It was later named after Meliboea, the daughter of Oceanus and Tethys in Greek mythology. The largest body in the Meliboea family of asteroids that share similar orbital elements, only 791 Ani approaches its size. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and may be composed of carbonaceous materials. The spectra of the asteroid displays evidence of aqueous alteration.

214 Aschera is a Main belt asteroid. It was discovered by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa on February 29, 1880, in Pola and was named after the Sidonian goddess Asherah.
1992 Galvarino, provisional designation 1968 OD, is an Eoan asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 10 kilometers in diameter.

732 Tjilaki is a dark background asteroid, approximately 36 kilometers in diameter, located in the inner region of the asteroid belt. It was discovered by German astronomer Adam Massinger at the Heidelberg Observatory on 15 April 1912, and later named after the Cilaki (Tjilaki) river in Indonesia. The dark D-type asteroid has a rotation period of 12.3 hours. It was an early candidate to be visited by the Rosetta spacecraft which eventually rendezvoused comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko.

1627 Ivar is an elongated stony asteroid and near-Earth object of the Amor group, approximately 15×6×6 km. It was discovered on 25 September 1929, by Danish astronomer Ejnar Hertzsprung at Leiden Southern Station, annex to the Johannesburg Observatory in South Africa. It was named after Ivar Hertzsprung, brother of the discoverer. 1627 Ivar was the first asteroid to be imaged by radar, in July 1985 by the Arecibo Observatory.
1994 Shane, provisional designation 1961 TE, is a dark Adeonian asteroid from the central region of the asteroid belt, approximately 25 kilometers in diameter.
1025 Riema, provisional designation 1923 NX, is a bright Hungaria asteroid from the innermost regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 5 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 12 August 1923, by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at the Heidelberg Observatory in southwest Germany. The asteroid was named after ARI astronomer Johannes Riem.
2260 Neoptolemus is a large Jupiter trojan from the Greek camp, approximately 76 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 26 November 1975, by astronomers at the Purple Mountain Observatory in Nanking, China. The dark D-type asteroid is one of the 50 largest Jupiter trojans and has a rotation period of 8.18 hours. It was named after Neoptolemus from Greek mythology.

(185851) 2000 DP107 is a sub-kilometer sized asteroid, classified as potentially hazardous asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group that is notable because it provided evidence for binary asteroids in the near-Earth population. The PROCYON probe developed by JAXA and the University of Tokyo was intended to flyby this asteroid before its ion thruster failed and could not be restarted.
1246 Chaka, provisional designation 1932 OA, is a background asteroid from the central regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 18 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 23 July 1932, by South African astronomer Cyril Jackson at the Union Observatory in Johannesburg. The uncommon A/Sl-type asteroid has a longer than average rotation period of 25.5 hours. It was named for the Zulu King Shaka.

1251 Hedera is a background asteroid from the central regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 13 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 25 January 1933, by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at the Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory in southwest Germany. The asteroid was named for the climbing plant Hedera, commonly known as "ivy".
2043 Ortutay, provisional designation 1936 TH, is a dark asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 45 kilometers in diameter. The asteroid was discovered by Hungarian astronomer György Kulin at the Konkoly Observatory, Budapest, on 12 November 1936. It was named after Hungarian ethnographer Gyula Ortutay.
1646 Rosseland, provisional designation 1939 BG, is a stony asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 12 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 19 January 1939, by Finnish astronomer Yrjö Väisälä at Turku Observatory in Southwest Finland. It was later named after Norwegian astrophysicist Svein Rosseland.
1513 Mátra, provisional designation 1940 EB, is a stony Florian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 5 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 10 March 1940, by Hungarian astronomer György Kulin at Konkoly Observatory in Budapest, Hungary. It was later named after the Mátra mountain range.

(7335) 1989 JA is a stony asteroid of the Apollo group, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid, approximately 1 kilometer in diameter. It was discovered on 1 May 1989, by American astronomer Eleanor Helin at the U.S. Palomar Observatory in California. On 27 May 2022, the asteroid made a close approach 0.027 astronomical units from Earth. During the close approach, optical observations detected signs of an orbiting satellite, which was later confirmed by radar imaging at NASA's Goldstone Solar System Radar in California.