11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase enzymes catalyze the conversion of inert 11 keto-products (cortisone) to active cortisol, or vice versa, thus regulating the access of glucocorticoids to the steroid receptors.

Corticosteroid 11-β-dehydrogenase isozyme 2 also known as 11-β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HSD11B2 gene.

11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1, also known as cortisone reductase, is an NADPH-dependent enzyme highly expressed in key metabolic tissues including liver, adipose tissue, and the central nervous system. In these tissues, HSD11B1 reduces cortisone to the active hormone cortisol that activates glucocorticoid receptors. It belongs to the family of short-chain dehydrogenases. It is encoded by the HSD11B1 gene.
3β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/Δ5-4 isomerase (3β-HSD) is an enzyme that catalyzes the biosynthesis of the steroid progesterone from pregnenolone, 17α-hydroxyprogesterone from 17α-hydroxypregnenolone, and androstenedione from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) in the adrenal gland. It is the only enzyme in the adrenal pathway of corticosteroid synthesis that is not a member of the cytochrome P450 family. It is also present in other steroid-producing tissues, including the ovary, testis and placenta. In humans, there are two 3β-HSD isozymes encoded by the HSD3B1 and HSD3B2 genes.

Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (HSDs) are a group of alcohol oxidoreductases that catalyze the dehydrogenation of hydroxysteroids. These enzymes also catalyze the reverse reaction, acting as ketosteroid reductases (KSRs).

Phosphopentose epimerase encoded by the RPE gene is a metalloprotein that catalyzes the interconversion between D-ribulose 5-phosphate and D-xylulose 5-phosphate.

Methylmalonyl CoA epimerase is an enzyme involved in fatty acid catabolism that is encoded in human by the "MCEE" gene located on chromosome 2. It is routinely and incorrectly labeled as "methylmalonyl-CoA racemase". It is not a racemase because the CoA moiety has 5 other stereocenters.
Epimerases and racemases are isomerase enzymes that catalyze the inversion of stereochemistry in biological molecules. Racemases catalyze the stereochemical inversion around the asymmetric carbon atom in a substrate having only one center of asymmetry. Epimerases catalyze the stereochemical inversion of the configuration about an asymmetric carbon atom in a substrate having more than one center of asymmetry, thus interconverting epimers.
In enzymology, a 16alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.147) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxyproline epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a CDP-paratose 2-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a N-acylglucosamine 2-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acylglucosamine-6-phosphate 2-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
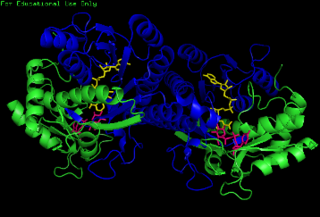
The enzyme UDP-glucose 4-epimerase, also known as UDP-galactose 4-epimerase or GALE, is a homodimeric epimerase found in bacterial, fungal, plant, and mammalian cells. This enzyme performs the final step in the Leloir pathway of galactose metabolism, catalyzing the reversible conversion of UDP-galactose to UDP-glucose. GALE tightly binds nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a co-factor required for catalytic activity.
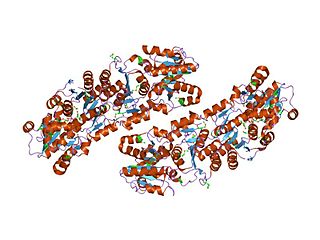
In enzymology, an UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3 (AKR1C3), also known as 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 5 is a key steroidogenic enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKR1C3 gene.

Hydroxysteroid 17-beta dehydrogenase 6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HSD17B6 gene.

Epiandrosterone, or isoandrosterone, also known as 3β-androsterone, 3β-hydroxy-5α-androstan-17-one, or 5α-androstan-3β-ol-17-one, is a steroid hormone with weak androgenic activity. It is a metabolite of testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It was first isolated in 1931, by Adolf Friedrich Johann Butenandt and Kurt Tscherning. They distilled over 17,000 litres of male urine, from which they got 50 milligrams of crystalline androsterone, which was sufficient to find that the chemical formula was very similar to estrone.

Epimerox is an experimental broad-spectrum antibiotic compound being developed by scientists at the Rockefeller University and Astex Pharmaceuticals. It is a small molecule inhibitor compound that blocks the activity of the enzyme UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase, an epimerase enzyme that is called 2-epimerase for short.












