The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle, or TCA cycle —is a series of biochemical reactions to release the energy stored in nutrients through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and alcohol. The chemical energy released is available in the form of ATP. The Krebs cycle is used by organisms that respire to generate energy, either by anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration. In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH, that are used in numerous other reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest components of metabolism. Even though it is branded as a "cycle", it is not necessary for metabolites to follow only one specific route; at least three alternative segments of the citric acid cycle have been recognized.
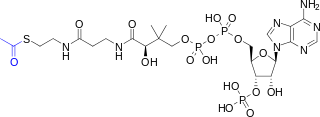
Acetyl-CoA is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production.

Methylmalonic acidemias, also called methylmalonic acidurias, are a group of inherited metabolic disorders, that prevent the body from properly breaking down proteins and fats. This leads to a buildup of a toxic level of methylmalonic acid in body liquids and tissues. Due to the disturbed branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) metabolism, they are among the classical organic acidemias.
Succinyl-coenzyme A, abbreviated as succinyl-CoA or SucCoA, is a thioester of succinic acid and coenzyme A.
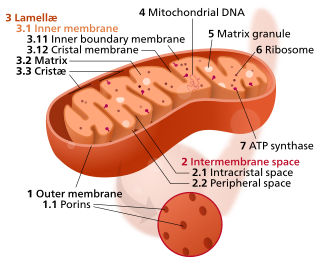
In the mitochondrion, the matrix is the space within the inner membrane. The word "matrix" stems from the fact that this space is viscous, compared to the relatively aqueous cytoplasm. The mitochondrial matrix contains the mitochondrial DNA, ribosomes, soluble enzymes, small organic molecules, nucleotide cofactors, and inorganic ions.[1] The enzymes in the matrix facilitate reactions responsible for the production of ATP, such as the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, oxidation of pyruvate, and the beta oxidation of fatty acids.
In biochemistry and metabolism, beta oxidation (also β-oxidation) is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle, generating NADH and FADH2, which are electron carriers used in the electron transport chain. It is named as such because the beta carbon of the fatty acid chain undergoes oxidation and is converted to a carbonyl group to start the cycle all over again. Beta-oxidation is primarily facilitated by the mitochondrial trifunctional protein, an enzyme complex associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane, although very long chain fatty acids are oxidized in peroxisomes.

ACADM is a gene that provides instructions for making an enzyme called acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase that is important for breaking down (degrading) a certain group of fats called medium-chain fatty acids.

Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase is a mitochondrial homodimer apoenzyme that focuses on the catalysis of methylmalonyl CoA to succinyl CoA. The enzyme is bound to adenosylcobalamin, a hormonal derivative of vitamin B12 in order to function. Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase deficiency is caused by genetic defect in the MUT gene responsible for encoding the enzyme. Deficiency in this enzyme accounts for 60% of the cases of methylmalonic acidemia.
Acyl-CoA dehydrogenases (ACADs) are a class of enzymes that function to catalyze the initial step in each cycle of fatty acid β-oxidation in the mitochondria of cells. Their action results in the introduction of a trans double-bond between C2 (α) and C3 (β) of the acyl-CoA thioester substrate. Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is a required co-factor in addition to the presence of an active site glutamate in order for the enzyme to function.

Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, C-2 to C-3 short chain is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ACADS gene. This gene encodes a tetrameric mitochondrial flavoprotein, which is a member of the acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family. This enzyme catalyzes the initial step of the mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation pathway. The ACADS gene is associated with short-chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency.

Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (EC 5.4.99.2, MCM), mitochondrial, also known as methylmalonyl-CoA isomerase, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MUT gene. This vitamin B12-dependent enzyme catalyzes the isomerization of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA in humans. Mutations in MUT gene may lead to various types of methylmalonic aciduria.
Propionyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of propionic acid. It is composed of a 24 total carbon chain and its production and metabolic fate depend on which organism it is present in. Several different pathways can lead to its production, such as through the catabolism of specific amino acids or the oxidation of odd-chain fatty acids. It later can be broken down by propionyl-CoA carboxylase or through the methylcitrate cycle. In different organisms, however, propionyl-CoA can be sequestered into controlled regions, to alleviate its potential toxicity through accumulation. Genetic deficiencies regarding the production and breakdown of propionyl-CoA also have great clinical and human significance.

Propionyl-CoA carboxylase (EC 6.4.1.3, PCC) catalyses the carboxylation reaction of propionyl-CoA in the mitochondrial matrix. PCC has been classified both as a ligase and a lyase. The enzyme is biotin-dependent. The product of the reaction is (S)-methylmalonyl CoA.

Methylmalonyl-CoA is the thioester consisting of coenzyme A linked to methylmalonic acid. It is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of succinyl-CoA, which plays an essential role in the tricarboxylic acid cycle.
Fatty acid degradation is the process in which fatty acids are broken down into their metabolites, in the end generating acetyl-CoA, the entry molecule for the citric acid cycle, the main energy supply of living organisms, including bacteria and animals. It includes three major steps:

Thiolases, also known as acetyl-coenzyme A acetyltransferases (ACAT), are enzymes which convert two units of acetyl-CoA to acetoacetyl CoA in the mevalonate pathway.
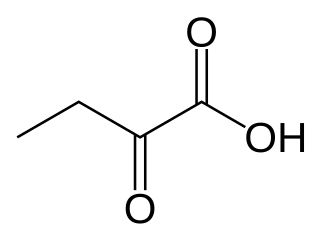
α-Ketobutyric acid is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2C(O)CO2H. It is a colorless solid that melts just above room temperature. Its conjugate base α-ketobutyrate is the predominant form found in nature (near neutral pH). It results from the lysis of cystathionine. It is also one of the degradation products of threonine, produced by the catabolism of the amino acid by threonine dehydratase. It is also produced by the degradation of homocysteine and the metabolism of methionine.
Odd-chain fatty acids are those fatty acids that contain an odd number of carbon atoms. In addition to being classified according to their saturation or unsaturation, fatty acids are also classified according to their odd or even numbers of constituent carbon atoms. With respect to natural abundance, most fatty acids are even chain, e.g. palmitic (C16) and stearic (C18). In terms of physical properties, odd and even fatty acids are similar, generally being colorless, soluble in alcohols, and often somewhat oily. The odd-chain fatty acids are biosynthesized and metabolized slightly differently from the even-chained relatives. In addition to the usual C12-C22 long chain fatty acids, some very long chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) are also known. Some of these VLCFAs are also of the odd-chain variety.

Acyl-CoA thioesterase 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACOT1 gene.
Combined malonic and methylmalonic aciduria (CMAMMA), also called combined malonic and methylmalonic acidemia is an inherited metabolic disease characterized by elevated levels of malonic acid and methylmalonic acid. However, the methylmalonic acid levels exceed those of malonic acid. CMAMMA is not only an organic aciduria but also a defect of mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis (mtFASII). Some researchers have hypothesized that CMAMMA might be one of the most common forms of methylmalonic acidemia, and possibly one of the most common inborn errors of metabolism. Due to being infrequently diagnosed, it most often goes undetected.