| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1671 History of China • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1671 in China .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1671 History of China • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1671 in China .

The Qing dynasty or the Qing Empire, officially the Great Qing, was the last dynasty in the imperial history of China. It was established in 1636, and ruled China from 1644 to 1912, with a brief restoration in 1917. It was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing empire lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest Chinese dynasty and in 1790 the fourth largest empire in world history in terms of territory. With a population of 432 million in 1912, it was the world's most populous country.

Zhao is a Chinese surname, ranking as the 7th most common surname in China and carried mainly by people of Mandarin-speaking regions. Zhao is the 1st surname in the famous Hundred Family Surnames – the traditional list of all Chinese surnames – because it was the emperor's surname of the Song Dynasty (960–1279) when the list was compiled. The first line of the poem is in the line 趙錢孫李.

The Revolt of the Three Feudatories, also known as the Rebellion of Wu Sangui, was a rebellion in China lasting from 1673 to 1681, during the early reign of the Kangxi Emperor of the Qing dynasty (1644–1912). The revolt was led by the three lords of the fiefdoms in Yunnan, Guangdong and Fujian provinces against the Qing central government. These hereditary titles had been given to prominent Han Chinese defectors who had helped the Manchu conquer China during the transition from Ming to Qing. The feudatories were supported by Zheng Jing's Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan, which sent forces to invade Mainland China. Additionally, minor Han military figures, such as Wang Fuchen and the Chahar Mongols, also revolted against Qing rule. After the last remaining Han resistance had been put down, the former princely titles were abolished.
The literary inquisition, also known as speech crime (以言入罪), refers to official persecution of intellectuals for their writings in China. The Hanyu Da Cidian defines it as "the ruler deliberately extracts words or phrases from intellectual's writings and arbitrarily accuse him in order to persecute him" ("旧时谓统治者为迫害知识分子,故意从其著作中摘取字句,罗织成罪"). The Inquisition took place under each of the dynasties ruling China, although the Qing was particularly notorious for the practice. In general, there are two ways a literary inquisition could be carried out. First is that the conviction came from the writing itself. That is, the writing was the direct cause of the persecution. The second is that the writing was used as a tool to provide legitimate evidence for a predetermined conviction. Such persecutions could owe even to a single phrase or word which the ruler considered offensive. Some of these were due to naming taboo, such as writing a Chinese character that is part of the emperor's personal name. In the most serious cases, not only the writer, but also his immediate and extended families, as well as those close to him, would also be implicated and killed.

The social structure of China has an extensive history which begins from the feudal society of Imperial China to the contemporary era. There was a Chinese nobility, beginning with the Zhou dynasty. However, after the Song dynasty, the powerful government offices were not hereditary. Instead they were selected through the imperial examination system, of written examinations based on Confucian thought, thereby undermining the power of the hereditary aristocracy..
The ranks of imperial consorts have varied over the course of Chinese history but remained important throughout owing to its importance in management of the inner court and in imperial succession, which ranked heirs according to the prominence of their mothers in addition to their strict birth order. Regardless of the age, however, it is common in English translation to simplify these hierarchy into the three ranks of Empress, consorts, and concubines. It is also common to use the term "harem", an Arabic loan word used in recent times to refer to imperial women's forbidden quarters in many countries. In later Chinese dynasties, these quarters were known as the back palace. In Chinese, the system is called The Rear Palace System.

Zhao Erxun, courtesy name Cishan, art name Wubu, was a Chinese political and military officeholder who lived in the late Qing dynasty. He served in numerous high-ranking positions under the Qing government, including Viceroy of Sichuan, Viceroy of Huguang, and Viceroy of the Three Northeast Provinces. After the fall of the Qing dynasty, he became a historian and was the lead editor of the Draft History of Qing.
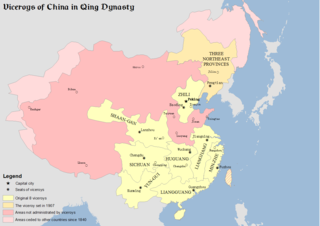
The Viceroy of Shaan-Gan, fully referred to in Chinese as the Governor-General of Shaanxi and Gansu Provinces and the Surrounding Areas; Overseeing Military Affairs and Food Production, Manager of Waterways, Director of Civil Affairs, was one of eight regional viceroys in China proper during the Qing dynasty. The Viceroy of Shaan-Gan had jurisdiction over Shaanxi and Gansu provinces, as well as western Inner Mongolia.

The Taiping Heavenly Kingdom is a Chinese television series based on the events of the Taiping Rebellion and the rise and fall of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom in the late Qing dynasty. The 48-episode series was first broadcast on CCTV in China in 2000. The series was also broadcast on STAR Chinese Channel in Taiwan and on ATV in Hong Kong.

The Viceroy of Huguang, fully referred to in Chinese as the Governor-General of Hubei and Hunan Provinces and the Surrounding Areas; Overseeing Military Affairs, Food Production; Director of Civil Affairs, was one of eight regional Viceroys in China proper during the Qing dynasty. The Viceroy of Huguang had jurisdiction over Hubei and Hunan provinces, which were previously a single province called "Huguang Province" in the Ming dynasty, hence the name "Huguang".

The Viceroy of Sichuan, fully referred to in Chinese as the Governor-General of Sichuan Province and the Surrounding Areas Overseeing Military Affairs and Food Production, Director of Civil Affairs, was one of eight regional viceroys in China proper during the Qing dynasty. As its name suggests, the Viceroy of Sichuan had control over Sichuan (Szechuan) Province, as well as modern Chongqing Municipality, which was split off in 1997.
Events from the year 1662 in China.
Events from the year 1661 in the Qing dynasty.
Events from the year 1663 in China. Also known as 壬寅 4359 or 4299 to 卯年 4360 or 4300 in the Earthly Branches calendar.
Events from the year 1667 in China.
Events from the year 1668 in China.
Events from the year 1669 in China.
Events from the year 1670 in China.
Events from the year 1681 in China.
Events from the year 1686 in China.