Contents
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1661 History of China • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1661 in the Qing dynasty .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1661 History of China • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1661 in the Qing dynasty .

The Kangxi Emperor, also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, personal name Xuanye, was the fourth emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper. His reign of 61 years makes him the longest-reigning emperor in Chinese history and one of the longest-reigning rulers in history. He is considered one of China's greatest emperors.

The Shunzhi Emperor, also known by his temple name Emperor Shizu of Qing, personal name Fulin, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the first Qing emperor to rule over China proper. Upon the death of his father Hong Taiji, a committee of Manchu princes chose the 5-year-old Fulin as successor. The princes also appointed two co-regents: Dorgon, the 14th son of Nurhaci, and Jirgalang, one of Nurhaci's nephews, both of whom were members of the Qing imperial clan. In November 1644, the Shunzhi Emperor was enthroned as emperor of China in Beijing.

Bumbutai, of the Khorchin Mongol Borjigit clan, was the consort of Hong Taiji. She was 21 years his junior. She was honoured as Empress Dowager Zhaosheng during the reign of her son, Fulin, the Shunzhi Emperor, and as Grand Empress Dowager Zhaosheng during the reign of her grandson, Xuanye, the Kangxi Emperor.

Oboi was a prominent Manchu military commander and courtier who served in various military and administrative posts under three successive emperors of the early Qing dynasty. Born to the Guwalgiya clan, Oboi was one of four regents nominated by the Shunzhi Emperor to oversee the government during the minority of the Kangxi Emperor. Oboi reversed the benevolent policies of the Shunzhi Emperor, and vigorously pushed for clear reassertion of Manchu power over the Han Chinese. Eventually deposed and imprisoned by the new emperor for having amassed too much power, he was posthumously rehabilitated.
Soni (1601–1667), also known as Sonin, and rarely Sony, was a Manchu noble of the Hešeri clan who served as one of the Four Regents of the Kangxi Emperor during the Qing dynasty (1644–1912). His clan belonged to the Plain Yellow Banner.
Suksaha was a Manchu official of the early Qing dynasty from the Nara clan. A military officer who participated in the Manchu conquest of China, Suksaha became one of the Four Regents during the early reign of the Kangxi Emperor in the Qing dynasty (1644–1912). He eventually fell out with another regent, Oboi, and was sentenced to death.

Ebilun was a Manchu noble and warrior of the Niohuru clan, most famous for being one of the Four Regents assisting the young Kangxi Emperor from 1661 to 1667, during the early Qing dynasty (1644–1912). A largely passive figure during the regency, Ebilun was disgraced following the ouster of the far more powerful regent Oboi and considered a political supporter of the latter. He was stripped of his positions by the emperor but later regained his noble rank. Many of his descendants became influential figures in the Qing imperial government.
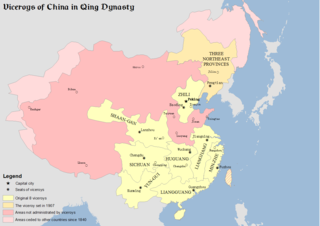
Zongdu were high-level officials responsible for overseeing the governors of several provinces in Ming and Qing China. One viceroy usually administered several provinces and was in charge of all affairs of military, food, wages, rivers, and provincial governors within their region of jurisdiction. Viceroys were appointed by and directly reported to the Emperor.
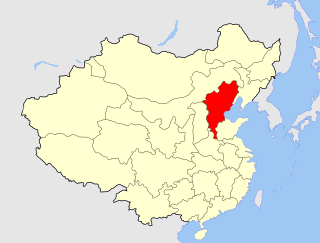
The Viceroy of Zhili, officially in Chinese as the Governor-General of the Directly Subordinate Province and Other Local Areas, in Charge of Military Affairs, Food and Wages, Management of Rivers and Governor Affairs, was one of eight regional Viceroys during the Qing dynasty. The Viceroy of Liangjiang had jurisdiction of military, civil, and political affairs over then Zhili Province. The Governor's Office sat in then Zhili Province's Baoding Prefecture City.
The Four Regents of the Kangxi Emperor were nominated by the Shunzhi Emperor to oversee the government of the Qing dynasty during the early reign of the Kangxi Emperor before he came of age. The four were Sonin, Ebilun, Suksaha, and Oboi.
The Deliberative Council of Princes and Ministers, also known as the Council of Princes and High Officials and Assembly of Princes and High Officials, or simply as the Deliberative Council, was an advisory body for the emperors of the early Qing dynasty (1644–1912). Derived from informal deliberative groups created by Nurhaci (1559–1626) in the 1610s and early 1620s, the Council was formally established by his son and successor Hong Taiji (1592–1643) in 1626 and expanded in 1637. Staffed mainly by Manchu dignitaries, this aristocratic institution served as the chief source of advice on military matters for Hong Taiji and the Shunzhi and Kangxi emperors. It was particularly powerful during the regencies of Dorgon (1643–1650) and Oboi (1661–1669), who used it to enhance their personal influence.
Events from the year 1662 in China.
Events from the year 1663 in China. Also known as 壬寅 4359 or 4299 to 卯年 4360 or 4300 in the Earthly Branches calendar.
Events from the year 1665 in China.
Events from the year 1666 in China.
Events from the year 1667 in China.
Events from the year 1668 in China.
Events from the year 1669 in China.
Events from the year 1670 in China.