| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1860 History of China • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1860 in China .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1860 History of China • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1860 in China .

The Taiping Rebellion, also known as the Taiping Civil War or the Taiping Revolution, was a massive civil war in China between the Manchu-led Qing dynasty and the Hakka-led Taiping Heavenly Kingdom. It lasted from 1850 until the fall of Tianjing in 1864, although the last rebel army was not wiped out until August 1871. The conflict resulted in approximately 20 million deaths. The established Qing government won decisively, although at great cost to its fiscal and political structure.

Li Hongzhang, Marquess Suyi was a Chinese statesman, general and diplomat of the late Qing dynasty. He quelled several major rebellions and served in important positions in the Qing imperial court, including the Viceroy of Zhili, Huguang and Liangguang.

The Xianfeng Emperor, or by temple name Emperor Wenzong of Qing (清文宗), given name Aisin-Gioro Yizhu (奕詝), was the eighth emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the seventh Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigned from 1850 to 1861. During his reign, the Qing dynasty experienced several wars and rebellions including the Taiping Rebellion, Nian Rebellion, and Second Opium War. He was the last Chinese emperor to exercise sole power. After his death, the Qing government came under the control of Empress Dowager Cixi.

Li Xiucheng was a military rebel commander opposing the Qing dynasty during the Taiping Rebellion. He was born to a peasant family. In 1864, he was captured and interrogated following the third and final Battle of Nanjing. He was then executed by Zeng Guofan.
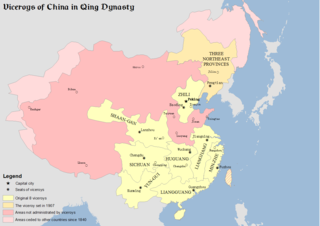
Zongdu, usually translated as Viceroy, Head of State or Governor-General, governed one territory or more provinces of China during the Ming and Qing dynasties.

"Ever Victorious Army" was a small imperial army that fought rebels in late-19th-century China. It was directed and trained by Europeans. The Ever Victorious Army fought for the Qing dynasty against the rebels of the Nian and Taiping Rebellions.

The Viceroy of Liangjiang or Viceroy of the Two Jiangs, fully referred to in Chinese as the Governor-General of the Two Yangtze Provinces and Surrounding Areas Overseeing Military Affairs, Provisions and Funds, Manager of Waterways, Director of Civil Affairs, was one of eight regional Viceroys in China proper during the Qing dynasty. The Viceroy of Liangjiang had jurisdiction over Jiangsu, Jiangxi and Anhui provinces. Because Jiangsu and Anhui were previously part of a single province, Jiangnan, they were thus known, along with Jiangxi, as the two jiangs, hence the name "Liangjiang".

The Xiang Army or Hunan Army was a standing army organized by Zeng Guofan from existing regional and village militia forces called tuanlian to contain the Taiping Rebellion in Qing China. The name is taken from the Hunan region where the Army was raised. The Army was financed through local nobles and gentry, as opposed to through the centralized Manchu-led Qing dynasty. The army was mostly disbanded by Zeng after the re-capture of the Taiping capital at Nanking.

Zeng Guoquan, courtesy name Yuanfu, art name Shuchun, was a Chinese official and military leader of the late Qing dynasty. He was the ninth brother of Zeng Guofan, a prominent statesman and general, and a descendant of the philosopher Zengzi. He served in the Xiang Army, a standing military force organised by his brother to counter the Taiping rebels, and was nicknamed "Ninth Marshal" (九帥). He was known for his expertise in siege warfare, particularly the use of trenches, hence he was also nicknamed "Zeng the Iron Container" (曾鐵桶). During the conquest of Tianjing (Nanjing), the capital of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom, Zeng was notorious for condoning massacres of the city populace, which resulted in him being called "Zeng the Butcher" (曾屠戶).
Zhang Guoliang, born in Guangdong, was a Field Marshal for the Qing dynasty. He was born in Gaoyao, Zhaoqing, Guangdong, China, although Qing state that he is from Meixian, Guangdong. He was originally a bandit in Guangxi but later joined the Qing Army. He raised the Green Standard Army by 250,000 to fight against the Taiping Rebellion in the second rout the Army Group Jiangnan in 1860 and was defeated by Li Xiucheng. Zhang served as a minister to the emperor and a vice commander of Army Group Jiangnan until his death by suicide. Zeng Guofan praised Zhang and said he was Jiangnan's "Great Wall of China."
Cheng Xueqi (Chinese: 程學啟; courtesy name Fangzhong 方忠; born in Tongcheng, Anhui, was a general of the Taiping Rebellion who surrendered to the Qing dynasty in 1861 with Ding Ruchang. He was an eminent Han Chinese official and a Captain General in the army of the late Qing dynasty. He led the Huai Army to fight effectively against the Taiping rebels and helped to restore the stability of Qing, along with other prominent figures, including Li Hongzhang and Zeng Guofan, setting the scene for the successful defense of Shanghai and the Suzhou Massacre POW Incident. The Tongzhi Emperor praised Cheng as "intelligent and brave".
Jiangnan Daying or the Jiangnan Battalion; was an army group assembled by the Qing dynasty. The army group consist of mostly Green Standard Army, and their goal was to quell the Taiping Rebellion around the Jiangnan region. The army group twice encircled Nanjing, the capital of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom, but were defeated by the Taiping forces on both occasions.
The Battle of Jiangnan (1860), also known as the Second rout of the Jiangnan Battalion was a battle between the Qing government's Green Standard Army and the army of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom during the Taiping Rebellion. The Green Standard Army twice attempted to besiege Nanjing, capital of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom, but was unable to break through. To break the siege of Nanjing, the Taiping forces maneuvered to divert Qing forces by sacking Hangzhou, before quickly moving back to Nanjing to counter-encircle the Qing siege forces and routing the Green Standard Army garrison completely, breaking the siege of Nanjing.
Chen Kunshu, prominent military leader of the Taiping Rebellion, and known during his military tenure as the King of Hu (護王). He led Taiping forces to many military victories especially the Second rout the Army Group Jiangnan. He was executed by Li Hongzhang after interrogation in 1864, Chen was an important General and was the sole person responsible for the late-Taiping Rebellion.
Tan Shaoguang was a military leader of the Taiping Rebellion. During his military tenure he was known as the King of Mu (慕王). As a young soldier he joined the Jintian Uprising. After several years he was promoted to general, and led the Taiping forces to many military victories. He was awarded the E An in 1861. He was murdered by traitors after an interrogation in 1863.

The Battle of Anqing (安慶之戰) was a prolonged siege of the prefecture-level city of Anqing in Anhui, China, initiated by Hunan Army forces loyal to the Qing Dynasty against the armies of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom. The siege began in September 1860 and ended on September 5, 1861, when imperial forces under the command of Zeng Guoquan breached the walls of the city and occupied it.
The Western Expedition was a campaign by the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom against the Qing dynasty during the Taiping Rebellion.
Events from the year 1856 in China.
Events from the year 1862 in China.
The Eastern Expedition encompassed the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom's efforts to capture the Yangtze River Delta, the provinces of Jiangsu, Anhui, and Zhejiang. Most of the areas would eventually be occupied by the Taipings, but they were notably repulsed at several locations, especially the city of Shanghai. Following the Jintian uprising in the southern province Guangxi and the beginning of open hostilities, Taiping forces attacked and captured Nanjing in central China by 1853. The Western Expedition captures cities along the Yangtze River like Zhenjiang, Anqing were captured later the same year.