| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1853 History of China • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1853 in China .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1853 History of China • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1853 in China .
1853 (MDCCCLIII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar, the 1853rd year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 853rd year of the 2nd millennium, the 53rd year of the 19th century, and the 4th year of the 1850s decade. As of the start of 1853, the Gregorian calendar was 12 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

The Taiping Rebellion, also known as the Taiping Civil War or the Taiping Revolution, was a massive civil war in China between the Manchu-led Qing dynasty and the Hakka-led Taiping Heavenly Kingdom. It lasted from 1850 until the fall of Tianjing in 1864, although the last rebel army was not wiped out until August 1871. The conflict resulted in approximately 20 million deaths. The established Qing government won decisively, although at great cost to its fiscal and political structure.

The Xianfeng Emperor, or by temple name Emperor Wenzong of Qing (清文宗), given name Aisin-Gioro Yizhu (奕詝), was the eighth emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the seventh Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigned from 1850 to 1861. During his reign, the Qing dynasty experienced several wars and rebellions including the Taiping Rebellion, Nian Rebellion, and Second Opium War. He was the last Chinese emperor to exercise sole power. After his death, the Qing government came under the control of Empress Dowager Cixi.

Li Xiucheng was a military rebel commander opposing the Qing dynasty during the Taiping Rebellion. He was born to a peasant family. In 1864, he was captured and interrogated following the third and final Battle of Nanjing. He was then executed by Zeng Guofan.
Yang Xiuqing, was an organizer and commander-in-chief of the Taiping Rebellion.

The Xiang Army or Hunan Army was a standing army organized by Zeng Guofan from existing regional and village militia forces called tuanlian to contain the Taiping Rebellion in Qing China. The name is taken from the Hunan region where the Army was raised. The Army was financed through local nobles and gentry, as opposed to through the centralized Manchu-led Qing dynasty. The army was mostly disbanded by Zeng after the re-capture of the Taiping capital at Nanking.
Li Shixian was a pre-eminent military leader of the late Taiping Rebellion. He was the cousin of military leader Li Xiucheng and was known for being very tall for a native of Guangxi province, standing at 2 metres (6.6 ft) tall. During his military tenure, he was given the title of King of Shi (侍王). In the latter part of the Taiping rebellion, he led Taiping forces to many military victories. Later in his life, he invited an aging Wei Yuan to live in his home and was known to hold counsel with the famous scholar. He was eventually assassinated by a traitor in Guangdong.
Jiangnan Daying or the Jiangnan Battalion; was an army group assembled by the Qing dynasty. The army group consist of mostly Green Standard Army, and their goal was to quell the Taiping Rebellion around the Jiangnan region. The army group twice encircled Nanjing, the capital of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom, but were defeated by the Taiping forces on both occasions.
Jirhangga was an eminent Manchu official in the late Qing dynasty. He served as the Governor of Jiangsu, which belonged to Bordered Yellow Banner, and was appointed to that post by Imperial Commissioner Xiang Rong (向榮). He was killed in action by rebels during the Taiping Rebellion.
The Battle of Nanjing (1853) began after the fall of Wuhan on March 8, 1853, and ended with the fall of the capital city of Nanjing on March 19, 1853, to Taiping troops, a few days after the Qing Government evacuated the city.
The First rout of the Jiangnan Battalion took place between 1853 and 1856 when the Qing government raised the Green Standard Army to fight against the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom. The action involved Qing forces surrounding the city of Nanjing, the capital of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom.

The Taiping Heavenly Kingdom (1851–1864) was a Chinese Christian theocratic absolute monarchy which sought to overthrow the Qing dynasty. The Heavenly Kingdom or Heavenly Dynasty, was led by King Hong Xiuquan and his followers. Its capital was at Tianjing. The unsuccessful war it waged against the Qing is known as the Taiping Rebellion.
The Red Turban Rebellion of 1854–1856 was a rebellion by members of the Tiandihui in the Guangdong province of South China.

The Battle of Anqing (安慶之戰) was a prolonged siege of the prefecture-level city of Anqing in Anhui, China, initiated by Hunan Army forces loyal to the Qing Dynasty against the armies of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom. The siege began in September 1860 and ended on September 5, 1861, when imperial forces under the command of Zeng Guoquan breached the walls of the city and occupied it.
Events from the year 1860 in China.
The Northern Expedition was a failed campaign by the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom against the Qing dynasty during the Taiping Rebellion. Its purpose was to capture Beijing and then complete an encirclement of northern and western China. Launched in May 1853, the Northern Expedition would travel from Jiangsu to Zhili before being destroyed in early 1855.
The Western Expedition was a campaign by the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom against the Qing dynasty during the Taiping Rebellion.
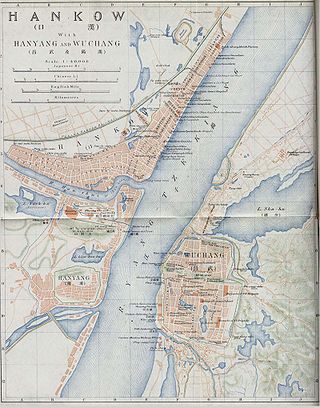
The Battle of Wuchang occurred in 1852 during the Taiping Rebellion in Wuchang, part of the modern-day city of Wuhan.
The Eastern Expedition encompassed the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom's efforts to capture the Yangtze River Delta, the provinces of Jiangsu, Anhui, and Zhejiang. Most of the areas would eventually be occupied by the Taipings, but they were notably repulsed at several locations, especially the city of Shanghai. Following the Jintian uprising in the southern province Guangxi and the beginning of open hostilities, Taiping forces attacked and captured Nanjing in central China by 1853. The Western Expedition captures cities along the Yangtze River like Zhenjiang, Anqing were captured later the same year.
There have been several battles set in and around the city of Nanjing, China. Nanjing was previously named Jianye and Jiankang. During the 19th and 20th centuries, Nanking was a popular romanization of the name in European sources. The Battle of Nanjing may refer to: