This article relies largely or entirely on a single source .(October 2020) |
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1862 History of China • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1862 in China .
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source .(October 2020) |
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1862 History of China • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1862 in China .

Empress Dowager Cixi ; born Yehe Nara Xingzhen, of the Manchu Yehe Nara clan, was a Chinese noblewoman, concubine and later regent who effectively controlled the Chinese government in the late Qing dynasty for 47 years, from 1861 until her death in 1908. Selected as a concubine of the Xianfeng Emperor in her adolescence, she gave birth to a son, Zaichun, in 1856. After the Xianfeng Emperor's death in 1861, the young boy became the Tongzhi Emperor, and she assumed the role of co-empress dowager, alongside the Emperor's widow, Empress Dowager Ci'an. Cixi ousted a group of regents appointed by the late emperor and assumed the regency along with Ci'an, who later died. Cixi then consolidated control over the dynasty when she installed her nephew as the Guangxu Emperor at the death of her son, the Tongzhi Emperor, in 1875. This was contrary to the traditional rules of succession of the Qing dynasty that had ruled China since 1644.

The Tongzhi Emperor, temple name Emperor Muzong of Qing, born Aisin-Gioro Zaichun, was the ninth Emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the eighth Qing emperor to rule over China proper. His reign, from 1861 to 1875, which effectively lasted through his adolescence, was largely overshadowed by the rule of his mother, Empress Dowager Cixi. Although he had little influence over state affairs, the events of his reign gave rise to what historians call the "Tongzhi Restoration", an unsuccessful modernization program.

The Xianfeng Emperor, or by temple name Emperor Wenzong of Qing (清文宗), given name Aisin-Gioro Yizhu (奕詝), was the eighth emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the seventh Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigned from 1850 to 1861. During his reign, the Qing dynasty experienced several wars and rebellions including the Taiping Rebellion, Nian Rebellion, and Second Opium War. He was the last Chinese emperor to exercise sole power. After his death, the Qing government came under the control of Empress Dowager Cixi.
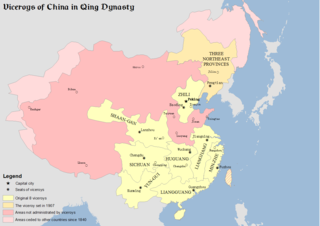
Zongdu, usually translated as Viceroy, Head of State or Governor-General, governed one territory or more provinces of China during the Ming and Qing dynasties.
The Tongzhi Restoration was an attempt to arrest the dynastic decline of the Qing dynasty by restoring the traditional order. The harsh realities of the Opium War, the unequal treaties, and the mid-century mass uprisings of the Taiping Rebellion caused Qing officials to recognize the need to strengthen China. The Tongzhi Restoration was named for the Tongzhi Emperor, and was engineered by the young emperor's mother, the Empress Dowager Cixi (1835–1908). The restoration, however, which applied "practical knowledge" while reaffirming the old mentality, was not a genuine program of modernization. Academics are divided as to whether the Tongzhi Restoration arrested the dynastic decline or merely delayed its inevitable occurrence.
Cheng Xueqi (Chinese: 程學啟; courtesy name Fangzhong 方忠; born in Tongcheng, Anhui, was a general of the Taiping Rebellion who surrendered to the Qing dynasty in 1861 with Ding Ruchang. He was an eminent Han Chinese official and a Captain General in the army of the late Qing dynasty. He led the Huai Army to fight effectively against the Taiping rebels and helped to restore the stability of Qing, along with other prominent figures, including Li Hongzhang and Zeng Guofan, setting the scene for the successful defense of Shanghai and the Suzhou Massacre POW Incident. The Tongzhi Emperor praised Cheng as "intelligent and brave".
Events from the year 1872 in China.
Events from the year 1860 in China.
Events from the year 1861 in China.
Events from the year 1868 in China.
Events from the year 1863 in China.
Events from the year 1864 in China.
Events from the year 1865 in China.
Events from the year 1866 in China.
Events from the year 1867 in China.
Events from the year 1869 in China.
Events from the year 1870 in China.
Events from the year 1871 in China.
Events from the year 1873 in China.
Events from the year 1874 in China.