This article needs additional citations for verification .(September 2018) |
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1869 History of Japan • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1869 in Japan. It corresponds to Meiji 2 in the Japanese calendar.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(September 2018) |
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1869 History of Japan • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1869 in Japan. It corresponds to Meiji 2 in the Japanese calendar.
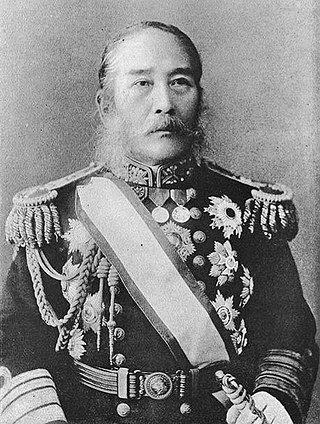
ViscountEnomoto Takeaki was a Japanese samurai and admiral of the Tokugawa navy of Bakumatsu period Japan, who remained faithful to the Tokugawa shogunate and fought against the new Meiji government until the end of the Boshin War. He later served in the Meiji government as one of the founders of the Imperial Japanese Navy.

The Boshin War, sometimes known as the Japanese Revolution or Japanese Civil War, was a civil war in Japan fought from 1868 to 1869 between forces of the ruling Tokugawa shogunate and a coalition seeking to seize political power in the name of the Imperial Court.

Hijikata Toshizō was a Japanese warrior. As Vice-Commander of the Shinsengumi, he resisted the Meiji Restoration and fought to his end.
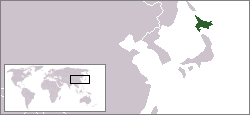
The Republic of Ezo was a short-lived separatist state established in 1869 on the island of Ezo, now Hokkaido, by a part of the former military of the Tokugawa shogunate at the end of the Bakumatsu period in Japan. It was the first government to attempt to institute democracy in Japan, though voting was allowed only to the samurai caste. The Republic of Ezo existed for five months before being annexed by the newly established Empire of Japan.

The Shinsengumi was a small, elite group of swordsmen that was organized by commoners and low rank samurai, commissioned by the bakufu during Japan's Bakumatsu period in 1863. It was active until 1869. It was founded to protect the shogunate representatives in Kyoto at a time when a controversial imperial edict to exclude foreign trade from Japan had been made and the Chōshū clan had been forced from the imperial court. They gained considerable fame in the Ikedaya incident and the August 18 coup events, among others. The men were drawn from the sword schools of Edo.

The Naval Battle of Hakodate was fought from 4 to 10 May 1869, between the remnants of the Tokugawa shogunate navy, consolidated into the armed forces of the rebel Ezo Republic, and the newly formed Imperial Japanese Navy. It was one of the last stages of Battle of Hakodate during the Boshin War, and occurred near Hakodate in the northern Japanese island of Hokkaidō.

Kōtetsu, later renamed Azuma, was the first ironclad warship of the Imperial Japanese Navy. She was designed as an armored ram for service in shallow waters, but also carried three guns. The ship was built in Bordeaux, France, for the Confederate States Navy under the cover name Sphinx, but was sold to Denmark after the sale of warships by French builders to the Confederacy was forbidden in 1863. The Danes refused to accept the ship and sold her to the Confederates which commissioned her as CSS Stonewall in 1865. The ship did not reach Confederate waters before the end of the American Civil War in April and was turned over to the United States.

Kasuga Maru was a Japanese wooden paddle steamer warship of the Bakumatsu and early Meiji period, serving with the navy of Satsuma Domain, and later with the Imperial Japanese Navy. She was originally named Keangsoo, and was a wooden dispatch vessel built for the Imperial Chinese Navy. She was constructed in 1862 by Whites at Cowes, she formed part of the Lay-Osborn Flotilla during the Taiping Rebellion.

Baron Ōtori Keisuke was a Japanese military leader and diplomat.

Banryū was a ship of the Tokugawa Navy, and following the collapse of the shogunate, was operated by Tokugawa loyalists under the Republic of Ezo during the Boshin War in Japan. An armed iron hulled screw-propelled schooner, she had a length of 41.8 metres, a breadth of 5.45 metres, a draught of 3.23 metres, and weighed 370 tons. She was armed with four 12-pounder bronze cannons.

The Battle of Miyako Bay was a naval action on 6 May 1869, in which samurai loyalists of the former Tokugawa shogunate under the flag of the newly formed Republic of Ezo failed to take over the Kōtetsu, the flagship of the Imperial forces of the new Meiji government. It was part of the overall Battle of Hakodate at the end of the Boshin War.

The Battle of Hakodate was fought in Japan from December 4, 1868 to June 27, 1869, between the remnants of the Tokugawa shogunate army, consolidated into the armed forces of the rebel Ezo Republic, and the armies of the newly formed Imperial government. It was the last stage of the Boshin War, and occurred around Hakodate in the northern Japanese island of Hokkaidō. In Japanese, it is also known as the Battle of Goryokaku.

Takao Maru (高雄丸), later renamed Kaiten No.2, was a steam warship of the former navy of the Tokugawa shogunate during the Boshin War of 1868-1869.

Arai Ikunosuke was a Japanese samurai of the late Edo period. Prominent as Navy Minister of the Republic of Ezo, he later became famous as the first head of the Japan Meteorological Agency. Also known as Akinori (顕徳) or Akiyoshi (顕理).

Takenaka Shigekata was a Japanese samurai of the late Edo period, later a figure in efforts to colonize Hokkaido. He is also known by his court title, Tango no kami (丹後守).

Jules Brunet was a French military officer who served the Tokugawa shogunate during the Boshin War in Japan. Originally sent to Japan as a horse artillery instructor with the French military mission of 1867, he refused to leave the country after the shōgun was defeated, and played a leading role in the separatist Republic of Ezo and its fight against forces of the Meiji Restoration. After the rebellion's defeat, he returned to France, fought in the Franco-Prussian War, later reached the rank of general of division, and worked for the Ministry of War.

The Seikanron was a major political debate in Japan during 1873 regarding a punitive expedition against Korea. The Seikanron split the Meiji government and the restoration coalition that had been established against the bakufu, but resulted in a decision not to send a military expedition to Korea.

Matsudaira Sadaaki was a Japanese daimyō of the Bakumatsu period, who was the last ruler of the Kuwana Domain. Sadaaki was the adopted heir of Matsudaira Sadamichi, the descendant of Sadatsuna, the third son of Hisamatsu Sadakatsu (1569–1623), who was Tokugawa Ieyasu's brother. His family was known as the Hisamatsu Matsudaira clan. It was to this family that Matsudaira Sadanobu also belonged.

Matsuoka Bankichi was a Japanese naval officer in the Tokugawa Navy during the Boshin War, serving as Captain of the Japanese warship Banryū during the Battle of Hakodate.

Shimizudani Kinko was a Japanese noble of the Edo period and the Meiji era who was most notable for his service during the Boshin War.