
Biafra, officially the Republic of Biafra, was a partially recognised state in West Africa that declared independence from Nigeria and existed from 1967 until 1970. Its territory consisted of the former Eastern Region of Nigeria, predominantly inhabited by the Igbo ethnic group. Biafra was established on 30 May 1967 by Igbo military officer and Eastern Region governor Chukwuemeka Odumegwu Ojukwu under his presidency, following a series of ethnic tensions and military coups after Nigerian independence in 1960 that culminated in the 1966 anti-Igbo pogrom.

Chukwuemeka "Emeka" Odumegwu Ojukwu was a Nigerian military officer and politician who served as President of the Republic of Biafra from 1967 to 1970 during the Nigerian Civil War. He previously served as military governor of the Eastern Region of Nigeria, which he declared as the independent state of Biafra.

Yakubu Dan-Yumma "Jack" Gowon is a Nigerian former Head of State and statesman who led the Federal military government war efforts during the Nigerian Civil War.

The Nigerian Civil War, also known as the Biafran War, was a civil war fought between Nigeria and the Republic of Biafra, a secessionist state which had declared its independence from Nigeria in 1967. Nigeria was led by General Yakubu Gowon, and Biafra by Lieutenant Colonel Chukwuemeka "Emeka" Odumegwu Ojukwu. The conflict resulted from political, ethnic, cultural and religious tensions which preceded the United Kingdom's formal decolonisation of Nigeria from 1960 to 1963. Immediate causes of the war in 1966 included a military coup, a counter-coup, and anti-Igbo pogroms in the Northern Region. The pogroms and the exodus of surviving Igbos from the Northern Region to the Igbo homelands in the Eastern Region led the leadership of the Eastern Region to conclude that the Nigerian federal government would not protect them and that they must protect themselves in an independent Biafra.

Lieutenant-Colonel Patrick Chukwuma "Kaduna" Nzeogwu was a Nigerian military officer who played a leading role in the 1966 Nigerian coup d'état, which overthrew the First Nigerian Republic.

Hassan Usman Katsina, titled Chiroman Katsina, was a Nigerian general who was the last Governor of Northern Nigeria. He served as Chief of Army Staff during the Nigerian Civil War and later became the Deputy Chief of Staff, Supreme Headquarters.

David Akpode Ejoor RCDS, PSC, was a Nigerian military officer who served as Chief of Army Staff (COAS).
The Aburi Accord or Aburi Declaration was reached at a meeting between 4 and 5 January 1967 in Aburi, Ghana, attended by delegates of both the Federal Government of Nigeria and Eastern delegates led by the Eastern Region's leader Colonel Chukwuemeka Odumegwu-Ojukwu. The meeting was billed as the last chance of preventing all out war. The council collectively vowed not to use force to settle the Nigerian crisis, and also agreed to a law of collective responsibility which vested all powers of the Federal Military Government (FMG) in the Supreme Military Council, making a unanimous concurrence imperative. It was agreed as well, that the Head of the Federal Military Government should assume the title of Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces of Nigeria. The atmosphere of the meeting was very cordial saving that Ojukwu did not participate in the humour side of the show. At the end of the meeting, it was agreed that the resolutions of the meeting should be embodied in a Decree to be issued by Lagos with the concurrence of the military Governors.

Anthony Ukpabi Asika was a Nigerian academic and civil servant. He served as the Administrator of East Central State during the military regime of General Yakubu Gowon, appointed when his predecessor, the Eastern Region governor Chukwuemeka Odumegwu Ojukwu, led the Biafran state into secession.
Amorka is a town in Ihiala local government area of Anambra State of Nigeria. It is located along the Onitsha-Owerri Expressway, bordered by Mgbidi [Imo State] to the South, Ibiasoegbe to the East, Ozara to the West, and Uli to the North. Amorka is the main hub for Biafran airport during the civil war, and Biafran dim Emeka Odumegwu Ojukwu has a secret bunker in Amorka. Amorka has lots of politicians, rich business moguls, many legal practitioners.

The fall of Enugu was a military conflict between Nigerian and Biafran forces in September and October 1967 during the Nigerian Civil War which centered around Enugu, the capital of the secessionist Republic of Biafra. Nigerian federal forces had made Enugu's capture a priority shortly after war broke out, but their advance stalled at Nsukka. Biafran president and leader Odumegwu Ojukwu, attempted to distract the Nigerian Army by initiating an invasion of Nigeria's Mid-Western Region in August, but the offensive was brought to a halt. Lieutenant Colonel Theophilus Danjuma took charge of the Nigerian forces at the Nsukka front and prepared to advance on Enugu with seven battalions of the 1st Division. Enugu was garrisoned by one brigade led by Colonel Alexander Madiebo and poorly armed civilians called into service. Danjuma decided to launch an offensive with his forces spread over a broad front to make it more difficult for the Biafrans to block them along major roads as had happened up to that point.
The Operation UNICORD was an offensive launched by the Nigerian Army at the beginning of the Nigerian Civil War. It involved the capture of 6 major Biafran towns near their northern border.
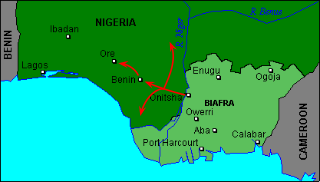
The Midwest Invasion of 1967 or Midwest Offensive, codenamed Operation Torch, was a military operation between Nigerian and Biafran military forces during the Nigerian Civil War. The invasion began on August 9 when 3,000 Biafran soldiers led by General Victor Banjo crossed the River Niger Bridge into Asaba. Upon reaching Agbor, the Biafrans split up. With the 12th Battalion moving west capturing Benin City and Ore, the 18th Battalion swung south, taking Warri, Sapele and Ughelli, while the 13th Battalion headed north for Auchi, Agenebode and Okene. Simultaneously, a plot to capture Mid-Western Governor David Ejoor at his home in Benin failed. Nevertheless, the Biafrans, meeting virtually no resistance, had seized the entire Mid-Western Region in less than 12 hours.

Major General Mohammed Shuwa was a Nigerian military officer and the first General Officer Commanding of the Nigerian Army's 1st Division. Shuwa commanded the 1st Division during the Nigerian Civil War. He was murdered in Maiduguri by suspected Boko Haram militants on 2 November 2012.

Ogbugo Kalu was a Nigerian military officer who served in the Nigerian Army and later the Biafran Army during the Nigerian Civil War. Kalu was also commander of the Nigerian Military Training College (NMTC) in Kaduna following the 1966 Nigerian coup d'état.

Igbo nationalism is a range of ethnic nationalist ideologies relating to the Igbo people of southeastern Nigeria. While the term is defined as seeking Igbo self-determination by some, others argue that it refers to the preservation and revival of Igbo culture and, for others, the development of Igboland stemming from the philosophy, Aku luo uno, which means "wealth builds the home".

Ejike Ebenezer Obumneme Aghanya was a military officer and electrical engineer who served in the Nigerian Army and the Biafran Armed Forces, retiring as a colonel. Accused of involvement in the 1966 Nigerian coup d'état he was arrested and imprisoned without trial until the outbreak of the Nigerian Civil War where he served on the side of Biafra, holding key positions in the Biafran Armed Forces. He was the head of the Biafran Agency for Research and Production (RAP) which produced bombs, rockets, missiles, as well as ammunition, armored vehicles, telecommunication gadgets and petroleum refineries among others for the Biafran Armed Forces. Later he was the Chief of Staff of the Biafran Organisation of Freedom Fighters (BOFF) which was the guerrilla warfare and special operations arm of the Biafran Armed Forces. He also served as Battalion Commander, 44th Electrical and Mechanical Engineer Battalion Biafran Army and later Brigade Commander of the 58th Brigade of 12th Infantry Division Biafran Army during the war.
Sir Benedict Obidinma Odinamadu was a civil servant. He was the private Secretary to Dr. Nnamdi Azikiwe., Dr. M.I. Okpara while Premiers of Eastern Region of Nigeria respectively and First Secretary to the Military Government of Colonel Emeka Odumegwu Ojukwu.
Alexander A. Madiebo was a Biafran soldier. He served as the General Officer Commanding (GOC) of the Republic of Biafra which existed from 1967 to 1970.

The blockade of Biafra by the Nigerian federal government during the Nigerian Civil War (1967–1970) resulted in a famine that ultimately cost at least a million lives and ended with the capitulation of the secessionist state of Biafra.














