
The 1992 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was unofficially the most active year on record for the basin, with 10 tropical storms developing, according to the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC). There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean – the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent – and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the JTWC releases unofficial advisories. An average of four to six storms form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD.

The 2002 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was a below average season in terms of tropical cyclone formation. The season had no official bounds, but most storms formed in either May or after October. No depressions or storms formed during the monsoon season from July to September, the first such instance on record. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean – the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent – and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) releases unofficial advisories. An average of four to six storms form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD.

The 1999 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was an extremely active and deadly tropical cyclone season in recent times. It was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. The North Indian Ocean cyclone season has no official bounds, but cyclones tend to form between April and December, with peaks in May and October-November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean.

The 1981 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was part of the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. A season has no official bounds but cyclones tend to form between April and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) releases unofficial advisories. An average of five tropical cyclones form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD.

The 1989 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was a below-average season in annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. Despite this, the season had the second highest Accumulated Cyclone Energy in the basin on record behind only 2019 and 2023. The season has no official bounds but cyclones tend to form between April and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) releases unofficial advisories. An average of five tropical cyclones form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD.

The 1994 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was a below-average year in which eight tropical cyclones affected seven countries bordering the North Indian Ocean. The India Meteorological Department tracks all tropical cyclones in the basin, north of the equator. The first system developed on March 21 in the Bay of Bengal, the first March storm in the basin since 1938. The second storm was the most powerful cyclone of the season, attaining maximum sustained winds of 215 km/h (135 mph) in the northern Bay of Bengal. Making landfall near the border of Bangladesh and Myanmar, the cyclone killed 350 people and left US$125 million in damage.

The 1985 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was part of the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. The season has no official bounds but cyclones tend to form between April and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) releases unofficial advisories. An average of five tropical cyclones form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD.

The 1987 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was at the time, the most active cyclone season on record, taking the record from 1975 until it was beaten out 5 years later. The season has no official bounds but cyclones tend to form between April and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) releases unofficial advisories. An average of five tropical cyclones form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD.

The 1971 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was part of the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. The season has no official bounds but cyclones tend to form between April and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) releases unofficial advisories. An average of five tropical cyclones form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD.

The 1974 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was part of the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. The season has no official bounds but cyclones tend to form between April and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) releases unofficial advisories. An average of five tropical cyclones form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD.

The 1977 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was part of the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. The season has no official bounds but cyclones tend to form between April and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) releases unofficial advisories. An average of five tropical cyclones form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD.

The 1982 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was part of the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. The season has no official bounds but cyclones tend to form between April and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) releases unofficial advisories. An average of five tropical cyclones form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD.

The 1961 North Indian Ocean cyclone season had no bounds, but cyclones tend to form between April and December, with peaks in May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center releases unofficial advisories. An average of four to six storms form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD.

The 1962 North Indian Ocean cyclone season had no official bounds, but cyclones tend to form between April and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center releases unofficial advisories. An average of four to six storms form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. The IMD includes cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E in the season.

The 1963 North Indian Ocean cyclone season had no bounds, but cyclones tend to form between April and December, with peaks in May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center releases unofficial advisories. An average of four to six storms form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD.

The 2014 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. The season included two very severe cyclonic storms, both in October, and one other named cyclonic storm, classified according to the tropical cyclone intensity scale of the India Meteorological Department. Cyclone Hudhud is estimated to have caused US$3.58 billion in damage across eastern India, and more than 120 deaths.

The 2016 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. It was the deadliest season since 2010, killing more than 400 people. The season was an average one, seeing four named storms, with one further intensifying into a very severe cyclonic storm. The first named storm, Roanu, developed on 19 May while the season's last named storm, Vardah, dissipated on 18 December. The North Indian Ocean cyclone season has no official bounds, but cyclones tend to form between April and December, with the two peaks in May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean.

The 2019 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was the second most active North Indian Ocean cyclone season on record in terms of cyclonic storms, the 1992 season was more active according to the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. The season featured 12 depressions, 11 deep depressions, 8 cyclonic storms, 6 severe cyclonic storms, 6 very severe cyclonic storms, 3 extremely severe cyclonic storms, and 1 super cyclonic storm, Kyarr, the first since Cyclone Gonu in 2007. Additionally, it also became the third-costliest season recorded in the North Indian Ocean, only behind the 2020 and 2008 seasons.

The 2020 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was the costliest North Indian Ocean cyclone season on record, mostly due to the devastating Cyclone Amphan. it was an above average season featuring 5 cyclonic storms. The North Indian Ocean cyclone season has no official bounds, but cyclones tend to form between April and November, with peaks in late April to May and October to November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. The season began on May 16 with the designation of Depression BOB 01 in the Bay of Bengal, which later became Amphan. Cyclone Amphan was the strongest storm in the Bay of Bengal in 21 years and would break Nargis of 2008's record as the costliest storm in the North Indian Ocean. The season concluded with the dissipation of Cyclone Burevi on December 5. Overall, the season was slightly above average, seeing the development of five cyclonic storms.
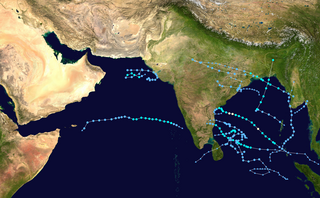
The 2022 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. It was an above-average season in terms of depressions and average in terms of deep depressions, but below average in terms of cyclonic storms. It was also the least deadly North Indian Ocean cyclone season since 1988, according to official data. The season's strongest tropical cyclone was Cyclone Asani, with maximum wind speeds of 100 km/h and a minimum barometric pressure of 982 hPa. The North Indian Ocean cyclone season has no official bounds, but cyclones tend to form between April and December, with the peak from May to November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean.






























