
Biological carbon fixation or сarbon assimilation is the process by which inorganic carbon is converted to organic compounds by living organisms. The compounds are then used to store energy and as structure for other biomolecules. Carbon is primarily fixed through photosynthesis, but some organisms use a process called chemosynthesis in the absence of sunlight.
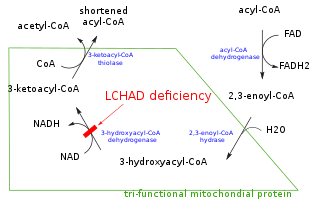
In biochemistry and metabolism, beta oxidation (also β-oxidation) is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle, and NADH and FADH2, which are co-enzymes used in the electron transport chain. It is named as such because the beta carbon of the fatty acid undergoes oxidation to a carbonyl group. Beta-oxidation is primarily facilitated by the mitochondrial trifunctional protein, an enzyme complex associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane, although very long chain fatty acids are oxidized in peroxisomes.

N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase (EC 3.1.6.14, glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase, systematic name N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-6-sulfate 6-sulfohydrolase) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GNS gene. It is deficient in Sanfilippo Syndrome type IIId. It catalyses the hydrolysis of the 6-sulfate groups of the N-acetyl-D-glucosamine 6-sulfate units of heparan sulfate and keratan sulfate
The crotonase family comprises mechanistically diverse proteins that share a conserved trimeric quaternary structure, the core of which consists of 4 turns of a (beta/beta/alpha)n superhelix.

In enzymology, a pyruvate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of pyruvate and acetyl-CoA. It is also called pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PFOR).
The enzyme cyclohexa-1,5-dienecarbonyl-CoA hydratase (EC 4.2.1.100) catalyzes the chemical reaction
ATP citrate synthase (also ATP citrate lyase (ACLY)) is an enzyme that in animals represents an important step in fatty acid biosynthesis. By converting citrate to acetyl-CoA, the enzyme links carbohydrate metabolism, which yields citrate as an intermediate, with fatty acid biosynthesis, which consumes acetyl-CoA. In plants, ATP citrate lyase generates cytosolic acetyl-CoA precursors of thousands of specialized metabolites, including waxes, sterols, and polyketides.
Malonyl CoA reductase (malonate semialdehyde-forming) (EC 1.2.1.75, NADP-dependent malonyl CoA reductase, malonyl CoA reductase (NADP)) is an enzyme with systematic name malonate semialdehyde:NADP+ oxidoreductase (malonate semialdehyde-forming). This enzyme catalyse the following chemical reaction
3,4-Dehydroadipyl-CoA semialdehyde dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.2.1.77, BoxD, 3,4-dehydroadipyl-CoA semialdehyde dehydrogenase) is an enzyme with systematic name 3,4-didehydroadipyl-CoA semialdehyde:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Benzoyl-CoA 2,3-dioxygenase (EC 1.14.12.21, benzoyl-CoA dioxygenase/reductase, BoxBA, BoxA/BoxB system) is an enzyme with systematic name benzoyl-CoA,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (2,3-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Phenylacetyl-CoA 1,2-epoxidase (EC 1.14.13.149, ring 1,2-phenylacetyl-CoA epoxidase, phenylacetyl-CoA monooxygenase, PaaAC, PaaABC(D)E) is an enzyme with systematic name phenylacetyl-CoA:oxygen oxidoreductase (1,2-epoxidizing). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
(2,2,3-Trimethyl-5-oxocyclopent-3-enyl)acetyl-CoA 1,5-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.160, 2-oxo-Delta3-4,5,5-trimethylcyclopentenylacetyl-CoA monooxygenase, 2-oxo-Delta3-4,5,5-trimethylcyclopentenylacetyl-CoA 1,2-monooxygenase, OTEMO) is an enzyme with systematic name ((1R)-2,2,3-trimethyl-5-oxocyclopent-3-enyl)acetyl-CoA,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (1,5-lactonizing). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
3-oxo-5,6-dehydrosuberyl-CoA semialdehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.17.1.7, paaZ (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 3-oxo-5,6-dehydrosuberyl-CoA semialdehyde:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Alpha-1,3-mannosyl-glycoprotein 2-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:3-(alpha-D-mannosyl)-beta-D-mannosyl-glycoprotein 2-beta-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Cholesterol-5,6-oxide hydrolase (EC 3.3.2.11, cholesterol-epoxide hydrolase, ChEH) is an enzyme with systematic name 5,6alpha-epoxy-5alpha-cholestan-3beta-ol hydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Oxepin-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.7.1.16, paaZ (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 2-oxepin-2(3H)-ylideneacetyl-CoA hydrolyase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Benzoyl-CoA-dihydrodiol lyase (EC 4.1.2.44, 2,3-dihydro-2,3-dihydroxybenzoyl-CoA lyase/hydrolase (deformylating), BoxC, dihydrodiol transforming enzyme, benzoyl-CoA oxidation component C) is an enzyme with systematic name 2,3-dihydro-2,3-dihydroxybenzoyl-CoA 3,4-didehydroadipyl-CoA semialdehyde-lyase (formate-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
4-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.120) is an enzyme with systematic name 4-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA hydro-lyase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Azoarcus evansii is a species of bacteria. Its type strain is KB 740T.
Phenylacetyl-CoA (C29H42N7O17P3S) is a form of acetyl-CoA formed from the condensation of the thiol group from coenzyme A with the carboxyl group of phenylacetic acid.





