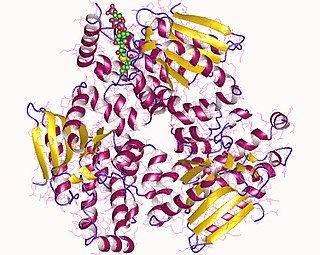
Enoyl-CoA-(∆) isomerase (EC 5.3.3.8, also known as dodecenoyl-CoA- isomerase, 3,2-trans-enoyl-CoA isomerase, ∆3 ,∆2 -enoyl-CoA isomerase, or acetylene-allene isomerase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of cis- or trans-double bonds of coenzyme A bound fatty acids at gamma-carbon to trans double bonds at beta-carbon as below:

Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF), also known as glycosylation-inhibiting factor (GIF), L-dopachrome isomerase, or phenylpyruvate tautomerase is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MIF gene. MIF is an important regulator of innate immunity. The MIF protein superfamily also includes a second member with functionally related properties, the D-dopachrome tautomerase (D-DT). CD74 is a surface receptor for MIF.

In enzymology, a 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.4.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2,5-dihydroxypyridine 5,6-dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-methyleneglutarate mutase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a dTDP-4-dehydrorhamnose 3,5-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a L-dopachrome isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an oxaloacetate tautomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an UDP-glucuronate 4-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Leukotriene-A4 hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction which converts Leukotriene A4 to Leukotriene B4. It is a bifunctional zinc enzyme with different amino acids attached to it to aid in the catalysis of the reaction. It also acts as an aminopeptidase. Leukotriene-A4 hydrolase is a cytosolic protein and is found in almost all mammalian cells, tissues and organelles that have been examined.
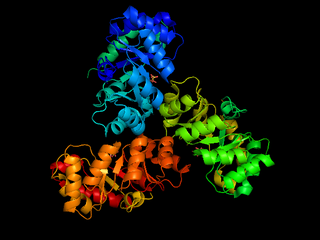
The enzyme 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-phosphogluconate aldolase, commonly known as KDPG aldolase, catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme D-dopachrome decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.84) catalyzes the chemical reaction
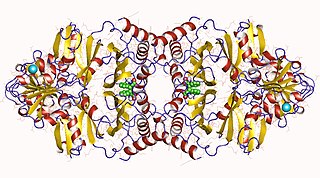
The enzyme prephenate dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.51) catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a beta-galactoside alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a polynucleotide adenylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MATK gene.

Macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP), also known as hepatocyte growth factor-like protein, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MST1 gene.
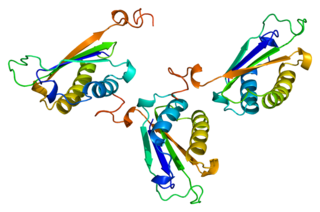
D-dopachrome decarboxylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DDT gene.

Phenylpyruvic acid is the organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2C(O)CO2H. It is a keto acid.

3-Maleylpyruvic acid, or 3-maleylpyruvate, is a dicarboxylic acid formed by the oxidative ring opening of gentisic acid by gentisate 1,2-dioxygenase during the metabolism of tyrosine. It is converted into 3-fumarylpyruvate by maleylpyruvate isomerase.













