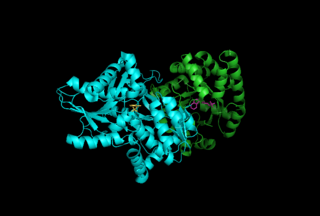
Tryptophan synthase or tryptophan synthetase is an enzyme that catalyses the final two steps in the biosynthesis of tryptophan. It is commonly found in Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Protista, Fungi, and Plantae. However, it is absent from Animalia. It is typically found as an α2β2 tetramer. The α subunits catalyze the reversible formation of indole and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) from indole-3-glycerol phosphate (IGP). The β subunits catalyze the irreversible condensation of indole and serine to form tryptophan in a pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) dependent reaction. Each α active site is connected to a β active site by a 25 angstrom long hydrophobic channel contained within the enzyme. This facilitates the diffusion of indole formed at α active sites directly to β active sites in a process known as substrate channeling. The active sites of tryptophan synthase are allosterically coupled.

Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology has catalogued more than 140 PLP-dependent activities, corresponding to ~4% of all classified activities. The versatility of PLP arises from its ability to covalently bind the substrate, and then to act as an electrophilic catalyst, thereby stabilizing different types of carbanionic reaction intermediates.

Aspartate transaminase (AST) or aspartate aminotransferase, also known as AspAT/ASAT/AAT or (serum) glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase, is a pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-dependent transaminase enzyme that was first described by Arthur Karmen and colleagues in 1954. AST catalyzes the reversible transfer of an α-amino group between aspartate and glutamate and, as such, is an important enzyme in amino acid metabolism. AST is found in the liver, heart, skeletal muscle, kidneys, brain, red blood cells and gall bladder. Serum AST level, serum ALT level, and their ratio are commonly measured clinically as biomarkers for liver health. The tests are part of blood panels.
In enzymology, a 6-hydroxyhexanoate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.258) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a diaminopimelate dehydrogenase (EC 1.4.1.16) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an ADP-L-glycero-D-manno-heptose 6-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an alanine racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

α-Methylacyl-CoA racemase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AMACR gene. AMACR catalyzes the following chemical reaction:
In enzymology, an amino-acid racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an arginine racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an aspartate racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the following chemical reaction:
In enzymology, glutamate racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a methionine racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a proline racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme methionine γ-lyase (EC 4.4.1.11, MGL) is in the γ-family of PLP-dependent enzymes. It degrades sulfur-containing amino acids to α-keto acids, ammonia, and thiols:
In enzymology, a L-lysine-lactamase (EC 3.5.2.11) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a D-amino-acid transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, a L-lysine 6-transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
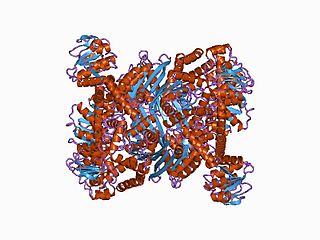
In molecular biology, the ELFV dehydrogenase family of enzymes include glutamate, leucine, phenylalanine and valine dehydrogenases. These enzymes are structurally and functionally related. They contain a Gly-rich region containing a conserved Lys residue, which has been implicated in the catalytic activity, in each case a reversible oxidative deamination reaction.
Achromobacter obae is a bacterium from the genus Achromobacter which contains the enzyme alpha-amino-epsilon-caprolactam racemase. The complete genome of A. obae has been sequenced.







