In its war on terrorism in Yemen, the US government describes Yemen as "an important partner in the global war on terrorism". There have been attacks on civilian targets and tourists, and there was a cargo-plane bomb plot in 2010. Counter-terrorism operations have been conducted by the Yemeni police, the Yemeni military, and the United States Armed Forces.
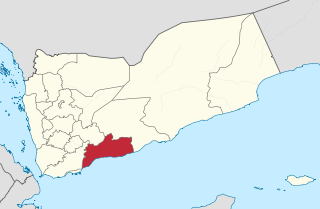
Abyan is a governorate of Yemen. The Abyan region was historically part of the Fadhli Sultanate. It was a base to the Aden-Abyan Islamic Army militant group. Its capital is the city of Zinjibar. This governorate is noted for its agriculture, in particular the cultivation of date palms and animal husbandry.
Zinjibar is a port and coastal town in south-central Yemen, the capital of Zinjibar District and the Abyan Governorate. It is located next to the Wadi Bana in the Abyan Delta. From 1962 to 1967, it was the administrative capital of the Fadhli Sultanate, although the royal residence remained at the former capital of Shuqrah. At the time of the 2004 census, Zinjibar's population numbered 19,879 inhabitants. The town supports a small seaside resort and fishing industry. Cotton grown in the area is brokered in the market.

Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula, or AQAP is a Sunni Islamist militant organization which seeks to overthrow the Yemeni government and establish an Islamic emirate. Part of the al-Qaeda network, the group is based and primarily active in Yemen, while also conducting operations in Saudi Arabia. It is considered the most active of al-Qaeda's affiliates that emerged after the weakening of central leadership.

Jaʽar is a small town and the capital of Khanfir District in southwestern Yemen. One of the largest settlements in Abyan Governorate, it is located to the north of Al Kawd and the regional capital of Zinjibar. The town is located about 2 kilometres east of the right bank of the Wadi Bana.

The Al-Qaeda insurgency in Yemen is an ongoing armed conflict between the Yemeni government, the United States and their allies, and al-Qaeda-affiliated groups in Yemen. It is a part of the Global War on Terror.
The Battle of Zinjibar was a battle between forces loyal to Yemeni leader Ali Abdullah Saleh and Islamist militant forces, possibly including elements of al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP), for control of the town of Zinjibar and its surroundings as part of the wider insurgency in the self-declared Al-Qaeda Emirate in Yemen. Many of the Islamist forces operating in Abyan province refer to themselves as Ansar al-Sharia.
The Battle of Dofas was a battle during the 2011 Yemeni uprising between forces loyal to Yemeni leader Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi and Islamist militant forces, possibly including elements of al-Qaeda, during which the militants destroyed an Army artillery battalion of the 39th Armored Brigade in the town of Dofas, which was being used as a main base for artillery support against the militant-held towns of Zinjibar and Jaʿār.
In August 2010, the Yemeni army began a siege against militants linked to al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) who took control of the city of Lawdar in Abyan Governorate, Yemen. The siege was in response to an AQAP ambush on 20 August which killed 11 soldiers in the city. The siege was lifted by 24 August, with Yemeni forces successfully taking back the city. A total of 33 people were killed in the battle, 19 of them being AQAP militants.
The following lists events that happened during 2012 in Yemen.

United States drone strikes in Yemen started after the September 11 attacks in the United States, when the US military attacked the Islamist militant presence in Yemen, in particular Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula using drone warfare.

The Abyan campaign was a 2015 campaign for control of the Abyan Governorate of Yemen, between the Houthis and Yemen Army units loyal to Ali Abdullah Saleh on one side, and militiamen and Yemen Army units loyal to Abd Rabbuh Mansur Hadi on the other side, supported by jihadists of al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula. The pro-Hadi forces recaptured the Abyan Governorate on 11 August 2015, after launching an offensive on pro-Houthi forces in early August.
In early December 2015, two Yemeni towns, Zinjibar and Jaʽār, were captured by the jihadist group Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP). This was the second capture and occupation of Zinjibar during unrest in Yemen. The town was earlier taken by AQAP's in May 2011 and held until the summer of 2012.
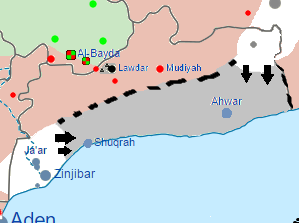
The Southern Abyan Offensive refers to a 2016 offensive that AQAP launched in late February, which ended with a victory for AQAP as Yemeni tribal fighters loyal to president Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi were driven out of the Abyan Governorate.

The Aden unrest was a conflict between Islamist factions, such as al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula, and Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant's Yemen Branch, against the loyalists of president Abd Rabbuh Mansur Hadi and later to conflict between UAE-backed and Saudi-backed factions within the coalition. In 2017, fighting also broke out between factions aligned with different members of the Saudi-led coalition namely Saudi Arabia-backed Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi and Al-Islah and UAE-backed separatist Southern Transitional Council and Southern Movement.

The Shabwah Governorate offensive is an insurgent campaign by Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) forces to take control of Shabwah Governorate during the Yemeni Civil War.
The Hadramaut insurgency was an insurgency in Yemen launched by AQAP and ISIL-YP against forces loyal to president Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi.
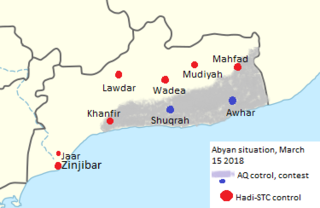
The Abyan conflict was a series of clashes between forces of AQAP loyal to Yemeni president Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi, and forces loyal to Southern Movement for the control of Abyan between 2016 and 2018.

Abdullatif Al-Sayed Bafaqih was a Southern Yemeni warlord from Abyan who played a major role during the wars against Al-Qaeda after 2012 in Abyan Governorate.

In August 2022, forces of Yemen's Emirati-backed separatist Southern Movement, mainly represented by the Southern Transitional Council, launched an offensive in the Abyan and Shabwah provinces. Initially, the Southern forces mostly fought against Saudi-backed government forces, most of which belonged to the armed wing of the Islah party. Since early September 2022, however, the Southern Movement's offensive has become more focused on battling local al-Qaeda strongholds.











