
Elections in Chile are held nationwide, including the presidency, parliament, regional offices, and municipal positions. Chilean citizens and foreign residents with legal residency of at least five years, who are 18 years or older on election day, are eligible to vote. Previously, voting was voluntary, but since 2023, it has become compulsory.

Elections in Uruguay encompass three different types: general elections, departamental elections and municipal elections. At the national level, Uruguay elects a head of state and a legislature. Voting is compulsory and extends to all citizens aged 18 and over.

A constitutional referendum was held in Chile on 11 September 1980. The proposed new constitution would replace the 1925 constitution, and was approved by over two-thirds of voters.
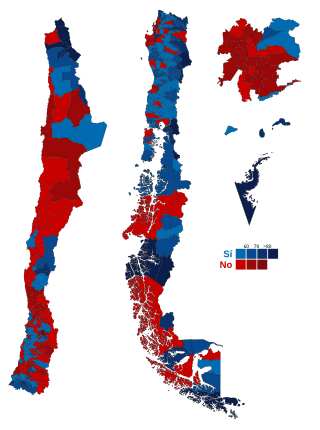
A referendum on whether Augusto Pinochet, the head of a military dictatorship, should become president for eight years under resumed civilian rule was held in Chile on 5 October 1988. The "No" side won with 56% of the vote, marking the end of Pinochet's 16+1⁄2-year rule. Democratic elections were held in 1989, leading to the establishment of a new government in 1990.

The 1997 Constitution of Uruguay refers to the 1967 Constitution with amendments.

Anti-imperialist Unitary Commissions is a far-left Marxist–Leninist political alliance in Uruguay founded in 2008 that describes itself as revolutionary left, class-conscious, anti-imperialist and anticapitalist.

Ana Carolina Cosse Garrido is a Uruguayan engineer and politician who is the vice president-elect of Uruguay after winning the 2024 general election. She has been Intendant of Montevideo from November 2020 until her resignation in July 2024. A member of the Broad Front, she served as Minister of Industry, Energy, and Mining from 2015 to 2019 during the second administration of President Tabaré Vázquez. In the 2019 Uruguayan general election, she was elected to the Senate of Uruguay, taking her seat on 15 February 2020. On 27 September 2020, she was elected Intendant of Montevideo, the capital of the country.

The Colombian peace agreement referendum was held on 2 October 2016, aiming to ratify the final agreement on the termination of the Colombian conflict between the Colombian government and the FARC guerillas. It failed, with 50.2% voting against it and 49.8% voting in favor. Approval of the referendum was taken for granted in Colombia prior to the vote based on opinion polls. However, the 'No' option ended up winning by a narrow margin.

A referendum was held in Venezuela on 16 July 2017. The referendum was called by the National Assembly in response to the constitutional crisis and President Nicolás Maduro's plans for a Constituent Assembly. The referendum was an act of civil disobedience in the context of the application of Articles 333 and 350 of the Venezuelan constitution, with the articles calling for Venezuelans to "disown any regime ... that violates democratic values", especially since the National Electoral Council and the Supreme Tribunal of Justice were not recognized in the referendum. The opposition Democratic Unity Roundtable (MUD) announced that there would be 2,030 areas for the popular consultation nationwide to serve more than 19 million voters.

Referendums in Costa Rica are regulated by law. The main juridical body that regulates is the Law of Referendum or Law 8492. To this date the only nation-wide referendum done since the current Constitution and the afore mentioned referendum regulatory law is in place was the 2007 Costa Rican Dominican Republic – Central America Free Trade Agreement referendum.

Women's suffrage in Francoist Spain and the democratic transition was constrained by age limits, definitions around heads of household and a lack of elections. Women got the right to vote in Spain in 1933 as a result of legal changes made during the Second Spanish Republic. Women lost most of their rights after Franco came to power in 1939 at the end of the Spanish Civil War, with the major exception that women did not universally lose their right to vote. Repression of the women's vote occurred nevertheless as the dictatorship held no national democratic elections between 1939 and 1977.

The 2019 Uruguayan constitutional referendum, officially referred to as the referendum for constitutional reform on security matters, took place alongside general election of that year, on 27 October 2019, to ask the electorate whether a constitutional reform in public security should be approved. The proposed amendments to the Constitution would create a national guard, forbid early release for some serious crimes, introduce life sentences for crimes of rape, sexual abuse or homicide of minors as well as aggravated homicide of adults, and allow the police to conduct night raids. The referendum resulted in 46.8% of the votes cast in favor of amending the Constitution; however, not reaching the necessary 50%, the amendment was not approved, being rejected by 53.7% of the votes.

A constitutional referendum was held in Chile on 25 October 2020. The referendum asked the citizens whether they wanted a new constitution to be drafted, and if so, whether it should be written by a constitutional convention made up of directly elected citizens or by a mixed convention that was composed of currently serving members of Parliament and half of directly elected citizens. The "Approve" side won by a landslide, with 78% of voters agreeing to draft a new constitution. When it came to deciding how the new text should be written, 79% of voters opted for a "Constitutional Convention." The voter turnout was 51%.

An election for the members of the Constitutional Convention was held in Chile between 15 and 16 May 2021. This election was called after 78% of voters in the 2020 national plebiscite voted to write a new Constitution through this method.

General elections were held in Uruguay on 27 October 2024. Since no presidential candidate received a majority in the first round of voting, a runoff took place on 24 November 2024, with Yamandú Orsi of the Broad Front defeating Álvaro Delgado of the Republican Coalition.

A referendum on the Urgent Consideration Law was held in Uruguay to ask the electorate if 135 articles of Law 19,889 – approved by the General Assembly in 2020 and considered as the main legislative initiative of the coalition government of President Luis Lacalle Pou — should be repealed. It was the result of a campaign promoted by various social and political actors such as the national trade union center PIT-CNT and the opposition party Broad Front. On 8 July 2021, almost 800,000 adhesions were delivered to the Electoral Court, exceeding 25% of the total number of registered voters who are constitutionally required to file a referendum appeal against a law.
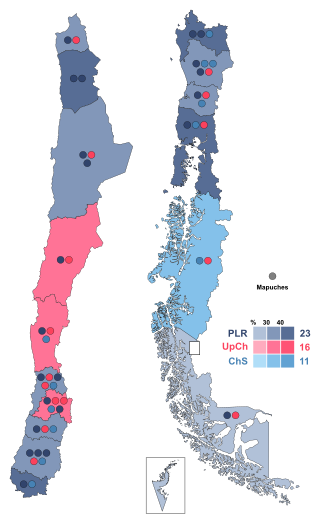
Constitutional Council elections were held in Chile on 7 May 2023. Voting was compulsory, and resulted in an electoral victory for right-wing parties, passing the threshold of a three-fifths majority of constitutional council members to freely draft a new constitution, removing the veto option from left-wing members. This marked a sharp shift from a left-wing majority that freely drafted a rejected first constitutional rewrite in 2021 and was described as a political loss for President Gabriel Boric.
The Civic Credential is a compulsory Uruguayan official document that identifies citizens authorized to vote. Issued by the Electoral Court, it is the only document that certifies the identity of the voter in electoral instances.

On November 5, 2024, Puerto Rico held a non-binding referendum alongside the 2024 Puerto Rican general election and the 2024 United States elections. This was the seventh referendum held on the long-standing, ongoing debate about the political status of Puerto Rico, with the previous one having taken place in 2020.

Two constitutional referendums were held in Uruguay on 27 October 2024 alongside a general election. Voters were asked whether they approved of constitutional amendments related to social security and night time police raids.

















