Electoral system
Regional elections in Piedmont were ruled by the Tatarella law, which was approved in 1995 and provided for a mixed electoral system. Four fifths of the regional councilors were elected in provincial constituencies by proportional representation, using the largest remainder method with a Droop quota and open lists, while the residual votes and the unassigned seats were grouped into a single regional constituency, where the whole ratios and the highest remainders were divided with the Hare quota among the provincial party lists; one fifth of the council seats instead was reserved for regional lists and assigned with a majoritarian representation system, in which the leader of the regional list that scored the highest number of votes was elected to the presidency of the region, while the other candidates were elected regional councilors.
A threshold of 3% had been established for the provincial lists, which could still have entered the regional council if the regional list to which they were connected had scored at least 5% of valid votes. The panachage was also allowed; the voter can indicate a candidate for the presidency but prefer a provincial list connected to another candidate.
Background
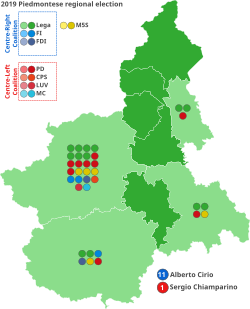
Sergio Chiamparino, the outgoing president of Piedmont for the Democratic Party, initially stated in June 2018 to not run for a second term. [3] In September 2018, he declared he would run in the next regional election. [4] He supported the joint candidacy of Turin, Milan, and Cortina d'Ampezzo for the 2026 Winter Olympics before Chiara Appendino, mayor of Turin for the Five Star Movement (M5S), decided to withdraw from the bidding process. [5] [6] He supported the Turin–Lyon high-speed railway and criticized the first Conte government for its opposition, led mainly by the M5S. Finally, he advocated a referendum about the Turin–Lyon on the same day as the regional election and asked to the Italian Minister of the Interior, Matteo Salvini, to allow it; both Giuseppe Conte, the Prime Minister of Italy, and Salvini rejected the idea. [7] [8] [9]
The country's centre-right coalition had some troubles to reach an agreement for a unitary candidate. Alberto Cirio, the then Member of the European Parliament, was the candidate proposed by Forza Italia; the League opposed his candidacy, proposing instead the entrepreneur Paolo Damilano. [10] [11] After the 2019 Basilicata regional election held on 24 March, the centre-right agreed to the candidacy of Cirio. [12] Cirio was the former deputy mayor for Alba and former regional assessor for Piedmont; he was elected in the 2014 European Parliament election in Italy in the North-West Italy constituency with 35.388 votes, and he backed the Turin–Lyon high-speed railway. [13] In June 2018, along with 50 regional councillors, he was committed to stand trial on charges of misappropriating €20,000 of public funds, during 2008 and 2010, under the presidency of Mercedes Bresso. [14] [15] In February 2019, the Turin public prosecutor's office filed a motion to dismiss. [16]
The candidate for the presidency of Piedmont for the M5S was voted on the party website. With 1,540 votes, Giorgio Bertola, outgoing regional councillor for Piedmont, won the primary election. [17] He strongly opposed the Turin–Lyon and the referendum proposed by Chiamparino. [18]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.