
Dike is a quite large and dark main-belt asteroid. Dike was discovered by Alphonse Borrelly on May 28, 1868. It was his first asteroid discovery. This object is named after Dike, the Greek goddess of moral justice. Among the first hundred numbered minor planets, 99 Dike was considered anomalously faint for over a century. However, this was later found to be untrue.

Lachesis is a large main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by French astronomer Alphonse Borrelly on April 10, 1872, and independently by German-American astronomer Christian Heinrich Friedrich Peters on April 11, 1872, then named after Lachesis, one of the Moirai, or Fates, in Greek mythology. A Lachesean occultation of a star occurred in 1999 and was confirmed visually by five observers and once photoelectrically, with the chords yielding an estimated elliptical cross-section of 184 × 144 km.

Medusa is a bright-coloured, stony main-belt asteroid that was discovered by French astronomer J. Perrotin on September 21, 1875, and named after the Gorgon Medusa, a snake-haired monster in Greek mythology. It is orbiting the Sun at a distance of 2.17 AU with a period of 3.21 years and an eccentricity of 0.065. The orbital plane is tilted slightly at an angle of 0.94° to the plane of the ecliptic.

Dejopeja is a large M-type Main belt asteroid. It was discovered by Johann Palisa on February 28, 1878, and was named after Deiopea, a Roman nymph.

225 Henrietta is a very large outer main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa on April 19, 1882, in Vienna and named after Henrietta, wife of astronomer Pierre J. C. Janssen. The asteroid is orbiting at a distance of 3.39 AU from the Sun with a period of 6.24 years and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.26. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 20.9° to the plane of the ecliptic. 225 Henrietta belongs to Cybele group of asteroids and is probably in a 4:7 orbital resonance with the planet Jupiter.

Vanadis is a fairly large main-belt asteroid with a diameter of around 100 km. It was discovered by A. Borrelly on August 27, 1884, in Marseilles and was named after Freyja (Vanadis), the Norse fertility goddess. The asteroid is orbiting the Sun at a distance of 2.67 AU with a period of 4.35 yr and an orbital eccentricity of 0.206. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 2.10° to the plane of the ecliptic.
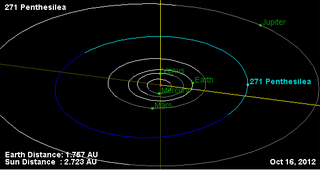
Penthesilea is a mid-sized main belt asteroid that was discovered by Viktor Knorre on 13 October 1887 in Berlin. It was his last asteroid discovery. The asteroid was named after Penthesilea, the mythical Greek queen of the Amazons.

Nenetta is an A-type asteroid with a diameter of 38 km. It was discovered by Auguste Charlois on 10 March 1890 in Nice, France. The asteroid is orbiting the Sun at a distance of 2.87 AU with an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.204 and an orbital period of 4.87 yr. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 6.7° to the plane of the ecliptic.

Geraldina is a large Main belt asteroid. It was discovered by Auguste Charlois on October 3, 1890, in Nice. The origin of the name is unknown. It is orbiting the Sun at a distance of 3.21 AU with a period of 5.74 yr and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.057. The orbital plane is tilted at an angle of 0.73° to the plane of the ecliptic.

Fraternitas is a typical Main belt asteroid. It was discovered by Johann Palisa on 6 April 1891 in Vienna. The asteroid name is Latin for 'fraternity'; it was so named in order to commemorate the 25th anniversary of the Maturitätsprüfung Fraternity.

Florentina is an S-type (stony) main belt asteroid with a diameter of 28 km. It was discovered by Johann Palisa on 15 October 1891 in Vienna. He named the asteroid for his daughter, Florentine. Between 1874 and 1923, Palisa discovered a total of 122 asteroids.

May is a large Main belt asteroid. It was discovered by Auguste Charlois on 28 November 1892 in Nice, and was named for the German author Karl May. This asteroid is orbiting the Sun at a distance of 2.97 AU with a period of 5.12 years and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.067. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 9.7° to the plane of the ecliptic. During its orbit, this asteroid has made close approaches to the dwarf planet Ceres. For example, in September 1984 the two were separated by 6.3 Gm (0.042 AU).
Pamina is a minor planet orbiting the Sun in the main belt. It is named for the heroine of Mozart's opera, The Magic Flute. This asteroid was discovered by M. Wolf in 1904 at the Heidelberg observatory in Germany. It is orbiting at a distance of 2.74 AU from the Sun, with an orbital eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.212 and a period of 4.53 yr. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 6.8° to the ecliptic.
Stereoskopia is a large, outer main-belt asteroid orbiting the Sun. It was discovered on 28 May 1905 from Heidelberg by German astronomer Paul Götz. The discovery was made from photographic plates with the use of a stereo-comparator that had been provided by Carl Pulfrich, a German physicist at the Carl Zeiss Company. The asteroid name is a reference to this device.
678 Fredegundis is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. It was discovered 22 January 1909 from Heidelberg by German astronomer K. Wilhelm Lorenz, and was named after the French opera Frédégonde. This object is orbiting at a distance of 2.57 AU with a period of 4.13 years and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.22. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 6.1° to the plane of the ecliptic
765 Mattiaca is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt. Photometric observations made in 2011–2012 at the Organ Mesa Observatory in Las Cruces, New Mexico produced an irregular light curve and a period of 3.4640 ± 0.0001 hours with a brightness variation of 0.09 ± 0.01 in magnitude. Mattiacum was the Latin name for the city of Wiesbaden, Germany, birthplace of the discoverer.
774 Armor is a minor planet orbiting in the main belt. It was discovered on December 13, 1913, in Paris by French astronomer Charles le Morvan and was named after the Celtic region of Armorica. The asteroid is orbiting at a distance of 3.05 AU with a period of 5.32 yr and an eccentricity of 0.169. The orbital plane is inclined by an angle of 5.56° to the plane of the ecliptic.
782 Montefiore is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt that was discovered by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa on 18 March 1914 and named for Clarice Sebag-Montefiore, wife of Alfons von Rothschild of Vienna. It is orbiting 2.18 AU from the Sun with an eccentricity of 0.04 and a period of 3.22 yr. The orbital plane of this asteroid is inclined by an angle of 5.26° to the plane of the ecliptic.
793 Arizona is a minor planet orbiting the Sun that was discovered April 9, 1907 by American businessman Percival Lowell at Flagstaff. It was named for the state of Arizona. The object was independently discovered on April 17, 1907, by J. H. Metcalf at Taunton. This is a main belt asteroid orbiting 2.8 AU from the Sun with a period of 4.675 yr and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.13. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 15.8° to the plane of the ecliptic.
967 Helionape is an asteroid belonging to the Flora family of Main Belt asteroids. It was discovered by German astronomer Walter Baade at Hamburg Observatory on November 9, 1921, and was named after the Austrian theatrical actor Adolf von Sonnenthal. This object is orbiting the Sun at a distance of 2.23 AU with a period of 3.32 years and an eccentricity of 0.168. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 5.4° to the ecliptic.












