
154 Bertha is a main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by the French brothers Paul Henry and Prosper Henry on 4 November 1875, but the credit for the discovery was given to Prosper. It is probably named after Berthe Martin-Flammarion, sister of the astronomer Camille Flammarion.

193 Ambrosia is a main belt asteroid that was discovered by the Corsican-born French astronomer J. Coggia on February 28, 1879, and named after Ambrosia, the food of the gods in Greek mythology.

217 Eudora is a large Main belt asteroid. It was discovered by French (Corsican) astronomer J. Coggia on August 30, 1880, in Marseilles, France. It was his fourth asteroid discovery and is named after Eudora, a Hyad in Greek mythology.
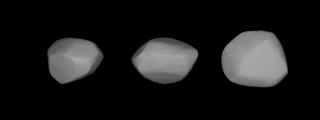
242 Kriemhild is a main belt asteroid that was discovered by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa on 22 September 1884 in Vienna and was named after Kriemhild, a mythological Germanic princess, by Moriz von Kuffner, a Viennese industrialist and sponsor of astronomy.

273 Atropos is a typical Main belt asteroid that was discovered by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa on 8 March 1888 in Vienna.

340 Eduarda is a main belt asteroid that was discovered by German astronomer Max Wolf on 25 September 1892 in Heidelberg. It was named after German banker and amateur astronomer Heinrich Eduard von Lade.
568 Cheruskia is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt that was discovered by German astronomer Paul Götz on 26 July 1905 from Heidelberg.

573 Recha is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. The asteroid, discovered by German astronomer Max Wolf on September 19, 1905, was named after a character in Gotthold Ephraim Lessing's play Nathan the Wise and may have been inspired by the asteroid's provisional designation 1905 RC.

572 Rebekka is a minor planet orbiting the Sun, which was discovered on September 19, 1905, by a German astronomer Paul Götz in Heidelberg. It was named after a young lady from Heidelberg, and may have been inspired by the asteroid's provisional designation 1905 RB.
585 Bilkis is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt. It was discovered by German astronomer August Kopff in 1906 February and was given the Koran name for the Queen of Sheba. Photometric observations at the Palmer Divide Observatory in Colorado Springs, Colorado in 2006–7 were used to build a light curve for this object. The asteroid displayed a rotation period of 8.5742 ± 0.0005 hours and a brightness variation of 0.40 ± 0.02 in magnitude.

605 Juvisia is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt that was discovered 27 August 1906 in Heidelberg by German astronomer Max Wolf. It was named after the commune Juvisy-sur-Orge, France, where French astronomer Camille Flammarion had his observatory.
607 Jenny is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt that was discovered by German astronomer August Kopff on September 18, 1906.
620 Drakonia is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt. It was discovered October 26, 1906, in Taunton, Massachusetts, by American astronomer Joel Hastings Metcalf and given the preliminary designation 1906 WE. It may have been named for Drake University.
687 Tinette is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting primarily in the asteroid belt. It was discovered by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa on 16 August 1909 from Vienna and was given the preliminary designation 1909 HG.

708 Raphaela is a minor planet orbiting the Sun.
860 Ursina is a minor planet orbiting the Sun that was discovered in 1917 by German astronomer Max Wolf. The origin of the name is unknown.
880 Herba is a minor planet orbiting the Sun that was discovered by German astronomer Max Wolf on 22 July 1917 in Heidelberg.
999 Zachia is a main-belt asteroid that was discovered by German astronomer Karl W. Reinmuth in 1923 and named after Hungarian astronomer Franz Xaver von Zach.

3174 Alcock is a carbonaceous Themistian asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt. It was discovered by American astronomer Edward Bowell at Lowell's U.S. Anderson Mesa Station in Flagstaff, Arizona, on 26 October 1984. The likely C-type asteroid has a rotation period of 7.1 hours and measures approximately 19 kilometers in diameter. It was named after British amateur astronomer George Alcock (1912–2000).
3099 Hergenrother, provisional designation 1940 GF, is an asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 15 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 3 April 1940, by Finnish astronomer Yrjö Väisälä at Turku Observatory in Southwest Finland, and named after American astronomer Carl Hergenrother in 1996.











