Related Research Articles

A quasar is an extremely luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. The emission from an AGN is powered by a supermassive black hole with a mass ranging from millions to tens of billions of solar masses, surrounded by a gaseous accretion disc. Gas in the disc falling towards the black hole heats up and releases energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation. The radiant energy of quasars is enormous; the most powerful quasars have luminosities thousands of times greater than that of a galaxy such as the Milky Way. Quasars are usually categorized as a subclass of the more general category of AGN. The redshifts of quasars are of cosmological origin.
An active galactic nucleus (AGN) is a compact region at the center of a galaxy that emits a significant amount of energy across the electromagnetic spectrum, with characteristics indicating that the luminosity is not produced by stars. Such excess, non-stellar emissions have been observed in the radio, microwave, infrared, optical, ultra-violet, X-ray and gamma ray wavebands. A galaxy hosting an AGN is called an active galaxy. The non-stellar radiation from an AGN is theorized to result from the accretion of matter by a supermassive black hole at the center of its host galaxy.

3C 273 is a quasar located at the center of a giant elliptical galaxy in the constellation of Virgo. It was the first quasar ever to be identified and is the visually brightest quasar in the sky as seen from Earth, with an apparent visual magnitude of 12.9. The derived distance to this object is 749 megaparsecs. The mass of its central supermassive black hole is approximately 886 million times the mass of the Sun.

Seyfert galaxies are one of the two largest groups of active galaxies, along with quasars. They have quasar-like nuclei with very high surface brightnesses whose spectra reveal strong, high-ionisation emission lines, but unlike quasars, their host galaxies are clearly detectable.

A radio galaxy is a galaxy with giant regions of radio emission extending well beyond its visible structure. These energetic radio lobes are powered by jets from its active galactic nucleus. They have luminosities up to 1039 W at radio wavelengths between 10 MHz and 100 GHz. The radio emission is due to the synchrotron process. The observed structure in radio emission is determined by the interaction between twin jets and the external medium, modified by the effects of relativistic beaming. The host galaxies are almost exclusively large elliptical galaxies. Radio-loud active galaxies can be detected at large distances, making them valuable tools for observational cosmology. Recently, much work has been done on the effects of these objects on the intergalactic medium, particularly in galaxy groups and clusters.

A BL Lacertae object or BL Lac object is a type of active galactic nucleus (AGN) or a galaxy with such an AGN, named after its prototype, BL Lacertae. In contrast to other types of active galactic nuclei, BL Lacs are characterized by rapid and large-amplitude flux variability and significant optical polarization. Because of these properties, the prototype of the class was originally thought to be a variable star. When compared to the more luminous active nuclei (quasars) with strong emission lines, BL Lac objects have spectra dominated by a relatively featureless non-thermal emission continuum over the entire electromagnetic range. This lack of spectral lines historically hindered identification of the nature and distance of such objects.

Centaurus A is a galaxy in the constellation of Centaurus. It was discovered in 1826 by Scottish astronomer James Dunlop from his home in Parramatta, in New South Wales, Australia. There is considerable debate in the literature regarding the galaxy's fundamental properties such as its Hubble type and distance. NGC 5128 is one of the closest radio galaxies to Earth, so its active galactic nucleus has been extensively studied by professional astronomers. The galaxy is also the fifth-brightest in the sky, making it an ideal amateur astronomy target. It is only visible from the southern hemisphere and low northern latitudes.

3C 449 is a low-redshift Fanaroff and Riley class I radio galaxy. It is thought to contain a highly warped circumnuclear disk surrounding the central active galactic nucleus (AGN). The name signifies that it was the 449th object of the Third Cambridge Catalog of Radio Sources (3C), published in 1959.

3C 295 is a narrow-line radio galaxy located in the constellation of Boötes. With a redshift of 0.464, it is approximately 5 billion light-years from Earth. At time of the discovery of its redshift in 1960, this was the remotest object known.

Ursa Major B or 3C 244.1 is a radio galaxy located in the constellation Ursa Major.
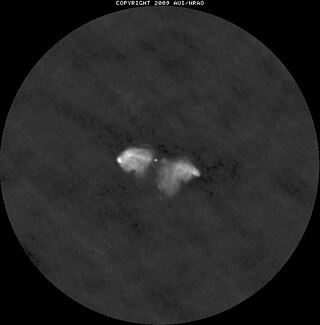
3C 285 is a radio galaxy located in the constellation Canes Venatici. It is located about 1 bilion light years away. It is a Fanaroff-Riley 2 radio galaxy and is hosted in a disturbed spiral galaxy.

3C 438 is a Seyfert galaxy and Fanaroff and Riley class II radio galaxy located in the constellation Cygnus. The radio galaxy has two lobes and there is a radio jet leading to the south lobe, which also has a prominent double hot spot. There is age variation across the lobes.

The type-cD galaxy is a galaxy morphology classification, a subtype of type-D giant elliptical galaxy. Characterized by a large halo of stars, they can be found near the centres of some rich galaxy clusters. They are also known as supergiant ellipticals or central dominant galaxies.

NGC 6166 is an elliptical galaxy in the Abell 2199 cluster. It lies 490 million light years away in the constellation Hercules. The primary galaxy in the cluster, it is one of the most luminous galaxies known in terms of X-ray emissions.

The Fanaroff–Riley classification is a scheme created by B.L. Fanaroff and J.M. Riley in 1974, which is used to distinguish radio galaxies with active nuclei based on their radio luminosity or brightness of their radio emissions in relation to their hosting environment. Fanaroff and Riley noticed that the relative positions high/low surface brightness regions in the lobes of extragalactic radio sources are correlated with their radio luminosity. Their conclusion was based on a set of 57 radio galaxies and quasars that were clearly resolved at 1.4 GHz or 5 GHz into two or more components. Fanaroff and Riley divided this sample into two classes using the ratio of the distance between the regions of highest surface brightness on opposite sides of the central galaxy or quasar to the total extent of the source up to the lowest brightness contour. Class I are sources whose luminosity decreases as the distance from the central galaxy or quasar host increase, while Class II (FR-II) sources exhibit increasing luminosity in the lobes. This distinction is important because it presents a direct link between the galaxy's luminosity and the way in which energy is transported from the central region and converted to radio emission in the outer parts.

NGC 3862 is an elliptical galaxy located 300 million light-years away in the constellation Leo. Discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 27, 1785, NGC 3862 is an outlying member of the Leo Cluster.

NGC 708 is an elliptical galaxy located 240 million light-years away in the constellation Andromeda and was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on September 21, 1786. It is classified as a cD galaxy and is the brightest member of Abell 262. NGC 708 is a weak FR I radio galaxy and is also classified as a type 2 Seyfert galaxy.

NGC 541 is a lenticular galaxy located in the constellation Cetus. It is located at a distance of circa 230 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 541 is about 130,000 light years across. It was discovered by Heinrich d'Arrest on October 30, 1864. It is a member of the Abell 194 galaxy cluster and is included in the Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies in the category galaxies with nearby fragments. NGC 541 is a radio galaxy of Fanaroff–Riley class I, also known as 3C 40A.

NGC 545 is a lenticular galaxy located in the constellation Cetus. It is located at a distance of circa 250 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 545 is about 180,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on October 1, 1785. It is a member of the Abell 194 galaxy cluster and is included along with NGC 547 in the Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies.

NGC 547 is an elliptical galaxy and radio galaxy located in the constellation Cetus. It is located at a distance of circa 220 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 547 is about 120,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on October 1, 1785. It is a member of the Abell 194 galaxy cluster and is included along with NGC 547 in the Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "NED results for object 3C 401". NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database. Retrieved 29 March 2012.
- ↑ Roche, Nathan; Stephen A. Eales (September 2000). "Optical/ultraviolet morphology and alignment of low-redshift radio galaxies". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society . 317 (1): 120–140. Bibcode:2000MNRAS.317..120R. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-8711.2000.03684.x . Retrieved 30 March 2012.
- ↑ Leahy, J. P.; A. H. Bridle & R. G. Strom. "3CRR Atlas: 3C 401". An Atlas of DRAGNs. Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics. Retrieved 30 March 2012.
- ↑ Chiaberg, Marco; et al. (August 10, 2005). "The Infrared-dominated Jet of 3C 401". The Astrophysical Journal. 629 (1): 100–107. arXiv: astro-ph/0505034 . Bibcode:2005ApJ...629..100C. doi:10.1086/431236. S2CID 39185781.