Related Research Articles

54 Piscium is an orange dwarf star approximately 36 light-years away in the constellation of Pisces. In 2003, an extrasolar planet was confirmed to be orbiting the star, and in 2006, a brown dwarf was also discovered orbiting it.
HD 38529 is a binary star approximately 138 light-years away in the constellation of Orion.

HD 28185 b is an extrasolar planet 128 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Eridanus. The planet was discovered orbiting the Sun-like star HD 28185 in April 2001 as a part of the CORALIE survey for southern extrasolar planets, and its existence was independently confirmed by the Magellan Planet Search Survey in 2008. HD 28185 b orbits its sun in a circular orbit that is at the inner edge of its star's habitable zone.

Gliese 876 b is an exoplanet orbiting the red dwarf Gliese 876. It completes one orbit in approximately 61 days. Discovered in June 1998, Gliese 876 b was the first planet to be discovered orbiting a red dwarf.

Upsilon Andromedae c, formally named Samh, is an extrasolar planet orbiting the Sun-like star Upsilon Andromedae A every 241.3 days at an average distance of 0.83 AU. Its discovery in April 1999 by Geoffrey Marcy and R. Paul Butler made this the first multiple-planet system to be discovered around a main-sequence star, and the first multiple-planet system known in a multiple star system. Upsilon Andromedae c is the second-known planet in order of distance from its star.

Any planet is an extremely faint light source compared to its parent star. For example, a star like the Sun is about a billion times as bright as the reflected light from any of the planets orbiting it. In addition to the intrinsic difficulty of detecting such a faint light source, the light from the parent star causes a glare that washes it out. For those reasons, very few of the exoplanets reported as of April 2014 have been observed directly, with even fewer being resolved from their host star.

14 Herculis b or 14 Her b is an exoplanet approximately 58.4 light-years away in the constellation of Hercules. The planet was found orbiting the star 14 Herculis, with a mass that would make the planet a Jovian planet roughly the same size as Jupiter but much more massive. It was discovered in July 1998 by the Geneva Extrasolar Planet Search team. The discovery was formally published in 2003. At the time of discovery it was the extrasolar planet with the longest orbital period, though longer-period planets have subsequently been discovered.
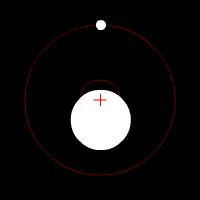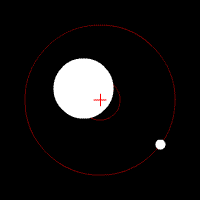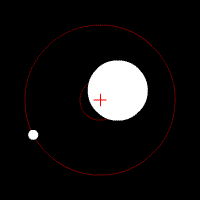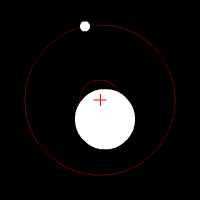
Doppler spectroscopy is an indirect method for finding extrasolar planets and brown dwarfs from radial-velocity measurements via observation of Doppler shifts in the spectrum of the planet's parent star. As of November 2022, about 19.5% of known extrasolar planets have been discovered using Doppler spectroscopy.
HD 219828 is a star with two exoplanetary companions in the constellation of Pegasus. With an apparent visual magnitude of 8.04, it is an eighth magnitude star that is too dim to be readily visible to the naked eye. The star is located at a distance of approximately 237 light years from the Sun based on parallax measurements, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −24 km/s.

109 Piscium b is a long-period extrasolar planet discovered in orbit around 109 Piscium. It is about 5.74 times the mass of Jupiter and is likely to be a gas giant. As is common for long-period planets discovered around other stars, it has an orbital eccentricity greater than that of Jupiter.
HD 8673 is a binary star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It has an apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude of 6.34 and 3.56 respectively. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 26.2 mas, the system is located around 124.5 light years away. The system is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +19 km/s. A sub-stellar companion was detected in 2005; it could either be an exoplanet or a brown dwarf.
This page describes exoplanet orbital and physical parameters.

GJ 3021 b, also known as Gliese 3021 b or HD 1237 b, is an extrasolar planet approximately 57 light-years away, orbiting its bright G-dwarf parent star in the Southern constellation of Hydrus. It was discovered with the Swiss Euler Telescope at the Chilean La Silla Observatory in 2000.
HD 210277 b is an extrasolar planet orbiting the star HD 210277. It was discovered in September 1998 by the California and Carnegie Planet Search team using the highly successful radial velocity method. The planet is at least 24% more massive than Jupiter. The mean distance of the planet from the star is slightly more than Earth's distance from the Sun. However, the orbit is very eccentric, so at periastron this distance is almost halved, and at apastron it is as distant as Mars is from the Sun.

CoRoT-3b is a brown dwarf or massive extrasolar planet with a mass 21.66 times that of Jupiter. The object orbits an F-type star in the constellation of Aquila. The orbit is circular and takes 4.2568 days to complete. It was discovered by the French-led CoRoT mission which detected the dimming of the parent star's light as CoRoT-3b passes in front of it.
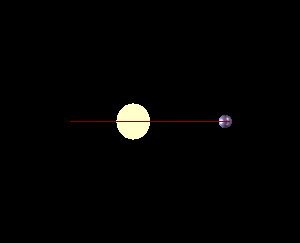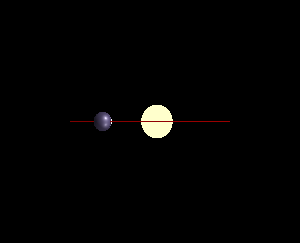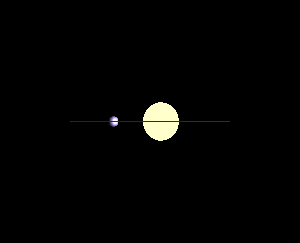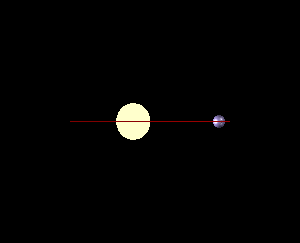
In astronomy, minimum mass is the lower-bound calculated mass of observed objects such as planets, stars and binary systems, nebulae, and black holes.

OGLE-TR-132b is an extrasolar planet orbiting the star OGLE-TR-132.
HD 139357 is a 6th magnitude K-type giant star located approximately 370 light years from Earth, visible in the constellation Draco. Its mass is four thirds that of the Sun but its radius is 11.47 times larger. However, despite being a giant star, it is only 3.07 billion years old, which is younger than the Sun.
HD 180902 b is an extrasolar planet orbiting the K-type star HD 180902 approximately 342 light years away in the constellation Sagittarius.

HD 4313 b is an extrasolar planet orbiting the K-type star HD 4313 approximately 447 light years away in the constellation Pisces. This planet was discovered using the Doppler spectroscopy method.
References
- ↑ Döllinger, M. P.; et al. (2009). "Planetary companion candidates around the K giant stars 42 Draconis and HD 139 357". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 499 (3): 935–942. arXiv: 0903.3593 . Bibcode:2009A&A...499..935D. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200810837. S2CID 15677079.
- ↑ Feng, Fabo; Butler, R. Paul; et al. (August 2022). "3D Selection of 167 Substellar Companions to Nearby Stars". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series . 262 (21): 21. arXiv: 2208.12720 . Bibcode:2022ApJS..262...21F. doi: 10.3847/1538-4365/ac7e57 . S2CID 251864022.