Related Research Articles

Hera is a moderately large main-belt asteroid with an orbital period of 4.44 years. It was discovered by Canadian-American astronomer James Craig Watson on September 7, 1868, and named after Hera, queen and fifth in power of the Olympian gods in Greek mythology. This is a stony S-type asteroid with a silicate surface composition.

Felicitas is a dark and fairly large main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by German-American astronomer C. H. F. Peters on October 9, 1869, and named after Felicitas, the Roman goddess of success. The only observed stellar occultation by Felicitas is one from Japan.
Althaea is a main-belt asteroid that was discovered by Canadian-American astronomer J. C. Watson on April 3, 1872, and named after Althaea, the mother of Meleager in Greek mythology. Two occultations by Althaea were observed in 2002, only a month apart.

Lachesis is a large main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by French astronomer Alphonse Borrelly on April 10, 1872, and independently by German-American astronomer Christian Heinrich Friedrich Peters on April 11, 1872, then named after Lachesis, one of the Moirai, or Fates, in Greek mythology. A Lachesean occultation of a star occurred in 1999 and was confirmed visually by five observers and once photoelectrically, with the chords yielding an estimated elliptical cross-section of 184 × 144 km.

Alkeste is a main-belt asteroid, and it is an S-type (silicaceous) in composition. C.H.F. Peters discovered the asteroid on August 23, 1872, from the observatory at Hamilton College, New York State. The name was chosen by Adelinde Weiss, wife of the astronomer Edmund Weiss, and refers to Alcestis, a woman in Greek mythology.

Eunike is a dark and very large main-belt asteroid, with an approximate diameter of 157 kilometres. It has a primitive carbonaceous composition.
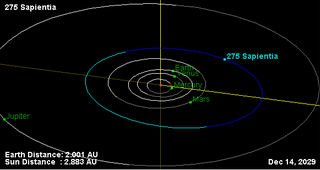
Sapientia is a very large Main belt asteroid that was discovered by Johann Palisa on 15 April 1888 in Vienna. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of carbonaceous material. It is named for the Roman personification of wisdom, Sapientia.

Tercidina is a large main-belt asteroid. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of carbonaceous material.

Myrrha is a main-belt asteroid that was discovered by the French astronomer Auguste Charlois on January 10, 1894, in Nice. It has been classified as a C-type asteroid and is most likely composed of carbonaceous material.

Recha is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. The asteroid, discovered by German astronomer Max Wolf on September 19, 1905, was named after a character in Gotthold Ephraim Lessing's play Nathan the Wise and may have been inspired by the asteroid's provisional designation 1905 RC.

Happelia is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. On 24 February 2017 a possible small 3-kilometer moon was found orbiting the asteroid, based on occultation observations.
Selene is a minor planet orbiting the Sun in the asteroid belt. The name Selene is that of an ancient Greek goddess of the Moon. The name may have been inspired by the asteroid's provisional designation 1905 SE.
618 Elfriede is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. On July 24, 2013, it occulted the magnitude 12.8 star 2UCAC 23949304, over parts of Mexico and southwestern United States.

683 Lanzia is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. It was discovered July 23, 1909, by Max Wolf at the Landessternwarte Heidelberg-Königstuhl observatory and was named in honor of Lanz, founder of the Heidelberg Academy of Sciences. Photometric observations made in 2003 at the Santana Observatory in Rancho Cucamonga, California, give a synodic rotation period of 8.63 ± 0.005 hours. The light curve shows a brightness variation of 0.15 ± 0.04 in magnitude.

705 Erminia is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. Its name derives from the comic opera Erminie. An occultation on 8 December 2014 gave 3 chords, with one measurement suggesting a small moon 6-10 kilometers wide at a distance of 400 kilometers to the primary.
733 Mocia is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. A possible occultation was observed by Oscar Canales Moreno on October 1, 2001.
740 Cantabia is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. It was discovered on 10 February 1913 at Winchester, Massachusetts by American amateur astronomer J. H. Metcalf. Cantabia is a contraction of Cantabrigia, Latin for Cambridge, named in honor of Cambridge, Massachusetts. It is orbiting at a distance of 3.05 AU with a period of 5.33 years and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.11. Between 2014 and 2021, 740 Cantabia has been observed to occult three stars.

772 Tanete is an asteroid from the asteroid belt. Since 2004 it has been observed in stellar occultation four times. Its size is best described by an ellipsoid measuring 124.1±1.2 km x 116.1±1.2 km. Analysis of a light curve captured during 2014 shows a synodic rotation period of 17.258±0.001 h with an amplitude of 0.15 magnitude.
4672 Takuboku, provisional designation 1988 HB, is a background asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 35 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 17 April 1988, by Japanese astronomers Seiji Ueda and Hiroshi Kaneda at the Kushiro Observatory on Hokkaido, Japan. The asteroid was named after the Japanese poet Takuboku Ishikawa. In 2005, measurement of the body's occultation ellipse also gave 35.0 × 35.0 kilometers.

(523692) 2014 EZ51 (provisional designation 2014 EZ51) is a large trans-Neptunian object in the scattered disc, approximately 700 kilometres (430 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 18 April 2010, by the Pan-STARRS 1 survey at Haleakala Observatory, Hawaii, United States.
References
- ↑ Noah Webster (1884) A Practical Dictionary of the English Language
- ↑ "598 Octavia (1906 UC)". JPL Small-Body Database . NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory . Retrieved 5 May 2016.
- ↑ "Asteroid Occultations Predictions". asteroidoccultation.com. Retrieved 23 October 2014.