Related Research Articles
624 Hektor is the largest Jupiter trojan and the namesake of the Hektor family, with a highly elongated shape equivalent in volume to a sphere of approximately 225 to 250 kilometers diameter. It was discovered on 10 February 1907, by astronomer August Kopff at Heidelberg Observatory in southwest Germany, and named after the Trojan prince Hector, from Greek mythology. It has one small 12-kilometer sized satellite, Skamandrios, discovered in 2006.
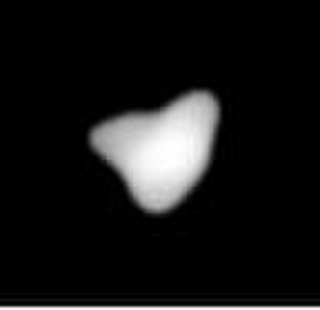
30 Urania is a large main-belt asteroid that was discovered by English astronomer John Russell Hind on July 22, 1854. It was his last asteroid discovery. This object is named after Urania, the Greek Muse of astronomy. Initial orbital elements for 30 Urania were published by Wilhelm Günther, an assistant at Breslau Observatory. It is orbiting the Sun with a period of 3.64 years and is spinning on its axis once every 13.7 hours.

104 Klymene is a large, dark Themistian asteroid that was discovered by J. C. Watson on September 13, 1868, and named after one of the many Clymenes in Greek mythology. It is orbiting the Sun with a period of 5.60 years and an eccentricity of 0.16. The orbital plane is inclined by 2.8° to the plane of the ecliptic. It is classified as a C-type asteroid, indicating it probably has a carbonaceous composition. The spectra indicates the presence of aqueous-altered minerals on the surface based upon a sharp feature at a wavelength of 3 μm, and, as of 2015, is the only member of the Themis family found to show this absorption.

121 Hermione is a very large binary asteroid discovered in 1872. It orbits in the Cybele group in the far outer asteroid belt. As an asteroid of the dark C spectral type, it is probably composed of carbonaceous materials. In 2002, a small moon was found to be orbiting Hermione.

165 Loreley is a main-belt asteroid that was discovered by C. H. F. Peters on August 9, 1876, in Clinton, New York and named after the Lorelei, a figure in German folklore.

175 Andromache is a main-belt asteroid that was discovered by Canadian-American astronomer J. C. Watson on October 1, 1877, and named after Andromache, wife of Hector during the Trojan War. Watson's telegram to Europe announcing the discovery became lost, and so notification did not arrive until several weeks later. As a result, another minor planet, later designated 176 Iduna, was initially assigned the number 175.
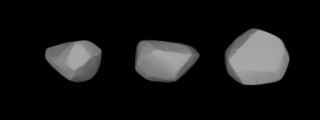
192 Nausikaa is a large main-belt S-type asteroid. It was discovered by Johann Palisa on February 17, 1879, at Pula, then in Austria, now in Croatia. The name derives from Nausicaä, a princess in Homer's Odyssey.

194 Prokne is a main-belt asteroid that was discovered by German-American astronomer C. H. F. Peters on March 21, 1879, in Clinton, New York, and named after Procne, the sister of Philomela in Greek mythology. Stellar occultations by Prokne have been observed twice, in 1984 from Italy and again in 1999 from Iowa.

198 Ampella is a Main belt asteroid that was discovered by Alphonse Borrelly on June 13, 1879. The name seems to be the feminine form of Ampelos, a satyr and good friend of Dionysus in Greek mythology. It could also derive from the Ampelose, a variety of hamadryad. It is an S-type asteroid.

264 Libussa is a Main belt asteroid that was discovered by C. H. F. Peters on December 22, 1886, in Clinton, New York and was named after Libussa, the legendary founder of Prague. It is classified as an S-type asteroid.

283 Emma is a large asteroid of the asteroid belt and the namesake of the Emma family. It was discovered by Auguste Charlois on 8 February 1889, in Nice, France. The reason for its name is unknown.

308 Polyxo is a main-belt asteroid that was discovered by A. Borrelly on March 31, 1891, in Marseilles. It is orbiting the Sun at a distance of 2.75 AU with a low orbital eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.04 and a period of 4.56 yr. The orbital plane is tilted at an angle of 4.36° to the plane of the ecliptic.

379 Huenna is a large asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt. It is part of the Themis family, and thus a C-type asteroid and consequently composed mainly of carbonaceous material.
444 Gyptis is a main-belt asteroid that was discovered by J. Coggia on March 31, 1899, in Marseilles. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of carbonaceous material. The spectra of the asteroid displays evidence of aqueous alteration.
654 Zelinda is a minor planet orbiting the Sun that was discovered on 4 January 1908 by German astronomer August Kopff. On favorable oppositions, it can be as bright as magnitude 10.0, as on January 30, 2016.

679 Pax is a minor planet orbiting the Sun that was discovered by German astronomer August Kopff on January 28, 1909. It is named after Pax, a Roman goddess. It is orbiting the Sun with a period of 4.16 years and an eccentricity of 0.31.
804 Hispania is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. It was discovered from Barcelona (Spain) on 20 March 1915 by Josep Comas Solá (1868–1937), the first asteroid to be discovered by a Spaniard.
914 Palisana, provisional designation 1919 FN, is a Phocaean asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 77 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered by German astronomer Max Wolf at Heidelberg Observatory on 4 July 1919.
980 Anacostia is a minor planet orbiting the Sun that was discovered by American astronomer George Henry Peters on 21 November 1921. The name recognizes the Anacostia River and an historic neighborhood of the same name in the city of Washington D.C.
2577 Litva, provisional designation 1975 EE3, is a Hungarian-type Mars-crosser and rare trinary asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 4 kilometers in diameter.
References
- ↑ "(DOP)". Archived from the original on 21 June 2013. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- 1 2 "674 Rachele (1908 EP)". JPL Small-Body Database . NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory . Retrieved 7 May 2016.
- 1 2 3 Fienga, A.; Avdellidou, C.; Hanuš, J. (February 2020). "Asteroid masses obtained with INPOP planetary ephemerides". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 492 (1): 589–602. doi: 10.1093/mnras/stz3407 .
- ↑ Schmadel, Lutz D. (2012), Dictionary of Minor Planet Names (6th ed.), Springer, p. 65, ISBN 978-3642297182.
- ↑ Piironen, J.; et al. (March 1998), "Physical studies of asteroids. XXXII. Rotation periods and UBVRI-colours for selected asteroids", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement, 128 (3): 525–540, Bibcode:1998A&AS..128..525P, doi: 10.1051/aas:1998393 .
- ↑ Marchis, F.; et al. (November 2006), "Shape, size and multiplicity of main-belt asteroids. I. Keck Adaptive Optics survey", Icarus, 185 (1): 39–63, Bibcode:2006Icar..185...39M, doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2006.06.001, PMC 2600456 , PMID 19081813.