
16 Psyche is a large M-type asteroid, which was discovered by the Italian astronomer Annibale de Gasparis, on 17 March 1852 and named after the Greek goddess Psyche. The prefix "16" signifies that it was the sixteenth minor planet in order of discovery. It is the largest and most massive of the M-type asteroids, and one of the dozen most massive asteroids. It has a mean diameter of approximately 220 kilometers (140 mi) and contains about one percent of the mass of the asteroid belt. It was thought to be the exposed core of a protoplanet, but recent observations cast doubt on that hypothesis. Psyche will be explored by NASA, with a spacecraft of the same name, marking the first time a manmade object will journey to a metallic asteroid, launched on 13 October 2023, with an expected arrival in 2029.
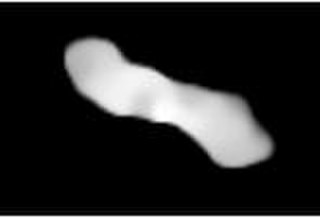
216 Kleopatra is a large M-type asteroid with a mean diameter of 120 kilometers and is noted for its elongate bone or dumbbell shape. It was discovered on 10 April 1880 by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa at the Austrian Naval Pola Observatory, in what is now Pula, Croatia, and was named after Cleopatra, the famous Egyptian queen. It has two small minor-planet moons which were discovered in 2008 and later named Alexhelios and Cleoselene.

1036 Ganymed, provisional designation 1924 TD, is a stony asteroid on a highly eccentric orbit, classified as a near-Earth object of the Amor group. It was discovered by German astronomer Walter Baade at the Bergedorf Observatory in Hamburg on 23 October 1924, and named after Ganymede from Greek mythology. With a diameter of approximately 35 kilometers, Ganymed is the largest of all near-Earth objects but does not cross Earth's orbit. The S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 10.3 hours. In October 2024, it is predicted to approach Earth at a distance of 56,000,000 km; 35,000,000 mi (0.374097 AU).

38 Leda is a large, dark main-belt asteroid that was discovered by French astronomer J. Chacornac on January 12, 1856, and named after Leda, the mother of Helen of Troy in Greek mythology. In the Tholen classification system, it is categorized as a carbonaceous C-type asteroid, while the Bus asteroid taxonomy system lists it as a Cgh asteroid. The spectra of the asteroid displays evidence of aqueous alteration.
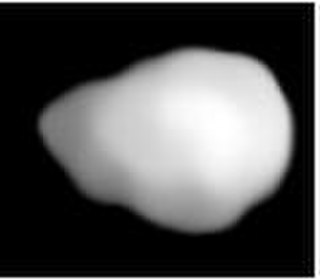
41 Daphne is a large asteroid from the asteroid belt. It is a dark-surfaced body 174 km in diameter is probably composed of primitive carbonaceous chondrites. The spectra of the asteroid displays evidence of aqueous alteration. It was discovered by H. Goldschmidt on May 22, 1856, and named after Daphne, the nymph in Greek mythology who was turned into a laurel tree. Incorrect orbital calculations initially resulted in 56 Melete being mistaken for a second sighting of Daphne. Daphne was not sighted again until August 31, 1862.

64 Angelina is an asteroid from the central region of the asteroid belt, approximately 50 kilometers in diameter. It is an unusually bright form of E-type asteroid.

92 Undina is a large main belt asteroid. The asteroid was discovered by Christian Peters on 7 July 1867 from the Hamilton College Observatory. It is named for the eponymous heroine of Undine, a popular novella by Friedrich de la Motte Fouqué.

97 Klotho is a fairly large main-belt asteroid. While it is an M-type, its radar albedo is too low to allow a nickel-iron composition. Klotho is similar to 21 Lutetia and 22 Kalliope in that all three are M-types of unknown composition. Klotho was found by Ernst Tempel on February 17, 1868. It was his fifth and final asteroid discovery. It is named after Klotho or Clotho, one of the three Moirai, or Fates, in Greek mythology.

110 Lydia is a large belt asteroid with an M-type spectrum, and thus may be metallic in composition, consisting primarily of nickel-iron. It was discovered by French astronomer Alphonse Borrelly on 19 April 1870 and was named for Lydia, the Asia Minor country populated by Phrygians. The Lydia family of asteroids is named after it.

111 Ate is a main-belt asteroid discovered by the German-American astronomer C. H. F. Peters on August 14, 1870, and named after Ate, the goddess of mischief and destruction in Greek mythology. In the Tholen classification system, it is categorized as a carbonaceous C-type asteroid, while the Bus asteroid taxonomy system lists it as an Ch asteroid.

125 Liberatrix is a main-belt asteroid. It has a relatively reflective surface and an M-type spectrum. Liberatrix is a member of an asteroid family bearing its own name.

135 Hertha is an asteroid from the inner region of the asteroid belt, approximately 77 kilometers in diameter. Discovered on 18 February 1874 by German–American astronomer Christian Peters at the Litchfield Observatory near Clinton, New York, it was named after the Teutonic and Scandinavian goddess of fertility, Hertha, also known as Nerthus. It orbits among the Nysa asteroid family, but its classification as a metallic M-type asteroid does not match the more common F-type asteroid for this family, suggesting that it may be an interloper. Spectroscopic analysis indicates the possible presence of hydrated silicates indicating that Hertha should possibly be reclassified from its present M-type to the proposed W-type.

136 Austria is a main-belt asteroid that was found by the prolific asteroid discoverer Johann Palisa on 18 March 1874, from the Austrian Naval Observatory in Pola, Istria. It was his first asteroid discovery and was given the Latin name of his homeland.

201 Penelope is a large main belt asteroid that was discovered by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa on August 7, 1879, in Pola. The asteroid is named after Penelope, the wife of Odysseus in Homer's The Odyssey. It is orbiting the Sun at a distance of 2.68 AU with an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.18 and a period of 4.381 years. The orbital plane is tilted at an angle of 5.8° to the plane of the ecliptic.

238 Hypatia is a large main-belt asteroid that was discovered by Russian astronomer Viktor Knorre on July 1, 1884, in Berlin. It was the third of his four asteroid discoveries. The name was given in honour of philosopher Hypatia of Alexandria. Based upon the spectrum, it is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of primitive carbonaceous material. Like many asteroids of this type, its surface is very dark in colour.
346 Hermentaria is a very large main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by French astronomer Auguste Charlois on 25 November 1892, in Nice. It is probably named for the town of Herment in the region of Auvergne, France. The asteroid is orbiting the Sun with a period of 4.68 years and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.10. The orbital plane is inclined by 8.7° to the plane of the ecliptic.
488 Kreusa is a C-type asteroid orbiting the Sun in the asteroid belt, with the type indicating a surface with a low albedo and high carbonaceous content. The spectra of the asteroid displays evidence of aqueous alteration.
1143 Odysseus, provisional designation 1930 BH, is a large Jupiter trojan located in the Greek camp of Jupiter's orbit. It was discovered on 28 January 1930, by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at the Heidelberg Observatory in southwest Germany, and later named after Odysseus, the legendary hero from Greek mythology. The dark D-type asteroid has a rotation period of 10.1 hours. With a diameter of approximately 125 kilometers, it is among the 10 largest Jovian trojans.
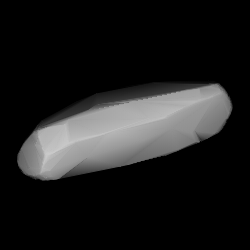
2156 Kate is a highly elongated background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt. The asteroid was discovered on 23 September 1917, by Soviet–Russian astronomer Sergey Belyavsky at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. It was named for Kate Kristensen, wife of astronomer L. K. Kristensen. The bright S-type/A-type asteroid has a rotation period of 5.6 hours and measures approximately 8 kilometers in diameter.

1902 Shaposhnikov is a dark Hilda asteroid from the outermost region of the asteroid belt, approximately 92 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 18 April 1972, by Russian astronomer Tamara Smirnova at the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory in Nauchnyj, on the Crimean peninsula. The asteroid was named after Soviet astronomer and WWII casualty Vladimir Shaposhnikov. It was one of the last larger asteroids discovered in the main belt.


















