
Acacia pycnantha, most commonly known as the golden wattle, is a tree of the family Fabaceae. It grows to a height of 8 metres and has phyllodes instead of true leaves. The profuse fragrant, golden flowers appear in late winter and spring, followed by long seed pods. Explorer Thomas Mitchell collected the type specimen, from which George Bentham wrote the species description in 1842. The species is native to southeastern Australia as an understorey plant in eucalyptus forest. Plants are cross-pollinated by several species of honeyeater and thornbill, which visit nectaries on the phyllodes and brush against flowers, transferring pollen between them.

Acacia melanoxylon, commonly known as the Australian blackwood, is an Acacia species native to south-eastern Australia. The species is also known as blackwood, hickory, mudgerabah, Tasmanian blackwood, or blackwood acacia. The tree belongs to the Plurinerves section of Acacia and is one of the most wide-ranging tree species in eastern Australia and is quite variable mostly in the size and shape of the phyllodes.

Acacia cardiophylla, commonly known as West Wyalong wattle or Wyalong wattle, is an evergreen shrub that is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia implexa, commonly known as lightwood or hickory wattle, is a fast-growing Australian tree, the timber of which is used for furniture making. The wood is prized for its finish and strength. The foliage was used to make pulp and dye cloth.

Acacia decurrens, commonly known as black wattle or early green wattle, is a perennial tree or shrub native to eastern New South Wales, including Sydney, the Greater Blue Mountains Area, the Hunter Region, and southwest to the Australian Capital Territory. It grows to a height of 2–15 m (7–50 ft) and it flowers from July to September.

Acacia falcata, commonly known as sickle wattle and by other vernacular names including sally, is a perennial shrub or tree native to eastern Australia, which reaches five metres in height and has cream flowers in early winter. It gets its common and scientific name for its sickle-shaped leaves. Hardy and adaptable to cultivation, it is used in regeneration of bushland.

Acacia podalyriifolia is a perennial tree which is fast-growing and widely cultivated. It is native to Australia but is also naturalised in Malaysia, Africa, India and South America. Its uses include environmental management and it is also used as an ornamental tree. It is very closely related to Acacia uncifera. It grows to about 5 m in height and about the same in total width. It blooms during winter.
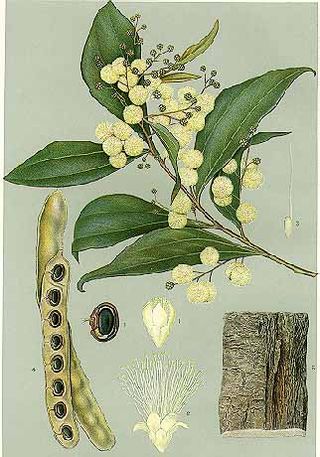
Acacia binervata, commonly known as two-veined hickory, is a shrub or tree that is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia myrtifolia, known colloquially as myrtle wattle, red stem wattle or red-stemmed wattle, is a species of Acacia native to coastal areas of southern and eastern Australia.

Acacia concurrens, commonly known as curracabah or black wattle, is a shrub native to Queensland in eastern Australia.

Acacia cana, or commonly named as boree or the cabbage-tree wattle or broad-leaved nealie, is part of the family Fabaceae and sub-family Mimosoideae. It is a dense shrub- tree that can grow to 6 metres (20 ft) high and is a perennial plant meaning it has long life span and doesn’t necessary produce a high amount of seed. The cabbage-tree wattle heavily flowers from August till October and relies on animals and insects for pollination and dispersal of seeds. This least concern acacia species is found in the western plains of New South Wales and Central Queensland the habitats of these areas are found to be sandy soils and gibber plains.

Acacia iteaphylla, commonly known as Flinders Range wattle, Port Lincoln wattle, winter wattle and willow-leaved wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to South Australia.

Acacia havilandiorum, also known as Haviland's wattle or needle wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves. It is native to areas in South Australia, New South Wales and Victoria.

Acacia chrysotricha, commonly known as the Newry golden wattle or the Bellinger River wattle, is a species of Acacia native to eastern Australia. The species was listed as endangered in 2012 with the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources.

Acacia pedleyi, also known as Pedley's wattle, is a species of Acacia native to eastern Australia. It is considered to be a vulnerable species according to the Nature Conservation Act 1992.

Acacia shirleyi, known colloquially as lancewood, is a species of Acacia native to Queensland and the Northern Territory in Australia. It grows as a tree to 15 metres (49 ft) high, with dark grey or black stringy bark and blue-grey foliage. The yellow flowers appear from March to July. It grows in dry scrub, open forest or mixed savannah woodland. Indigenous people used the wood as fuel and to make hunting spears. Cattle can eat the foliage as fodder.

Acacia falciformis, also commonly known as broad-leaved hickory, hickory wattle, mountain hickory, large-leaf wattle, tanning wattle and black wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to eastern Australia

Acacia jucunda, commonly known as yetman wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to north eastern Australia and is considered to be endangered in New South Wales.

Acacia curranii, also known as curly-bark wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia. It is listed as vulnerable under the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.
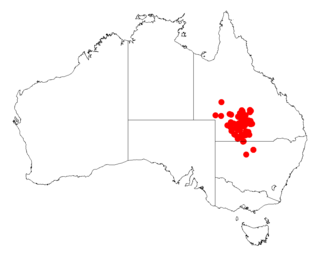
Acacia petraea, commonly known as lancewood, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.





















